Abstract
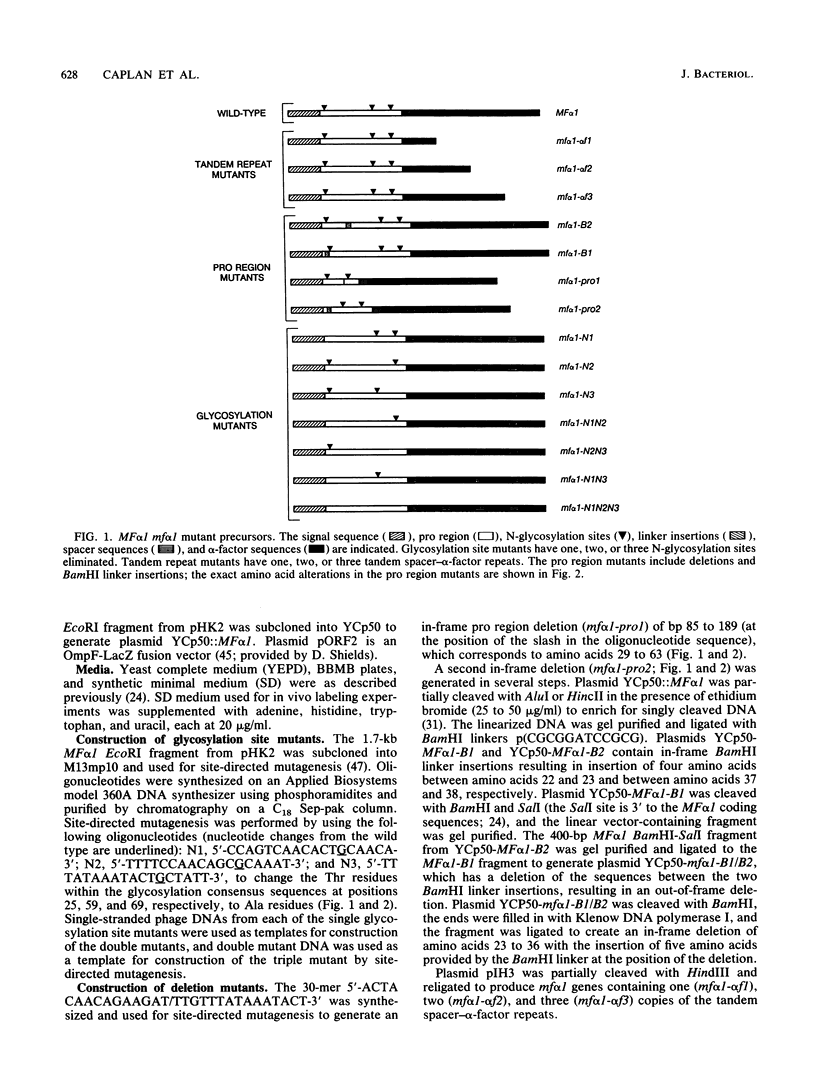
The MF alpha 1 gene encodes a precursor, prepro-alpha-factor, that undergoes several proteolytic processing steps within the classical secretory pathway to produce the mature peptide pheromone, alpha-factor. To investigate the role of structural features of the MF alpha 1 precursor in alpha-factor production, we analyzed the effect of mf alpha 1 mutations that alter precursor structure in a number of ways. These mutations resulted in decreased alpha-factor secretion and intracellular accumulation of pro-alpha-factor. With the exception of the mutant lacking all three N glycosylation sites, the pro-alpha-factor forms that accumulated were core glycosylated but had not yet undergone the addition of outer chain carbohydrate. The delay, therefore, occurred at a step prior to the first proteolytic processing step involved in maturation of the precursor and was probably due to inefficient endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transport. Elimination of all three N-glycosylation sites caused a delay in disappearance of intracellular precursor, and alpha-factor secretion was also slowed. These data indicate that N glycosylation is important but not essential for transport of the precursor through the secretory pathway. The decreased alpha-factor secretion and increased precursor accumulation seen with many different structural changes of pro-alpha-factor indicate that the secretory pathway is extremely sensitive to changes in precursor structure. This sensitivity could cause inefficient secretion of heterologous proteins and hybrids between MF alpha 1 and heterologous proteins in yeast cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achstetter T., Wolf D. H. Hormone processing and membrane-bound proteinases in yeast. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):173–177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02333.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison D. S., Young E. T. Single-amino-acid substitutions within the signal sequence of yeast prepro-alpha-factor affect membrane translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1915–1922. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Julius D. J., Thorner J. A functional prepro-alpha-factor gene in Saccharomyces yeasts can contain three, four, or five repeats of the mature pheromone sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1440–1450. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J. Secretion of heterologous proteins directed by the yeast alpha-factor leader. Biotechnology. 1989;13:269–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bücking-Throm E., Duntze W., Hartwell L. H., Manney T. R. Reversible arrest of haploid yeast cells in the initiation of DNA synthesis by a diffusible sex factor. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Trimble R. B., Maley F. The effect of carbohydrate depletion on the properties of yeast external invertase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8691–8693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F., Hartwell L. H., Jackson C., Konopka J. B. Conjugation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:429–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowska A., Dignard D., Henning D., Thomas D. Y., Bussey H. Yeast KEX1 gene encodes a putative protease with a carboxypeptidase B-like function involved in killer toxin and alpha-factor precursor processing. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Bole D. G., Kaufman R. J. The relationship of N-linked glycosylation and heavy chain-binding protein association with the secretion of glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2665–2674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duntze W., MacKay V., Manney T. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a diffusible sex factor. Science. 1970 Jun 19;168(3938):1472–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3938.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emter O., Mechler B., Achstetter T., Müller H., Wolf D. H. Yeast pheromone alpha-factor is synthesized as a high molecular weight precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):822–829. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. The nonglycosylated glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is temperature-sensitive and undergoes intracellular aggregation at elevated temperatures. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3600–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Kramer R. A., Shields D. Misplacement of the amino-terminal positive charge in the prepro-alpha-factor signal peptide disrupts membrane translocation in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2963–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Schaber M. D., Shields D., Kramer R. Secretion of somatostatin by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Correct processing of an alpha-factor-somatostatin hybrid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7558–7565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Blair L., Brake A., Sprague G., Thorner J. Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozutsumi Y., Segal M., Normington K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. The presence of malfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum signals the induction of glucose-regulated proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):462–464. doi: 10.1038/332462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukuruzinska M. A., Bergh M. L., Jackson B. J. Protein glycosylation in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:915–944. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Tunicamycin--an inhibitor of yeast glycoprotein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Alpha-factor structural gene mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on alpha-factor production and mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):787–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Transport of secretory and membrane glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. A rate-limiting step in protein maturation and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2107–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Florkiewicz R. Z., Rose J. K. A single N-linked oligosaccharide at either of the two normal sites is sufficient for transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein to the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3074–3083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzuk M. M., Boime I. The role of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharides of the alpha subunit in the secretion and assembly of human chorionic gonadotrophin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1049–1059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Arai K. Use of a cDNA expression-cloning vector and a secretion vector for mammalian gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology. 1989;13:281–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normington K., Kohno K., Kozutsumi Y., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. S. cerevisiae encodes an essential protein homologous in sequence and function to mammalian BiP. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1223–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Watson R. M., Vinograd J. Mapping of closed circular DNAs by cleavage with restriction endonucleases and calibration by agarose gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):851–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Schekman R. Clathrin: a role in the intracellular retention of a Golgi membrane protein. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2675311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Misra L. M., Vogel J. P. KAR2, a karyogamy gene, is the yeast homolog of the mammalian BiP/GRP78 gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Webb J. R., Ammerer G., Meyer D. I. Secretion in yeast: structural features influencing the post-translational translocation of prepro-alpha-factor in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3455–3463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A., Chen E. Y., Lugovoy J. M., Chang C. N., Hitzeman R. A., Seeburg P. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains two discrete genes coding for the alpha-factor pheromone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4049–4063. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Evans E. A., Blobel G. Prepro-alpha-factor has a cleavable signal sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6209–6214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., ap Rhys C., Berman M. L., Hampar B., Jackson D., Silhavy T. J., Weisemann J., Zweig M. Open reading frame expression vectors: a general method for antigen production in Escherichia coli using protein fusions to beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4432–4436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]