Abstract
In Pseudomonas putida PaW85, the ortho-cleavage pathway is used for catechol degradation. The 11.4-kb XhoI fragment cloned from phenol degradation plasmid pEST1226 into pKT240 (recombinant plasmid pAT1140) contains the inducible pheBA operon that encodes catechol 1,2-dioxygenase (gene pheB) and phenol monooxygenase (gene pheA), the first two enzymes for the phenol degradation pathway. The promoter of the pheBA operon is mapped 1.5 kb upstream of the pheB gene. The plasmid pAT1140, when introduced into P. putida PaW85, enables the bacteria to use the hybrid plasmid-chromosome-encoded pathway for phenol degradation. The synthesis of the plasmid-encoded phenol monooxygenase and catechol 1,2-dioxygenase is induced by cis,cis-muconate. The expression studies of the deletion subclones derived from pAT1140 revealed that the transcription of the pheBA operon is positively controlled by a regulatory protein that is chromosomally encoded in P. putida. cis,cis-Muconate in cooperation with positive transcription factor CatR activates the transcription of the chromosomal ortho-pathway genes catA and catBC in P. putida (R. K. Rothmel, T. L. Aldrich, J. E. Houghton, W. M. Coco, L. N. Ornston, and A. M. Chakrabarty, J. Bacteriol. 172:922-931, 1990). The inability to express the pheBA operon in a P. putida CatR- background and activation of transcription of the pheBA operon in Escherichia coli in the presence of the catR-expressing plasmid demonstrated that the transcription of the pheBA operon in P. putida PaW85 carrying pEST1226 is controlled by the chromosomally encoded CatR.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich T. L., Chakrabarty A. M. Transcriptional regulation, nucleotide sequence, and localization of the promoter of the catBC operon in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1297–1304. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1297-1304.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich T. L., Frantz B., Gill J. F., Kilbane J. J., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence determination of the catB gene encoding cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUCHOP T., ELSDEN S. R. The growth of micro-organisms in relation to their energy supply. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:457–469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M. M., Amann E., Lurz R., Rückert B., Bagdasarian M. Activity of the hybrid trp-lac (tac) promoter of Escherichia coli in Pseudomonas putida. Construction of broad-host-range, controlled-expression vectors. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley S. A., Duggleby C. J., Worsey M. J., Williams P. A., Hardy K. G., Broda P. Two modes of loss of the Tol function from Pseudomonas putida mt-2. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jul 20;154(2):203–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00330838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beadle C. A., Smith A. R. The purification and properties of 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase from a strain of Acinetobacter species. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):323–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg P., Wagner E. G., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: the duplex between the antisense RNA, CopA, and its target, CopT, is processed specifically in vivo and in vitro by RNase III. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2331–2340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Bedouelle H., Winter G. Improved oligonucleotide site-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo J. D., Barletta R. G., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr A novel transposon trap for mycobacteria: isolation and characterization of IS1096. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7772–7780. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7772-7780.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaar M., Hõrak R., Kasak L., Heinaru A., Habicht J. Selection of independent plasmids determining phenol degradation in Pseudomonas putida and the cloning and expression of genes encoding phenol monooxygenase and catechol 1,2-dioxygenase. Plasmid. 1990 Jul;24(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaar M., Kasak L., Nurk A. Sequence of the plasmid-encoded catechol 1,2-dioxygenase-expressing gene, pheB, of phenol-degrading Pseudomonas sp. strain EST1001. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90098-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurk A., Kasak L., Kivisaar M. Sequence of the gene (pheA) encoding phenol monooxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. EST1001: expression in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90531-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
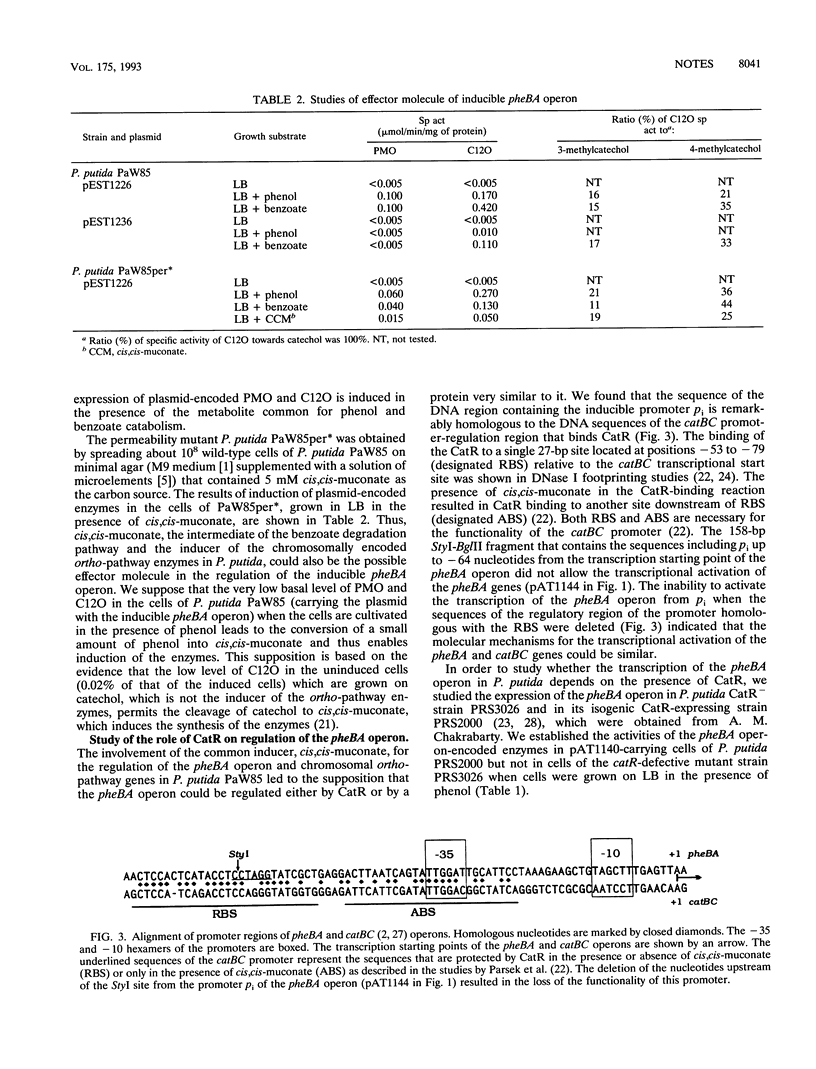
- Nurk A., Tamm A., Hôrak R., Kivisaar M. In-vivo-generated fusion promoters in Pseudomonas putida. Gene. 1993 May 15;127(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. IV. Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3800–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsek M. R., Shinabarger D. L., Rothmel R. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Roles of CatR and cis,cis-muconate in activation of the catBC operon, which is involved in benzoate degradation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7798–7806. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7798-7806.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothmel R. K., Aldrich T. L., Houghton J. E., Coco W. M., Ornston L. N., Chakrabarty A. M. Nucleotide sequencing and characterization of Pseudomonas putida catR: a positive regulator of the catBC operon is a member of the LysR family. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.922-931.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothmel R. K., Shinabarger D. L., Parsek M. R., Aldrich T. L., Chakrabarty A. M. Functional analysis of the Pseudomonas putida regulatory protein CatR: transcriptional studies and determination of the CatR DNA-binding site by hydroxyl-radical footprinting. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4717–4724. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4717-4724.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B., Kahn M. The nucleotide sequence of IS5 from Escherichia coli. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Minegishi K., Iino T. Toluene transposons Tn4651 and Tn4653 are class II transposons. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1386–1393. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1386-1393.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis M. L., Ornston L. N. Genetic control of enzyme induction in the -ketoadipate pathway of Pseudomonas putida: deletion mapping of cat mutations. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):790–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.790-795.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]