Abstract
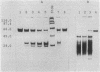
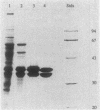
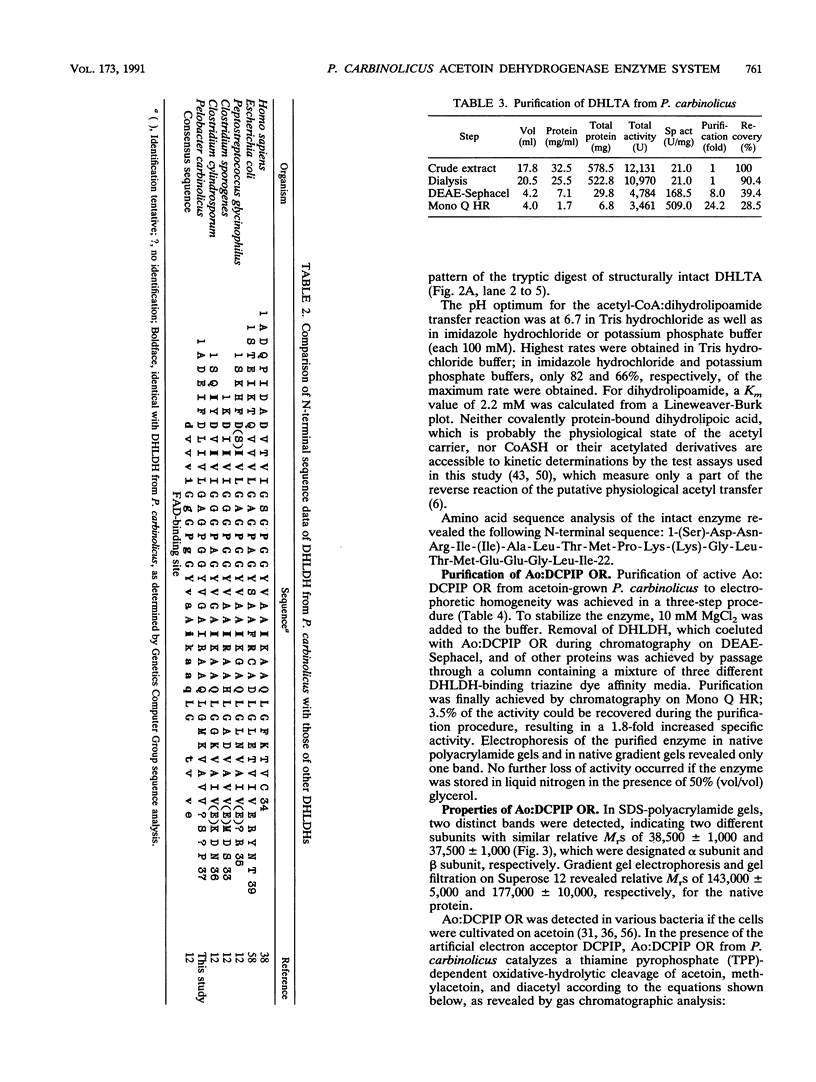
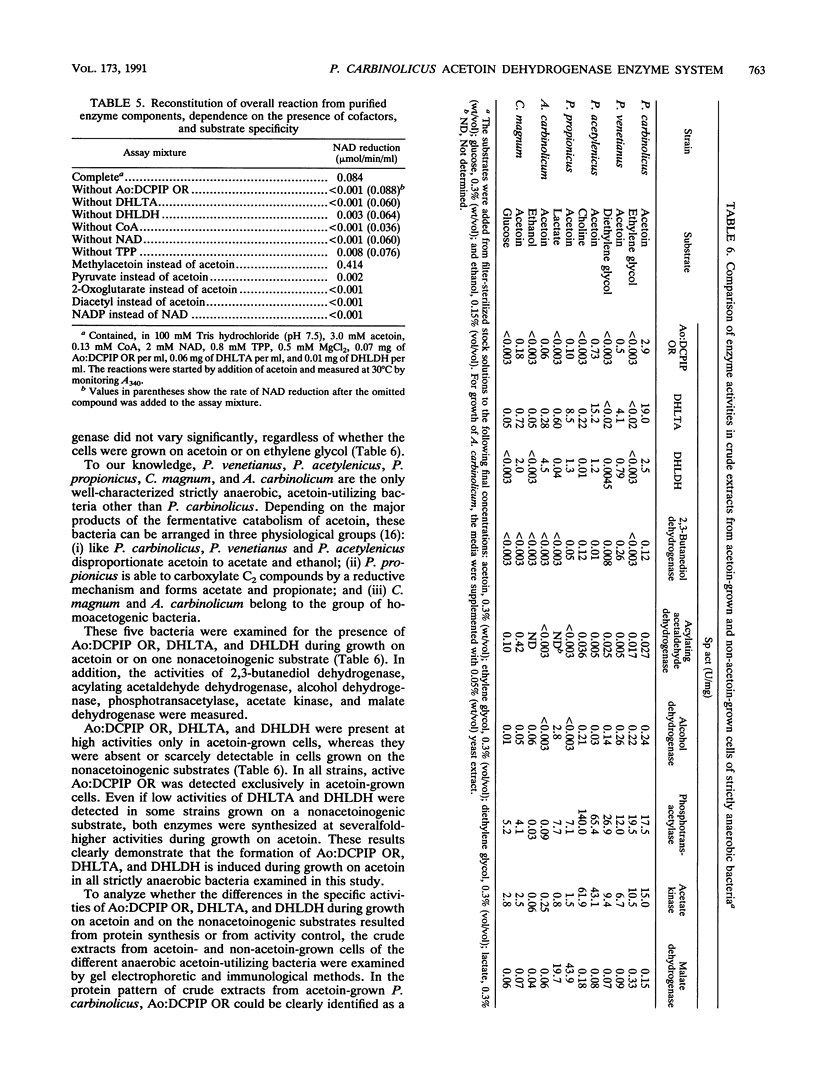
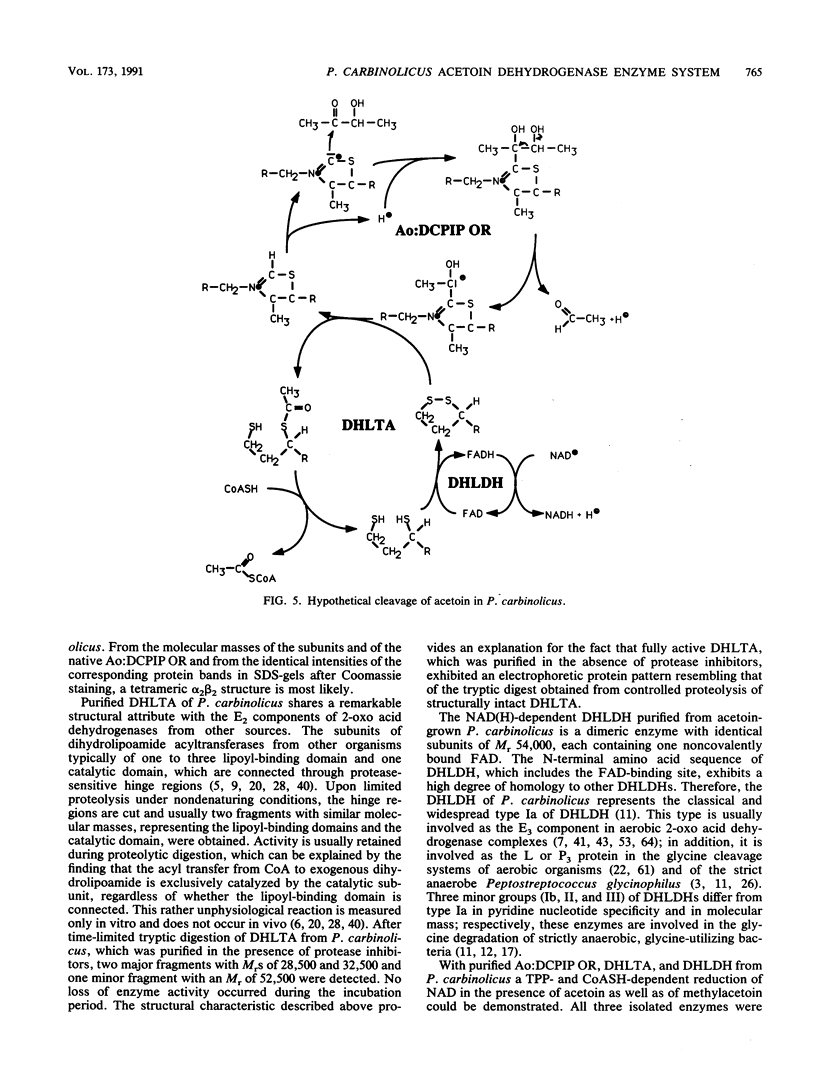
Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DHLDH), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (DHLTA), and acetoin: 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol oxidoreductase (Ao:DCPIP OR) were purified from acetoin-grown cells of Pelobacter carbinolicus. DHLDH had a native Mr of 110,000, consisted of two identical subunits of Mr 54,000, and reacted only with NAD(H) as a coenzyme. The N-terminal amino acid sequence included the flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding site and exhibited a high degree of homology to other DHLDHs. DHLTA had a native Mr of greater than 500,000 and consisted of subunits identical in size (Mr 60,000). The enzyme was highly sensitive to proteolytic attack. During limited tryptic digestion, two major fragments of Mr 32,500 and 25,500 were formed. Ao:DCPIP OR consisted of two different subunits of Mr 37,500 and 38,500 and had a native Mr in the range of 143,000 to 177,000. In vitro in the presence of DCPIP, it catalyzed a thiamine pyrophosphate-dependent oxidative-hydrolytic cleavage of acetoin, methylacetoin, and diacetyl. The combination of purified Ao:DCPIP OR, DHLTA, and DHLDH in the presence of thiamine pyrophosphate and the substrate acetoin or methylacetoin resulted in a coenzyme A-dependent reduction of NAD. In the strictly anaerobic acetoin-utilizing bacteria P. carbinolicus, Pelobacter venetianus, Pelobacter acetylenicus, Pelobacter propionicus, Acetobacterium carbinolicum, and Clostridium magnum, the enzymes Ao:DCPIP OR, DHLTA, and DHLDH were induced during growth on acetoin, whereas they were absent or scarcely present in cells grown on a nonacetoinogenic substrate.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. -O., Borg H., Mikaelsson M. Molecular weight estimations of proteins by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels of graded porosity. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 1;20(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80793-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson T., Hammond P. M., Hartwell R. D., Hughes P., Scawen M. D., Sherwood R. F., Small D. A., Bruton C. J., Harvey M. J., Lowe C. R. Triazine-dye affinity; chromatography. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Aug;9(4):290–293. doi: 10.1042/bst0090290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleile D. M., Hackert M. L., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Subunit structure of dihydrolipoyl transacetylase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from bovine heart. