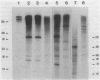
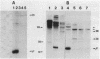
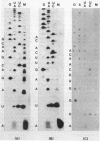
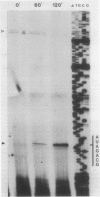
Abstract
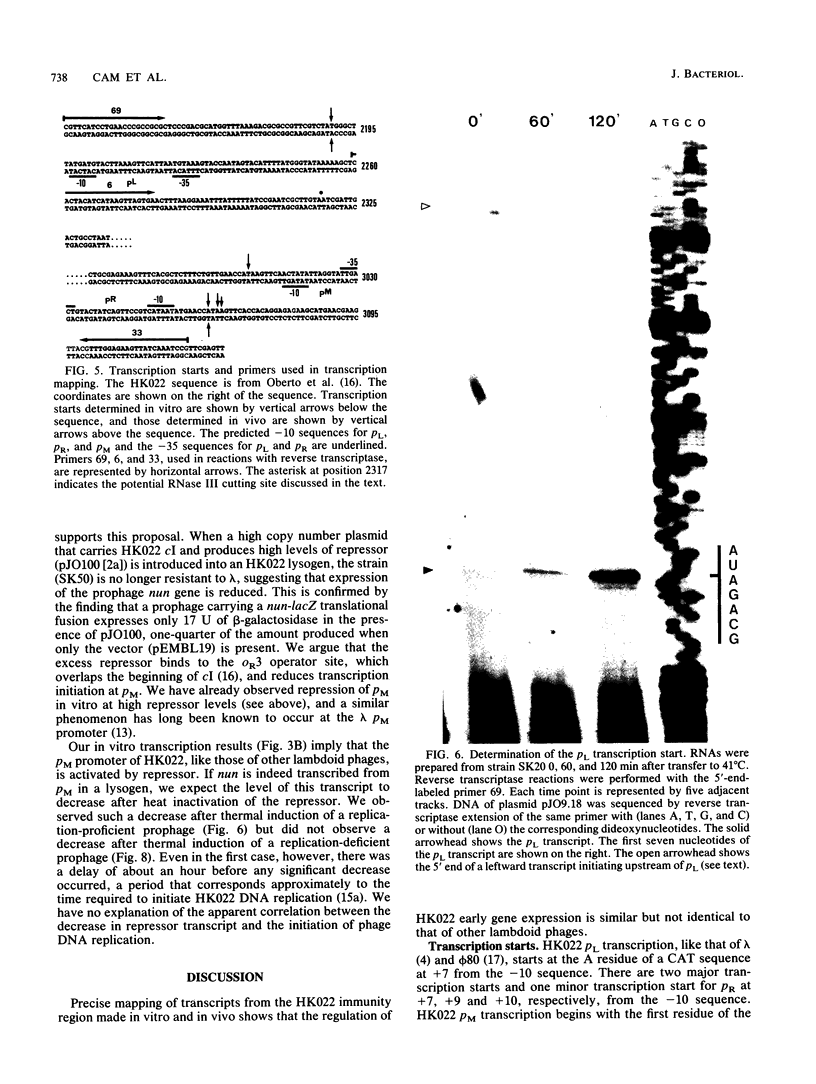
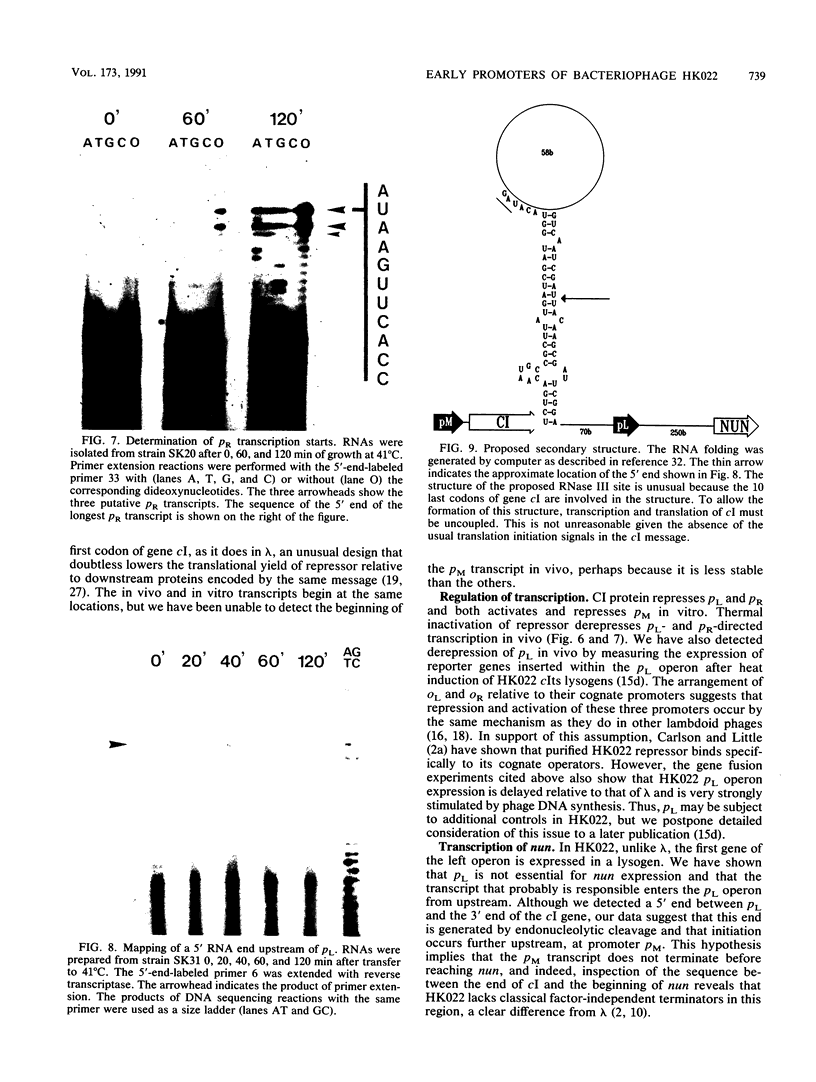
The pL, pR and pM promoters of lambdoid phages direct the transcription of early phage genes and the prophage repressor gene. We have determined the start points of transcription for these three promoters in the lambdoid phage HK022 and have shown that the HK022 repressor represses the early promoters, pL and pR, and activates the repressor promoter, pM. HK022 resembles other phages of the lambda family in these respects, as it does in the functional organization of most of its early genes and sites. One exception is nun, the first gene of the HK022 pL operon, which is expressed in the presence of prophage repressor and thus differs from its lambda counterpart, gene N. We show that transcription of nun in a lysogen does not initiate at pL but instead starts upstream at the pM promoter. This difference in transcription fits the different roles of Nun and N proteins in the physiology of the two phages: Nun protects HK022 lysogens against superinfection with certain other lambdoid phages, while N promotes the transcription of early lambda genes.
Full text
PDF

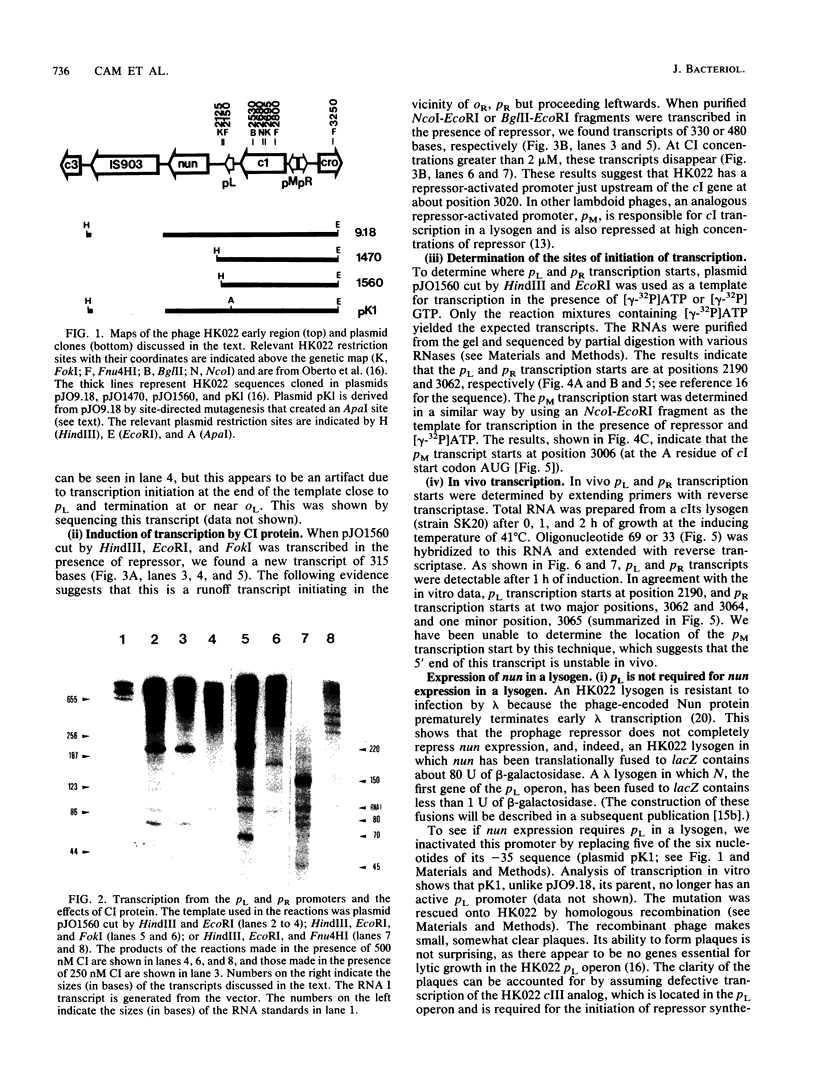
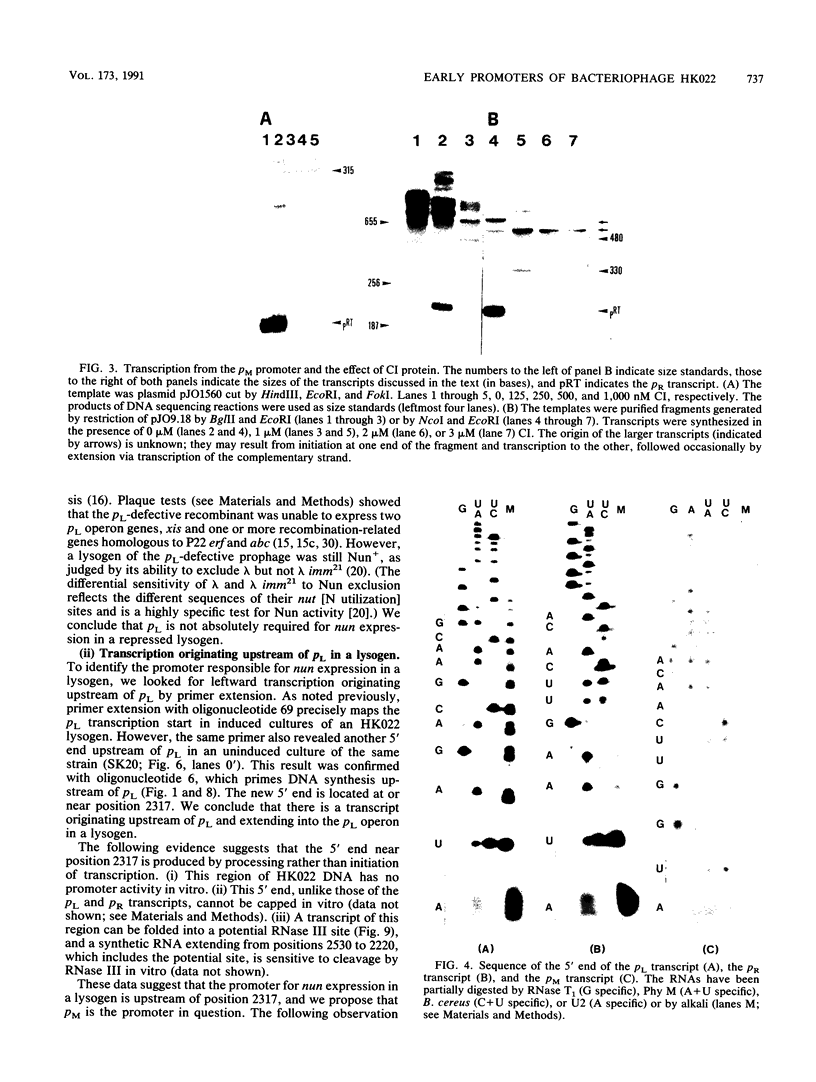

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barik S., Ghosh B., Whalen W., Lazinski D., Das A. An antitermination protein engages the elongating transcription apparatus at a promoter-proximal recognition site. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):885–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Hamm G. H., Trifonov E. N. Terminators of transcription with RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli: what they look like and how to find them. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):705–723. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Blattner F. R. Sequence of the promoter-operator proximal region of the major leftward RNA of bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1441–1458. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon T. S., Dhillon E. K., Lai A. N. Genetic recombination between phage HK022, lambda, and phi 80. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):198–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon T. S., Dhillon E. K. Studies on bacteriophage distribution. II. Isolation and host rage based classification of phages active on three species of Enterobacteriaceae. Jpn J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;16(4):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1972.tb00662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon T. S., Dhillon E. K. Temperate coliphage HK022. Clear plaque mutants and preliminary vegetative map. Jpn J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;20(5):385–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1976.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. The red plaque test: a rapid method for identification of excision defective variants of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz R. J., Li J., Greenblatt J. An elongation control particle containing the N gene transcriptional antitermination protein of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsmann J., Kröger M., Hobom G. The rex region of bacteriophage lambda: two genes under three-way control. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A., Silver D., Seed B. Minimal size plasmids containing an M13 origin for production of single-strand transducing particles. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):507–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukata H., Tomizawa J. Control of primer formation for ColE1 plasmid replication: conformational change of the primer transcript. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90491-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. J., Kleid D. G., Ptashne M. Lambda repressor turns off transcription of its own gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4785–4789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. C., Fenton A. C., Poteete A. R. Sequence of the bacteriophage P22 anti-recBCD (abc) genes and properties of P22 abc region deletion mutants. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberto J., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Structure and function of the nun gene and the immunity region of the lambdoid phage HK022. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):675–693. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Masukata H., Tomizawa J. Transcriptional regulation of early functions of bacteriophage phi 80. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J., Sloan S. B., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E., Robledo R., Harbrecht D. The remarkable specificity of a new transcription termination factor suggests that the mechanisms of termination and antitermination are similar. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90644-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robledo R., Gottesman M. E., Weisberg R. A. Lambda nutR mutations convert HK022 Nun protein from a transcription termination factor to a suppressor of termination. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90226-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmientos P., Sylvester J. E., Contente S., Cashel M. Differential stringent control of the tandem E. coli ribosomal RNA promoters from the rrnA operon expressed in vivo in multicopy plasmids. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1337–1346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard S. F., Howe M. M. Localization and regulation of bacteriophage Mu promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3440–3448. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3440-3448.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. Control of development in temperate bacteriophages. 3. Which prophage genes are and which are not trans-activable in the presence of immunity? J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Pirrotta V., Ineichen K. Lambda repressor regulates the switch between PR and Prm promoters. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):665–669. doi: 10.1038/262665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiffenbach B., Rogers D. T., Haber J. E., Zoller M., Russell D. W., Smith M. Deletions and single base pair changes in the yeast mating type locus that prevent homothallic mating type conversions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3401–3405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hatfield G. W. Examination of the internal promoter, PE, in the ilvGMEDA operon of E. coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2763–2777. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil E., Dolev S., Oberto J., Kislev N., Ramaiah N., Weisberg R. A. Determinants of site-specific recombination in the lambdoid coliphage HK022. An evolutionary change in specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):695–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. Q., Gangopadhyay T., Padmanabha K. P., Deutscher M. P. Escherichia coli rna gene encoding RNase I: cloning, overexpression, subcellular distribution of the enzyme, and use of an rna deletion to identify additional RNases. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3146–3151. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3146-3151.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]