Abstract
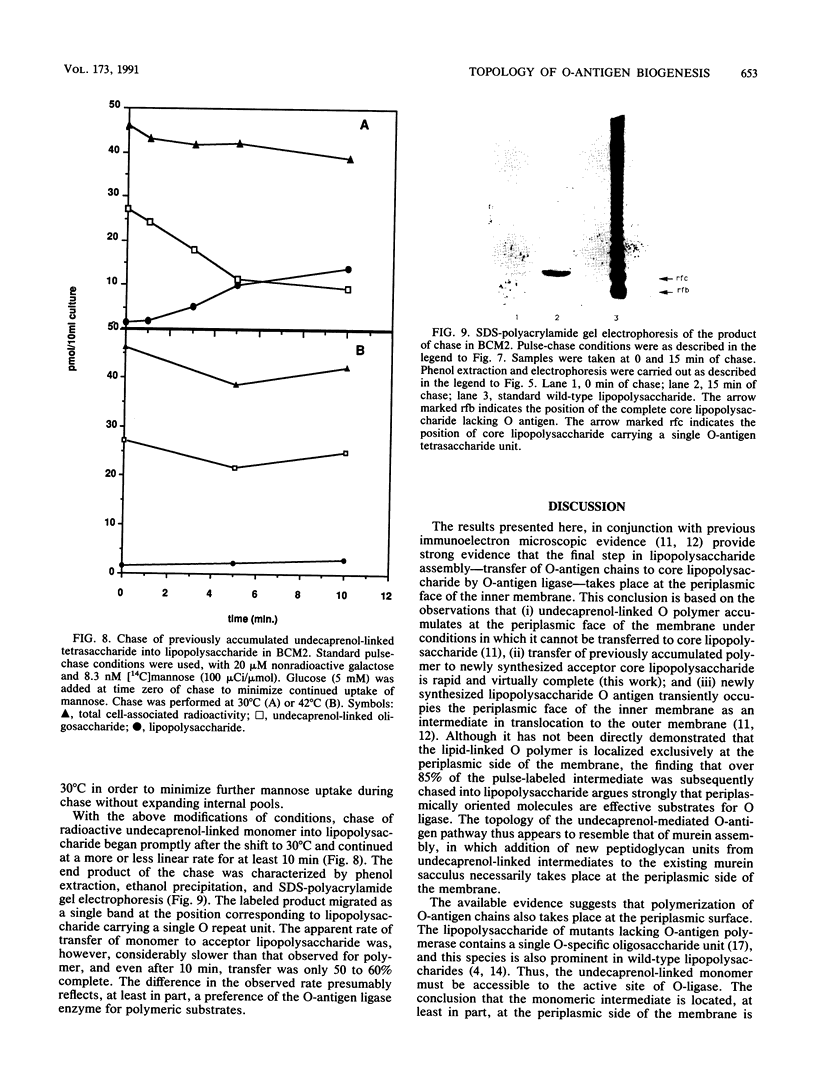
Previous immunoelectron microscopic studies have shown that both the final intermediate in O-antigen synthesis, undecaprenol-linked O polymer, and newly synthesized O-antigenic lipopolysaccharide are localized to the periplasmic face of the inner membrane (C. A. Mulford and M. J. Osborn, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:1159-1163, 1983). In vivo pulse-chase experiments now provide further evidence that attachment of O antigen to core lipopolysaccharide, as well as polymerization of O-specific polysaccharide chains, takes place at the periplasmic face of the membrane. Mutants doubly conditional in lipopolysaccharide synthesis [kdsA(Ts) pmi] were constructed in which synthesis of core lipopolysaccharide and O antigen are temperature sensitive and mannose dependent, respectively. Periplasmic orientation of O antigen:core lipopolysaccharide ligase was established by experiments showing rapid chase of undecaprenol-linked O polymer, previously accumulated at 42 degrees C in the absence of core synthesis, into lipopolysaccharide following resumption of core formation at 30 degrees C. In addition, chase of the monomeric O-specific tetrasaccharide unit into lipopolysaccharide was found in similar experiments in an O-polymerase-negative [rfc kdsA(Ts) pmi] mutant, suggesting that polymerization of O chains also occurs at the external face of the inner membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Creeger E. S., Rothfield L. I. Cloning of genes for bacterial glycosyltransferases. I. Selection of hybrid plasmids carrying genes for two glucosyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):804–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Hunt F. Mechanism of O-antigen distribution in lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5352–5359. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5352-5359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Wright A. Mechanism of polymerization of the Salmonella O-antigen: utilization of lipid-linked intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):951–958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent J. L., Osborn M. J. Properties of the O-specific hapten formed in vivo by mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Boulnois G., Roberts I., Bitter-Suermann D., Golecki J. R., Jann B., Jann K. Expression of the Escherichia coli K5 capsular antigen: immunoelectron microscopic and biochemical studies with recombinant E. coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1085–1091. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1085-1091.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulford C. A., Osborn M. J. An intermediate step in translocation of lipopolysaccharide to the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Site of synthesis of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3973–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick P. D., Osborn M. J. Isolation of a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium dependent on D-arabinose-5-phosphate for growth and synthesis of 3-deoxy-D-mannoctulosonate (ketodeoxyoctonate). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]