Abstract
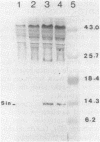
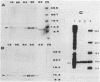
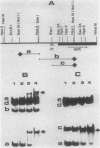
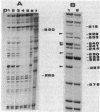
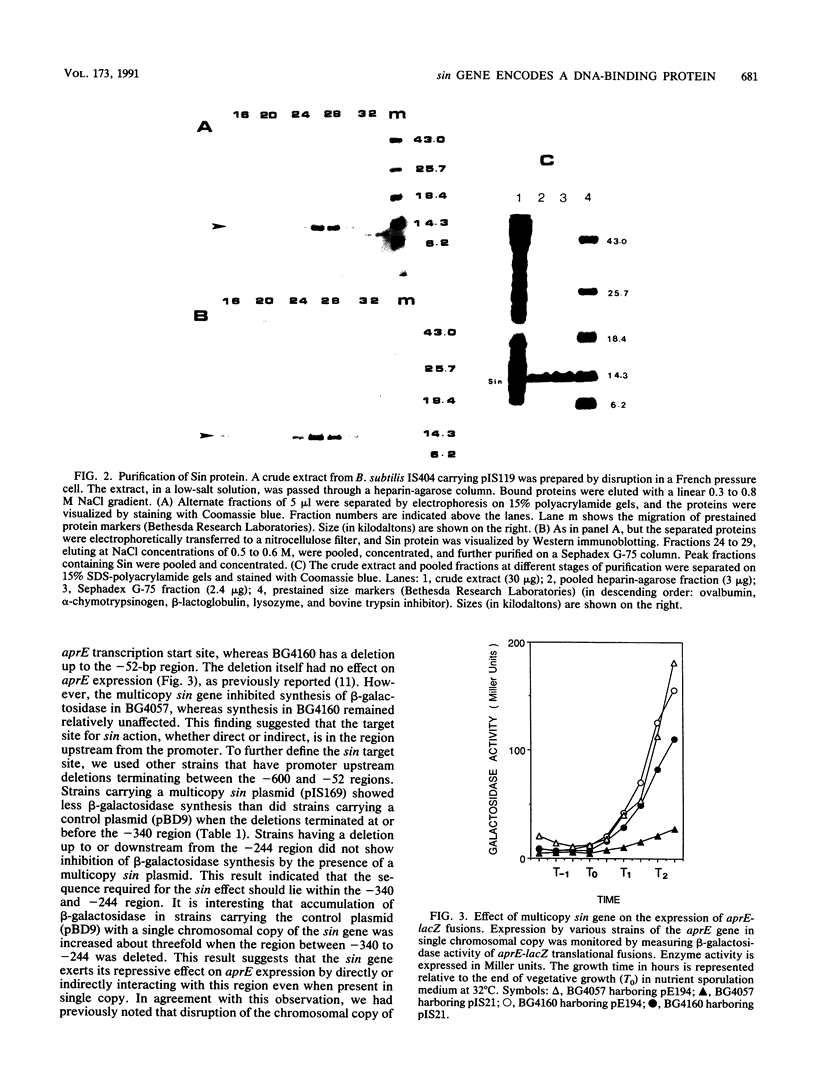
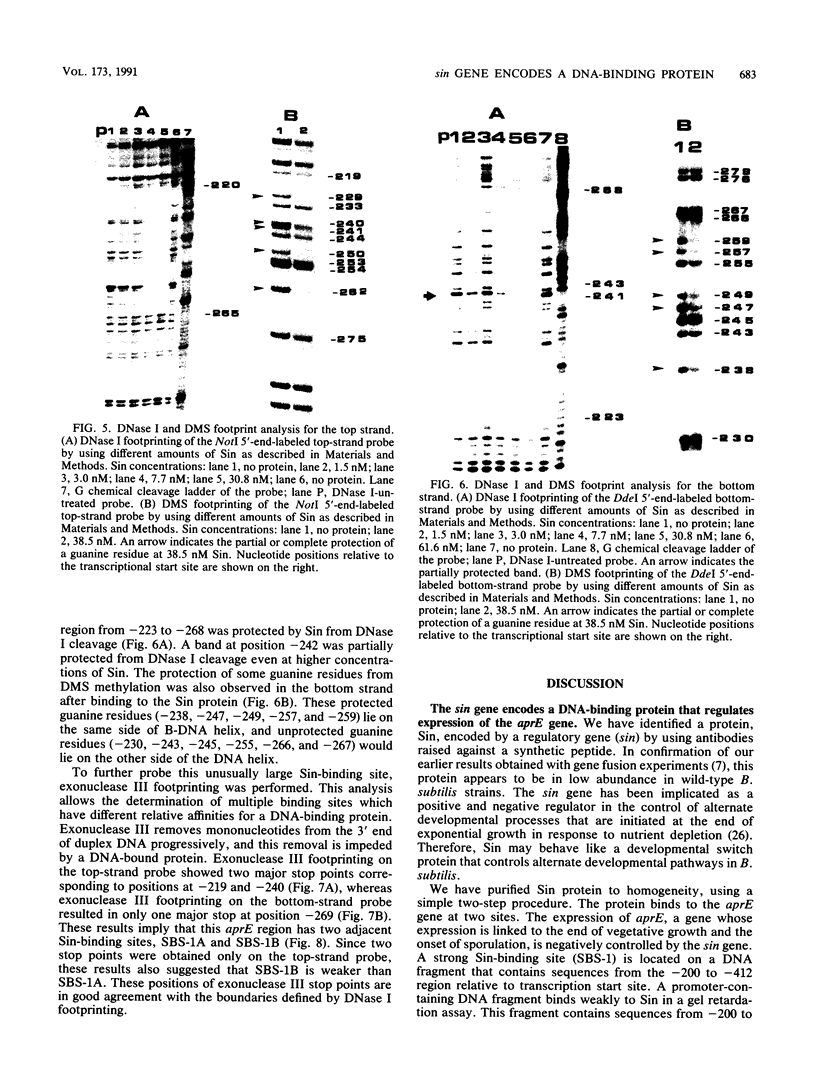
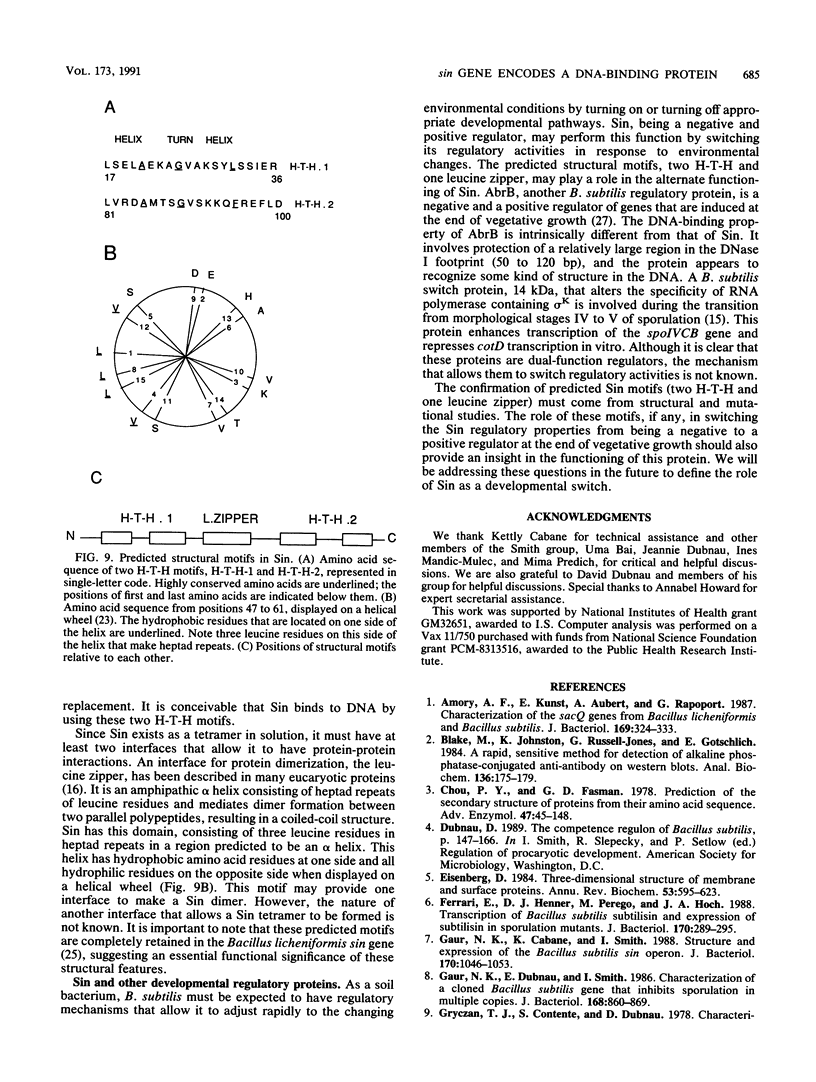
The sin gene of Bacillus subtilis encodes a dual-function regulatory protein, Sin, which is a negative as well as a positive regulator of alternate developmental processes that are induced at the end of vegetative growth in response to nutrient depletion. Sin has been purified to homogeneity by using a simple two-step procedure. It was found to bind to the developmentally regulated aprE (alkaline protease) gene at two sites in vitro. The stronger Sin-binding site (SBS-1) is located more than 200 bp upstream from the transcription start site. It is required for Sin repression of aprE expression in vivo, as strains bearing SBS-1 deletions were not affected by the sin gene. The second, weaker Sin-binding site lies on a DNA fragment that contains the aprE promoter. Results of DNase I, exonuclease III, and dimethyl sulfate footprinting analysis of SBS-1 suggested that Sin binding involves two adjacent binding sites which appear to contain two different partial dyad symmetries. An analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence of Sin revealed a potential leucine zipper protein dimerization motif which is flanked by two helix-turn-helix motifs that could be involved in recognizing two different dyad symmetries.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amory A., Kunst F., Aubert E., Klier A., Rapoport G. Characterization of the sacQ genes from Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):324–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.324-333.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari E., Henner D. J., Perego M., Hoch J. A. Transcription of Bacillus subtilis subtilisin and expression of subtilisin in sporulation mutants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):289–295. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.289-295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Cabane K., Smith I. Structure and expression of the Bacillus subtilis sin operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1046–1053. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1046-1053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Dubnau E., Smith I. Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):860–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.860-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillen N., Weinrauch Y., Dubnau D. A. Cloning and characterization of the regulatory Bacillus subtilis competence genes comA and comB. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5354–5361. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5354-5361.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Ferrari E., Perego M., Hoch J. A. Location of the targets of the hpr-97, sacU32(Hy), and sacQ36(Hy) mutations in upstream regions of the subtilisin promoter. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):296–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.296-300.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higerd T. B., Hoch J. A., Spizizen J. Hyperprotease-producing mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):1026–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.1026-1028.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetics of bacterial sporulation. Adv Genet. 1976;18:69–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo M., Nakayama A., Fukazawa K., Kawamura K., Ando K., Hori M., Furutani Y. A novel Bacillus subtilis gene involved in negative control of sporulation and degradative-enzyme production. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1783–1790. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1783-1790.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kunkel B., Losick R. Switch protein alters specificity of RNA polymerase containing a compartment-specific sigma factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):526–529. doi: 10.1126/science.2492118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Hoch J. A. Sequence analysis and regulation of the hpr locus, a regulatory gene for protease production and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2560–2567. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2560-2567.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi J., Ezaki B., Kodama K., Akamatsu T. Molecular cloning of a gene affecting the autolysin level and flagellation in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1611–1621. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi J., Ohsu H., Kuroda A., Moriyama H., Akamatsu T. Nucleotide sequences of the Bacillus subtilis flaD locus and a B. licheniformis homologue affecting the autolysin level and flagellation. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jul;136(7):1223–1230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-7-1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Spiegelman G. B., Perego M., Johnson W. C., Burbulys D., Hoch J. A. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1615–1621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kawata M., Nagami Y., Uchiyama H. prtR enhances the mRNA level of the Bacillus subtilis extracellular proteases. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3044–3050. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3044-3050.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Wang L. F., Doi R. H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of senN, a novel 'Bacillus natto' (B. subtilis) gene that regulates expression of extracellular protein genes. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Dec;134(12):3269–3276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-12-3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Ferrari E., Chen E., Henner D. J. Identification of the pleiotropic sacQ gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.113-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Shimotsu H., Ferrari E., Henner D. J. Characterization and mapping of the Bacillus subtilis prtR gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):434–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.434-437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]