Abstract
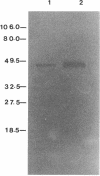
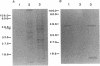
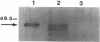
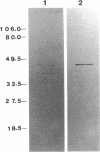
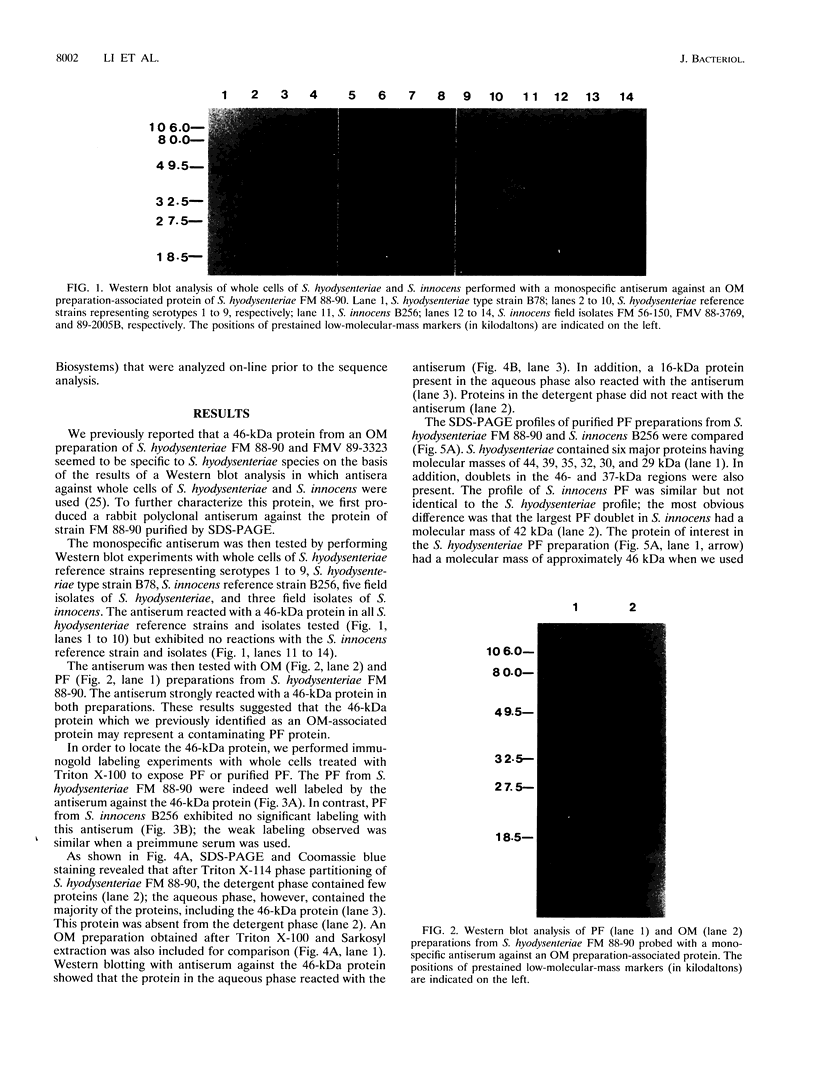
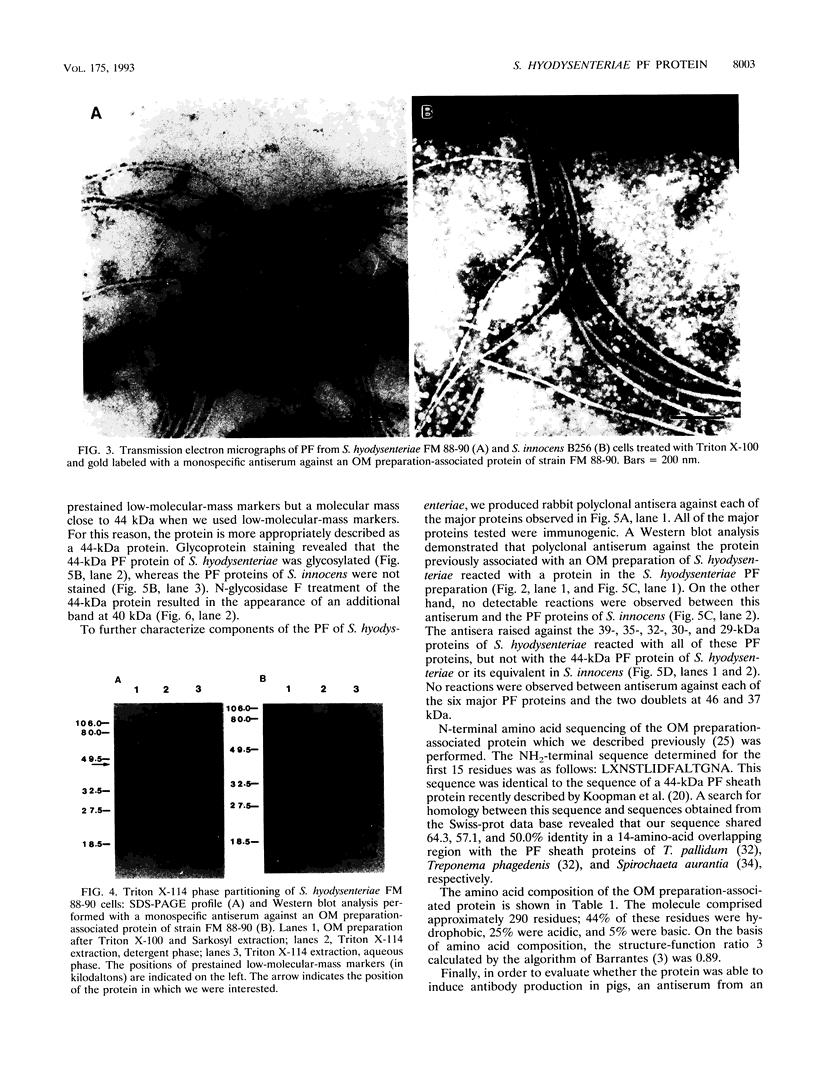
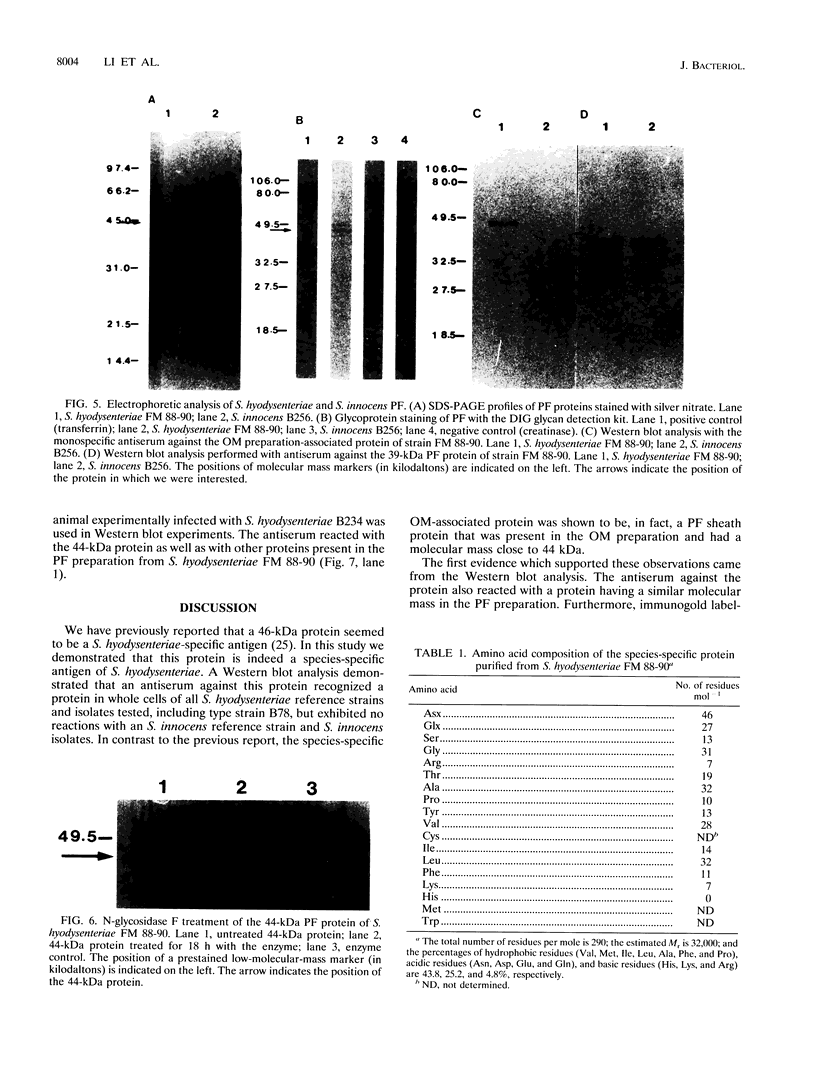
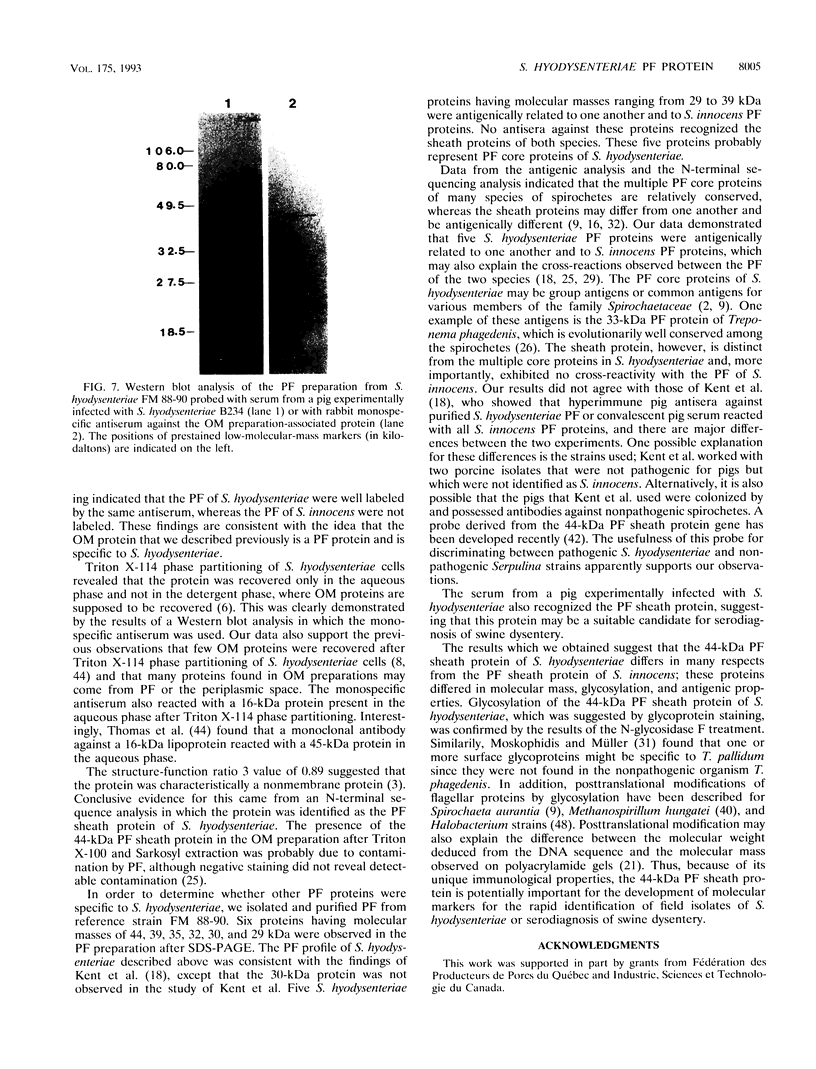
We have previously reported that a 46-kDa protein present in an outer membrane protein preparation seemed to be a species-specific antigen of Serpulina hyodysenteriae (Z. S. Li, N. S. Jensen, M. Bélanger, M.-C. L'Espérance, and M. Jacques, J. Clin. Microbiol. 30:2941-2947, 1992). The objective of this study was to further characterize this antigen. A Western blot (immunoblot) analysis and immunogold labeling with a monospecific antiserum against this protein confirmed that the protein was present in all S. hyodysenteriae reference strains but not in the nonpathogenic organism Serpulina innocens. The immunogold labeling results also indicated that the protein was associated with the periplasmic flagella of S. hyodysenteriae. N-terminal amino acid sequencing confirmed that the protein was in fact a periplasmic flagellar sheath protein. The molecular mass of this protein, first estimated to be 46 kDa by Western blotting, was determined to be 44 kDa when the protein was evaluated more precisely by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the protein was glycosylated, as determined by glycoprotein staining and also by N-glycosidase F treatment. Five other periplasmic flagellar proteins of S. hyodysenteriae, which may have been the core proteins and had molecular masses of 39, 35, 32, 30, and 29 kDa, were antigenically related and cross-reacted with the periplasmic flagellar proteins of S. innocens. Finally, serum from a pig experimentally infected with S. hyodysenteriae recognized the 44-kDa periplasmic flagellar sheath protein. Our results suggest that the 44-kDa periplasmic flagellar sheath protein of S. hyodysenteriae is a species-specific glycoprotein antigen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Antigenic cross-reactivity between Treponema pallidum and other pathogenic members of the family Spirochaetaceae. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.116-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrantes F. J. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor : different compositions evidenced by statistical analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):407–414. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M., Allis D. Purification and characterization of axial filaments from Treponema phagedenis biotype reiterii (the Reiter treponeme). J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1434–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1434-1442.