Abstract
A 3,466-bp nucleotide sequence containing the katE gene of Escherichia coli has been determined. An open reading frame of 2,259 bp was found and was preceded by a potential ribosome-binding site. The predicted N-terminal sequence agreed with the sequence determined by direct amino acid sequencing, and the predicted direction of transcription was confirmed by expression of the gene cloned in both directions behind a T7 promoter. The start site of transcription was determined to be 127 bp upstream from the start of the open reading frame, and a potential RNA polymerase-binding site similar to a sequence preceding the xthA gene, which is also controlled by the KatF protein, was identified. The predicted sequence of the 753-amino-acid protein was compared with known sequences of other catalases, revealing significant similarity to the shorter catalases, including the residues in the putative active site and residues involved in heme binding.
Full text
PDF




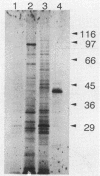
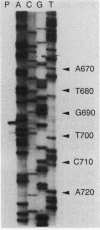
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Najarian R. C., Mullenbach G. T., Hallewell R. A. cDNA sequence coding for human kidney catalase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5561–5562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethards L. A., Skadsen R. W., Scandalios J. G. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the Cat2 gene in maize and its homology with other catalases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6830–6834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne A., Fridovich I. Purification of the o-dianisidine peroxidase from Escherichia coli B. Physicochemical characterization and analysis of its dual catalatic and peroxidatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4245–4252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne A., Malinowski D. P., Fridovich I. Purification and characterization of hydroperoxidase II of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11664–11668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fita I., Rossmann M. G. The NADPH binding site on beef liver catalase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1604–1608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fita I., Rossmann M. G. The active center of catalase. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):21–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta S., Hayashi H., Hijikata M., Miyazawa S., Osumi T., Hashimoto T. Complete nucleotide sequence of cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of rat liver catalase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):313–317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig A., Ruis H. Nucleotide sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTT1 gene and deduced amino-acid sequence of yeast catalase T. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):487–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C. Isolation of catalase-deficient Escherichia coli mutants and genetic mapping of katE, a locus that affects catalase activity. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):622–626. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.622-626.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Switala J. Purification and characterization of catalase HPII from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;64(7):638–646. doi: 10.1139/o86-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Switala J., Triggs-Raine B. L. Catalases HPI and HPII in Escherichia coli are induced independently. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):144–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90782-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L. Genetic mapping of katF, a locus that with katE affects the synthesis of a second catalase species in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):668–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.668-675.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L., George C. S., Hrabarchuk B. E. Genetic mapping of katG, a locus that affects synthesis of the bifunctional catalase-peroxidase hydroperoxidase I in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.661-667.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L., Klassen G. R., Weiner J. H. Identification and physical characterization of a Col E1 hybrid plasmid containing a catalase gene of Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;61(12):1315–1321. doi: 10.1139/o83-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loprasert S., Negoro S., Okada H. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the Bacillus stearothermophilus peroxidase gene (perA). J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4871–4875. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4871-4875.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Skorupa E. S., Kemper B. Single stranded DNA SP6 promoter plasmids for engineering mutant RNAs and proteins: synthesis of a 'stretched' preproparathyroid hormone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1103–1118. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M. R., Loewen P. C. Nucleotide sequence of katF of Escherichia coli suggests KatF protein is a novel sigma transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9979–9991. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M. R., Sorby P. A., Triggs-Raine B. L., Loewen P. C. Cloning and physical characterization of katE and katF required for catalase HPII expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy M. R., Reid T. J., 3rd, Sicignano A., Tanaka N., Rossmann M. G. Structure of beef liver catalase. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):465–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Ueda M., Sugaya T., Atomi H., Mozaffar S., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Okazaki K., Takechi T., Kamiryo T. Catalase gene of the yeast Candida tropicalis. Sequence analysis and comparison with peroxisomal and cytosolic catalases from other sources. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):105–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J. Bacterial glycogen synthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:419–458. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sak B. D., Eisenstark A., Touati D. Exonuclease III and the catalase hydroperoxidase II in Escherichia coli are both regulated by the katF gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3271–3275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammartano L. J., Tuveson R. W., Davenport R. Control of sensitivity to inactivation by H2O2 and broad-spectrum near-UV radiation by the Escherichia coli katF locus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.13-21.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saporito S. M., Smith-White B. J., Cunningham R. P. Nucleotide sequence of the xth gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4542–4547. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4542-4547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B., Apell G., Fang R. S., Bonaventura J. The complete amino acid sequence of bovine liver catalase and the partial sequence of bovine erythrocyte catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):397–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Park Y. K., Tirgari S., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Identification and characterization of starvation-regulated genetic loci in Salmonella typhimurium by using Mu d-directed lacZ operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.345-351.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo J., Fita I., Switala J., Loewen P. C. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of catalase HPII from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 20;213(2):219–220. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati E., Danchin A. Cloning and characterization of the pH 2.5 acid phosphatase gene, appA: cyclic AMP mediated negative regulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):499–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00328146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggs-Raine B. L., Doble B. W., Mulvey M. R., Sorby P. A., Loewen P. C. Nucleotide sequence of katG, encoding catalase HPI of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4415–4419. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4415-4419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggs-Raine B. L., Loewen P. C. Physical characterization of katG, encoding catalase HPI of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., McSharry R. Phosphate-controlled gene expression in Escherichia coli K12 using Mudl-directed lacZ fusions. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):347–363. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]