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):514–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth P. J., Tsai C. S., Eley M. H., Roche T. E., Reed L. J. A kinetic study of dihydrolipoyl transacetylase from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1921–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers D. J., Pons G., Patel M. S. Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: functional similarities and divergent evolution of the pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 1;268(2):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen P. Paracatalytic enzyme modification by oxidation of enzyme-substrate carbanion intermediates. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:48–54. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang D. T., Hu C. C., Ku L. S., Niu W. L., Myers D. E., Cox R. P. Catalytic and structural properties of the dihydrolipoyl transacylase component of bovine branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9277–9284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. P., Cronan J. E., Jr Acetaldehyde coenzyme A dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):179–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.179-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLIN M. I. Diacetyl oxidation by Streptococcus faecalis, a lipoic acid dependent reaction. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jan;69(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.1.51-58.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrichs D., Andreesen J. R. Purification and comparative studies of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases from the anaerobic, glycine-utilizing bacteria Peptostreptococcus glycinophilus, Clostridium cylindrosporum, and Clostridium sporogenes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):243–251. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.243-251.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrichs D., Meyer M., Schmidt B., Andreesen J. R. Purification of NADPH-dependent electron-transferring flavoproteins and N-terminal protein sequence data of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases from anaerobic, glycine-utilizing bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2088–2095. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2088-2095.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg W., Dietrichs D., Lebertz H., Andreesen J. R. Isolation of an atypically small lipoamide dehydrogenase involved in the glycine decarboxylase complex from Eubacterium acidaminophilum. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1346–1354. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1346-1354.