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossé M., Handl C. E., Lortié L. A., Harel J., Dubreuil J. D. Fusion of the genes encoding Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin b (STb) and the maltose-binding protein to obtain mature STb enterotoxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Mar;139(3):631–638. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-3-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyden D. A., Albert F. G., Robinson C. S. Cloning and characterization of Treponema hyodysenteriae antigens and protection in a CF-1 mouse model by immunization with a cloned endoflagellar antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3808–3815. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3808-3815.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahamsha B., Greenberg E. P. Biochemical and cytological analysis of the complex periplasmic flagella from Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4023–4032. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4023-4032.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bélanger M., Jacques M. Evaluation of the An-Ident system and an indole spot test for the rapid differentiation of porcine treponemes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1727–1729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1727-1729.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield S. N., Fernie D. S., Penn C., Dougan G. Identification of the major antigens of Treponema hyodysenteriae and comparison with those of Treponema innocens. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1070–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1070-1075.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J. M., Wannemuehler M. J. Pathogenesis of Treponema hyodysenteriae: induction of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by a treponemal butanol/water extract (endotoxin). Microb Pathog. 1989 Oct;7(4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Kinyon J. M., Mullin M. T., Glock R. D. Isolation and propagation of spirochetes from the colon of swine dysentery affected pigs. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Jan;36(1):74–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs R. D., Hanke J. H., Guzman-Verduzco L. M., Newport G., Agabian N., Norgard M. V., Lukehart S. A., Radolf J. D. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of the 37-kilodalton endoflagellar sheath protein gene of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3403–3411. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3403-3411.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Marquez R. B. Molecular characterization of proteins from porcine spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):893–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.893-896.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Sellwood R., Lemcke R. M., Burrows M. R., Lysons R. J. Analysis of the axial filaments of Treponema hyodysenteriae by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1625–1632. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman M. B., Baats E., van Vorstenbosch C. J., van der Zeijst B. A., Kusters J. G. The periplasmic flagella of Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae are composed of two sheath proteins and three core proteins. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Dec;138(12):2697–2706. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman M. B., de Leeuw O. S., van der Zeijst B. M., Kusters J. G. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae gene encoding a periplasmic flagellar sheath protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2920–2925. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2920-2925.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre N., Matsudaira P. Direct protein microsequencing from Immobilon-P Transfer Membrane. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. S., Bélanger M., Jacques M. Serotyping of Canadian isolates of Treponema hyodysenteriae and description of two new serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2794–2797. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2794-2797.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Jensen N. S., Bélanger M., L'Espérance M. C., Jacques M. Molecular characterization of Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae isolates representing serotypes 8 and 9. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2941–2947. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2941-2947.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Antiserum to the 33,000-dalton periplasmic-flagellum protein of "Treponema phagedenis" reacts with other treponemes and Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1030–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1030-1032.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysons R. J., Kent K. A., Bland A. P., Sellwood R., Robinson W. F., Frost A. J. A cytotoxic haemolysin from Treponema hyodysenteriae--a probable virulence determinant in swine dysentery. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Feb;34(2):97–102. