Abstract
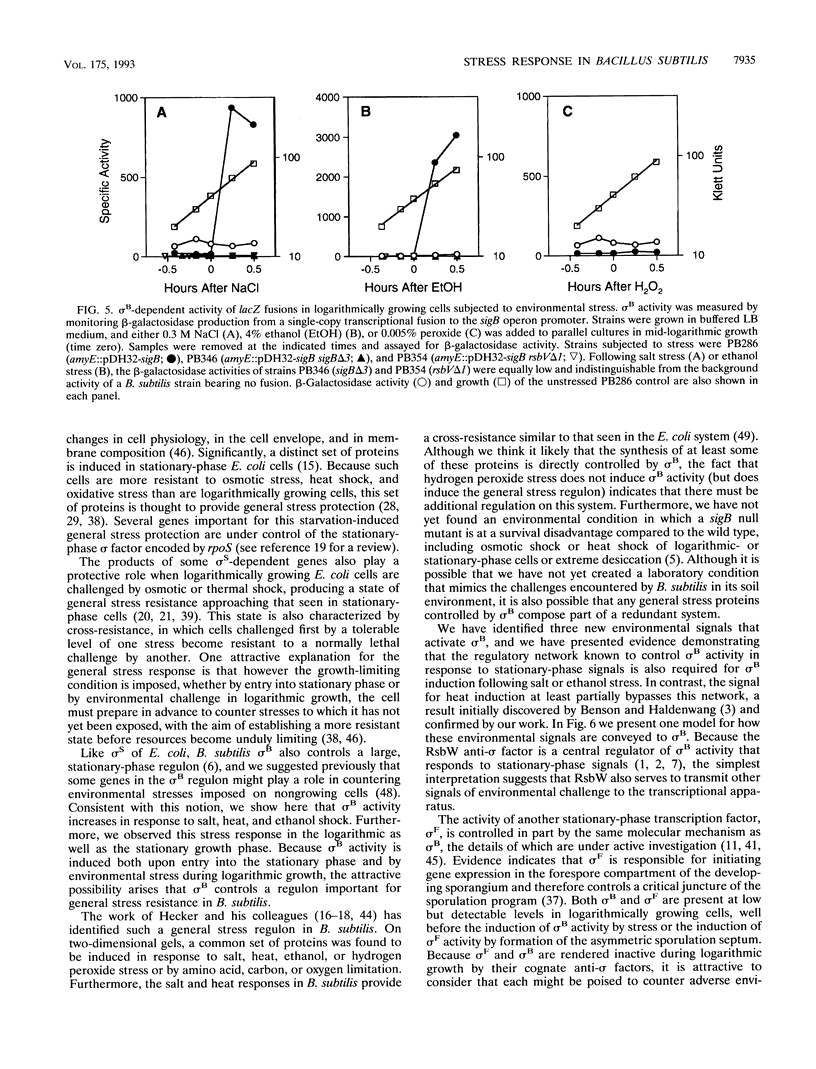
The alternative transcription factor sigma B of Bacillus subtilis is activated during the stationary growth phase by a regulatory network responsive to stationary-phase signals. On the basis of the results reported here, we propose that sigma B controls a general stress regulon that is induced when cells encounter a variety of growth-limiting conditions. Expression of genes controlled by sigma B, including the ctc gene and the sigB operon that codes for sigma B and its associated regulatory proteins, was dramatically induced in both the exponential and stationary phases by environmental challenges known to elicit a general stress response. After cells were subjected to salt stress, the increased expression of lacZ transcriptional fusions to the ctc and sigB genes was entirely dependent on sigma B, and primer extension experiments confirmed that the sigma B-dependent transcriptional start site was used during salt induction of sigB operon expression. Western blotting (immunoblotting) experiments measuring the levels of sigma B protein indicated that ethanol addition and heat stress also induced sigma B activity during logarithmic growth. Salt and ethanol induction during logarithmic growth required RsbV, the positive regulator of sigma B activity that is normally necessary for activity in stationary-phase cells. However, heat induction of sigma B activity was largely independent of RsbV, indicating that there are two distinct pathways by which these environmental signals are conveyed to the transcriptional apparatus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson A. K., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma B is regulated by a binding protein (RsbW) that blocks its association with core RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. K., Haldenwang W. G. Characterization of a regulatory network that controls sigma B expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):749–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.749-757.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. K., Haldenwang W. G. The sigma B-dependent promoter of the Bacillus subtilis sigB operon is induced by heat shock. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):1929–1935. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.1929-1935.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnie C., Lampe M., Losick R. Gene encoding the sigma 37 species of RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5943–5947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Redfield A. R., Price C. W. Transcription factor sigma B of Bacillus subtilis controls a large stationary-phase regulon. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):3957–3963. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.3957-3963.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Rutherford A., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Activation of Bacillus subtilis transcription factor sigma B by a regulatory pathway responsive to stationary-phase signals. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3695–3706. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3695-3706.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Thomas M. D., Price C. W. Genetic method to identify regulons controlled by nonessential elements: isolation of a gene dependent on alternate transcription factor sigma B of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7856–7866. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7856-7866.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan L., Losick R. SpoIIAB is an anti-sigma factor that binds to and inhibits transcription by regulatory protein sigma F from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2325–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. L., Kalman S. S., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Gene encoding the 37,000-dalton minor sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase: isolation, nucleotide sequence, chromosomal locus, and cryptic function. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.771-778.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever H. M., Styrvold O. B., Kaasen I., Strøm A. R. Biochemical and genetic characterization of osmoregulatory trehalose synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2841–2849. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2841-2849.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schultz J. E., Zychlinsky E., Bockman A., Matin A. Starvation proteins in Escherichia coli: kinetics of synthesis and role in starvation survival. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.486-493.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Heim C., Völker U., Wölfel L. Induction of stress proteins by sodium chloride treatment in Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol. 1988;150(6):564–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00408250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Richter A., Schroeter A., Wölfel L., Mach F. Synthese von Hitzeschockproteinen nach einer Aminosäure- und Sauerstofflimitation in Bacillus subtilis relA+ - und relA-Stämmen. Z Naturforsch C. 1987 Jul-Aug;42(7-8):941–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R., Klein W., Lange R., Rimmele M., Boos W. Trehalose synthesis genes are controlled by the putative sigma factor encoded by rpoS and are involved in stationary-phase thermotolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7918–7924. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7918-7924.