Abstract
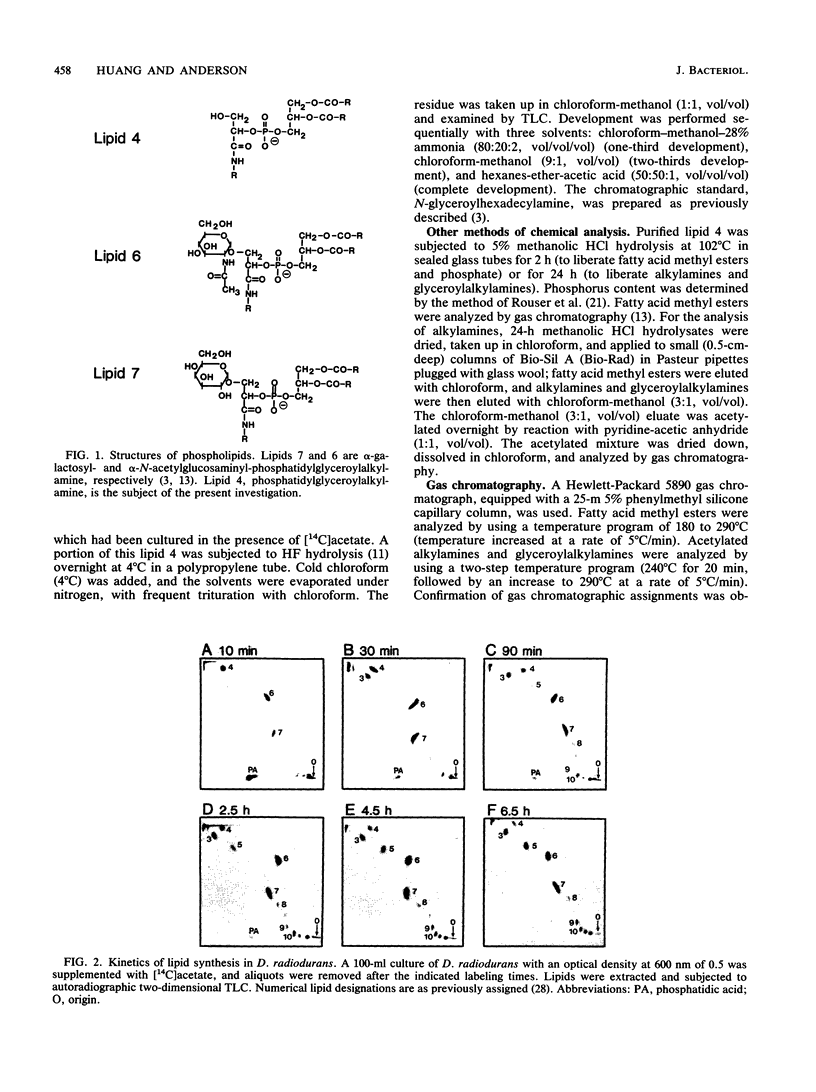
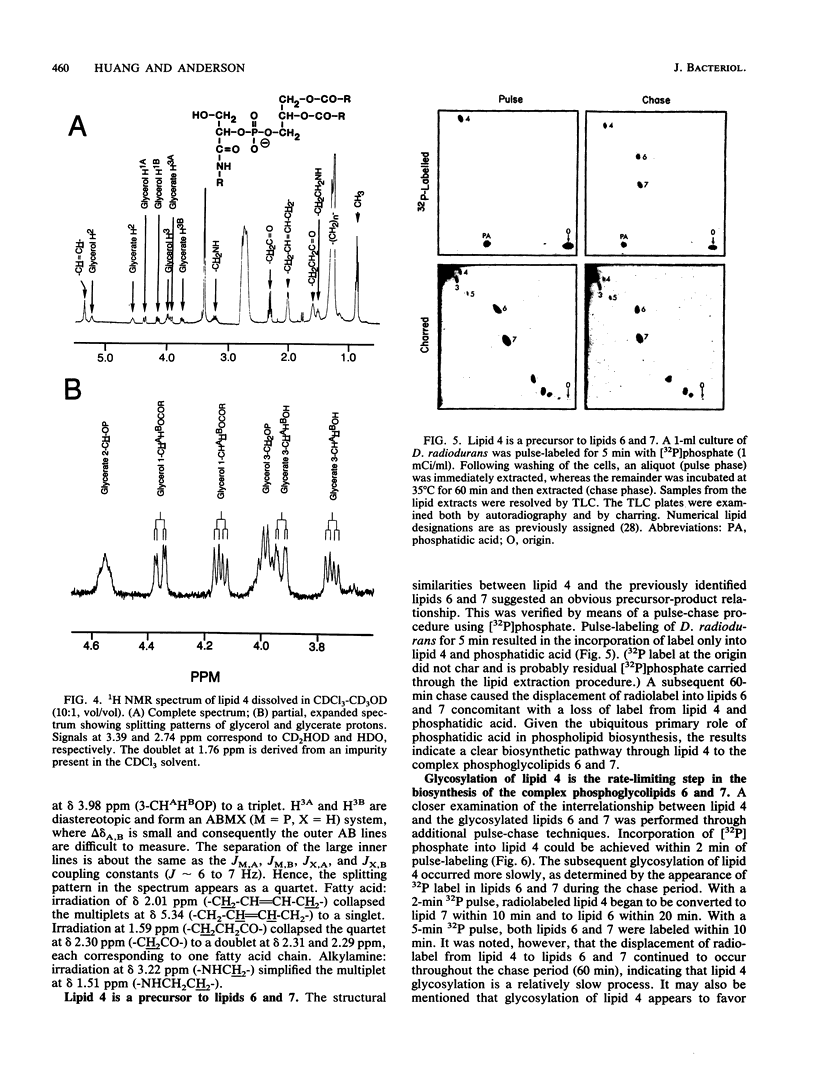
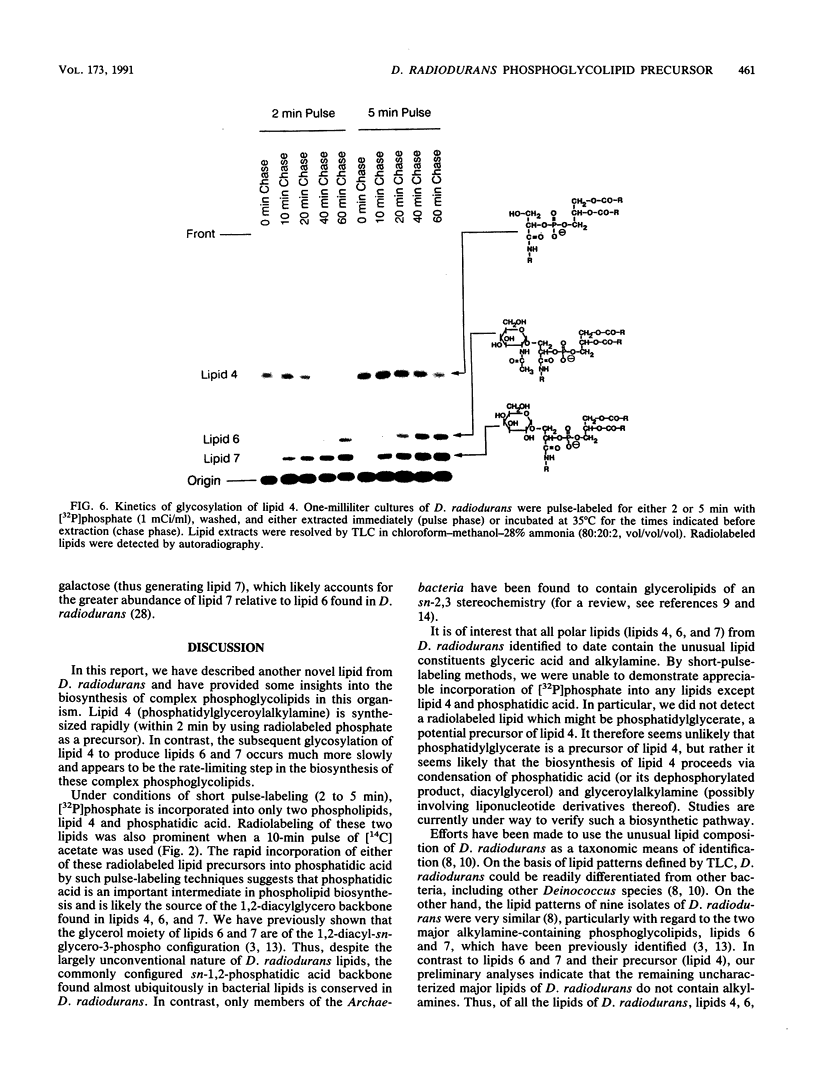
We report here the structure of a previously uncharacterized phospholipid in the radiation-resistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. This phospholipid, designated lipid 4, was shown by chemical analysis, HF hydrolysis, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to be phosphatidylglyceroylalkylamine. Lipid 4 thus contains the unusual lipid constituents glyceric acid and alkylamines, which have previously been identified in two complex phosphoglycolipids from this organism. By [32P]phosphate pulse-chase labeling techniques, lipid 4 was shown to be the precursor of the complex phosphoglycolipids alpha-galactosyl- and alpha-N-acetylglucosaminylphosphatidylglyceroylalkylamine. While phosphatidylglyceroylalkylamine is rapidly biosynthesized from Pi, its subsequent glycosylation occurs much more slowly. Therefore, we conclude that the final glycosylation step is the rate-limiting event in the biosynthesis of the complex phosphoglycolipids alpha-galactosyl- and alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyl-phosphatidylglyceroylalkylamine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R., Hansen K. Structure of a novel phosphoglycolipid from Deinococcus radiodurans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12219–12223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister W., Kübler O. Topographic study of the cell surface of micrococcus radiodurans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5525–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonneau M. A., Melin A. M., Perromat A., Clerc M. The action of free radicals on Deinococcus radiodurans carotenoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 15;275(1):244–251. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Gliozzi A. Structure, biosynthesis, and physicochemical properties of archaebacterial lipids. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):70–80. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.70-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Ishizuka I., Landgraf H. R., Herrmann J. Glycerophosphoryl diglucosyl diglyceride, a new phosphoglycolipid from Streptococci. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 8;296(3):527–545. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y., Anderson R. Structure of a novel glucosamine-containing phosphoglycolipid from Deinococcus radiodurans. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18667–18672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. The phytanyl ether-linked polar lipids and isoprenoid neutral lipids of extremely halophilic bacteria. Prog Chem Fats Other Lipids. 1978;15(4):301–342. doi: 10.1016/0079-6832(77)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancy P., Jr, Murray R. G. The envelope of Micrococcus radiodurans: isolation, purification, and preliminary analysis of the wall layers. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):162–176. doi: 10.1139/m78-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRICK T. P., BRUCE A. K. RADIATION RESPONSE OF POTASSIUM EFFLUX IN MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS AND SARCINA LUTEA. Radiat Res. 1965 Apr;24:612–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSELEY B. E., SCHEIN A. H. RADIATION RESISTANCE AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BASE COMPOSITION OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS. Nature. 1964 Sep 19;203:1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2031298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Mundy A. R., Blackford H. N., Stephenson T. P. Transvesical phenolisation of the pelvic plexuses: a simple technique for the treatment of refractory detrusor instability and hyperreflexia. Urol Int. 1986;41(3):202–206. doi: 10.1159/000281198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeyrotte N., Rebeyrotte P., Maviel M. J., Montaudon D. Lipides et lipopolyosides de Micrococcus radiodurans. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1979 Nov-Dec;130B(4):407–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW J. K., DUGGAN D. E. THE RESISTANCE OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS TO ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION. I. ULTRAVIOLET-INDUCED LESIONS IN THE CELL'S DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 12;87:664–668. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. W., Maxcy R. B. Isolation of radiation-resistant bacteria without exposure to irradiation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):436–439. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.436-439.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein A. H. The deoxyribonucleic acid of Micrococcus radiodurans. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):647–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1010647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Kocur M., Glauert A. M., Thornley M. J. A study by freeze-etching of the fine structure of Micrococcus radiodurans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 4;94(1):77–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00414079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. G., Anderson R., Murray R. G. Unusual polar lipids of Micrococcus radiodurans strain Sark. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Dec;26(12):1408–1411. doi: 10.1139/m80-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornley M. J., Horne R. W., Glauert A. M. The fine structure of Micrococcus radiodurans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1965 Jul 20;51(3):267–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00408143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E. AMINO ACIDS OF WALLS OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1107–1109. doi: 10.1038/2011107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Work E., Griffiths H. Morphology and chemistry of cell walls of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):641–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.641-657.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]