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-2-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Brown D. M., Glazer A. N. The formation of bacterial flagella. 3. Characterization of the subunits of the flagella of Bacillus subtilis and Spirillum serpens. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. P., Toivio-Kinnucan M., Wu G., Wilt G. R. Ultrastructural and electrophoretic analysis of Treponema hyodysenteriae axial filaments. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):786–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular characterization of glycoprotein antigens on surface of Treponema pallidum: comparison with nonpathogenic Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):867–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.867-869.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Charon N. W., Cook R. G., Fuentes M. D., Limberger R. J. Antigenic relatedness and N-terminal sequence homology define two classes of periplasmic flagellar proteins of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum and Treponema phagedenis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4072–4082. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4072-4082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuessen M. E., Joens L. A., Glock R. D. Involvement of lipopolysaccharide in the pathogenicity of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):997–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parales J., Jr, Greenberg E. P. N-terminal amino acid sequences and amino acid compositions of the Spirochaeta aurantia flagellar filament polypeptides. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1357–1359. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1357-1359.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Bailey M. J., Cockayne A. The axial filament antigen of Treponema pallidum. Immunology. 1985 Apr;54(4):635–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Cockayne A., Bailey M. J. The outer membrane of Treponema pallidum: biological significance and biochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Luke C. J. Bacterial flagellar diversity and significance in pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):331–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Kent K. A., Burrows M. R., Lysons R. J., Bland A. P. Antibodies to a common outer envelope antigen of Treponema hyodysenteriae with antibacterial activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Aug;135(8):2249–2257. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-8-2249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. C., Roddick F., Ling S., Gerraty N. L., Coloe P. J. Biochemical and immunochemical characterisation of strains of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Jul;24(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90048-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southam G., Kalmokoff M. L., Jarrell K. F., Koval S. F., Beveridge T. J. Isolation, characterization, and cellular insertion of the flagella from two strains of the archaebacterium Methanospirillum hungatei. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3221–3228. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3221-3228.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B. Proposal to change the genus designation Serpula to Serpulina gen. nov. containing the species Serpulina hyodysenteriae comb. nov. and Serpulina innocens comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):189–190. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W., Sellwood R., Lysons R. J. A 16-kilodalton lipoprotein of the outer membrane of Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3111–3116. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3111-3116.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W., Sellwood R. Molecular cloning, expression, and DNA sequence analysis of the gene that encodes the 16-kilodalton outer membrane lipoprotein of Serpulina hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):1136–1140. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.1136-1140.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Borenstein L. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Analysis of outer membrane ultrastructure of pathogenic Treponema and Borrelia species by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5585–5588. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5585-5588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemuehler M. J., Hubbard R. D., Greer J. M. Characterization of the major outer membrane antigens of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3032–3039. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3032-3039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F., Paul G., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are sulfated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15180–15185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Huurne A. A., van Houten M., Koopman M. B., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. Characterization of Dutch porcine Serpulina (Treponema) isolates by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Sep;138(9):1929–1934. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-9-1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]