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R., Lange R., Henneberg N., Fischer D. Osmotic regulation of rpoS-dependent genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):259–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.259-265.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R. Survival of hunger and stress: the role of rpoS in early stationary phase gene regulation in E. coli. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90655-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Losick R. Regulation of a promoter that is utilized by minor forms of RNA polymerase holoenzyme in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M., Lampe M., Ray C., Schafer W., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Genetic studies of a secondary RNA polymerase sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3464–3469. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3464-3469.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireton K., Grossman A. D. Interactions among mutations that cause altered timing of gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3185–3195. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3185-3195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Chaisson S. A., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against osmotic challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2779–2781. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2779-2781.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Schultz J. E., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against heat or H2O2 challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3910–3914. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3910-3914.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalman S., Duncan M. L., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Similar organization of the sigB and spoIIA operons encoding alternate sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5575–5585. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5575-5585.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaji H., Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Influence of molecular size and osmolarity of sugars and dextrans on the synthesis of outer membrane proteins O-8 and O-9 of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):843–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.843-847.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Price C. W. The minCD locus of Bacillus subtilis lacks the minE determinant that provides topological specificity to cell division. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(4):601–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Stragier P. Crisscross regulation of cell-type-specific gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):601–604. doi: 10.1038/355601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis P., Driks A., Losick R. Establishment of cell type by compartmentalized activation of a transcription factor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1948031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A. The molecular basis of carbon-starvation-induced general resistance in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):3–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann M. P., Kidwell J. P., Matin A. The putative sigma factor KatF has a central role in development of starvation-mediated general resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4188–4194. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4188-4194.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. T., Hilditch C. M., Diederich B., Errington J., Yudkin M. D. Sigma F, the first compartment-specific transcription factor of B. subtilis, is regulated by an anti-sigma factor that is also a protein kinase. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90520-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. T., Yudkin M. D. Activity of mutant sigma F proteins truncated near the C terminus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7144–7148. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7144-7148.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., Losick R. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus subtilis promoter recognized by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase containing sigma 37. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5979–5990. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Margolis P., Duncan L., Coppolecchia R., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Control of developmental transcription factor sigma F by sporulation regulatory proteins SpoIIAA and SpoIIAB in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9221–9225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Kolter R. Life after log. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.345-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of sigma 32. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):348–351. doi: 10.1038/329348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varón D., Boylan S. A., Okamoto K., Price C. W. Bacillus subtilis gtaB encodes UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and is controlled by stationary-phase transcription factor sigma B. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):3964–3971. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.3964-3971.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Völker U., Mach H., Schmid R., Hecker M. Stress proteins and cross-protection by heat shock and salt stress in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Oct;138(10):2125–2135. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-10-2125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]