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P. A., Flournoy D. S., Gruys K., Yang Y. S. Intermediates in reductive transacetylation catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fründ C., Priefert H., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Biochemical and genetic analyses of acetoin catabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6539–6548. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6539-6548.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanemaaijer R., de Kok A., Jolles J., Veeger C. The domain structure of the dihydrolipoyl transacetylase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga K., Kikuchi G. The mitochondrial glycine cleavage system. Purification and properties of glycine decarboxylase from chicken liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11664–11670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson J. A., Lowe P. N., Perham R. N. Wild-type and mutant forms of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):463–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2110463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNI E., HEYM G. A. A cyclic pathway for the bacterial dissimilation of 2, 3-butanediol, acetylmethylcarbinol, and diacetyl. I. General aspects of the 2, 3-butanediol cycle. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):425–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.425-432.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S. M., Sagers R. D. Glycine metabolism. 3. A flavin-linked dehydrogenase associated with the glycine cleavage system in Peptococcus glycinophilus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):297–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochetov G. A. Determination of transketolase activity via ferricyanide reduction. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):43–44. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresze G. B., Ronft H. Bovine kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Limited proteolysis and molecular structure of the lipoate acetyltransferase component. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):589–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresze G. B., Ronft H. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from baker's yeast. 1. Purification and some kinetic and regulatory properties. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):573–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. N., Leeper F. J., Perham R. N. Stereoisomers of tetrahydrothiamin pyrophosphate, potent inhibitors of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):150–157. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López J. M., Thoms B., Rehbein H. Acetoin degradation in Bacillus subtilis by direct oxidative cleavage. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Mayhew S. G. Temperature-difference spectra of flavins and flavoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;66:350–360. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(80)66480-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann F. B., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Evidence for oxidative thiolytic cleavage of acetoin in Pelobacter carbinolicus analogous to aerobic oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 1;51(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otulakowski G., Robinson B. H. Isolation and sequence determination of cDNA clones for porcine and human lipoamide dehydrogenase. Homology to other disulfide oxidoreductases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17313–17318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N., Roberts G. C. Domain structure and 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2170219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED L. J., KOIKE M., LEVITCH M. E., LEACH F. R. Studies on the nature and reactions of protein-bound lipoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):143–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N. Design and operation of a completely automated Beckman microsequencer. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):538–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Stieb M. Fermentative degradation of polyethylene glycol by a strictly anaerobic, gram-negative, nonsporeforming bacterium, Pelobacter venetianus sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1905–1913. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1905-1913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. R., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XII. Effects of acetylation on the activity and structure of the dihydrolipoyl transacetylase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6074–6079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga K., Horiike K., Nishina Y., Otani S., Watari H., Yamano T. A study of flavin-protein and flavoprotein-ligand interactions. Binding aspects and spectral properties of D-amino acid oxidase and riboflavin binding protein. J Biochem. 1979 Apr;85(4):931–941. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M. Quantitative determination of noncovalently bound flavins: types and methods of analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:419–429. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokatch J. R., McCully V., Gebrosky J., Sokatch D. J. Isolation of a specific lipoamide dehydrogenase for a branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.639-646.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann H., Francksen H., Macko V. Potato proteins: genetic and physiological changes, evaluated by one- and two-dimensional PAA-gel-techniques. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Nov-Dec;28(11):722–732. doi: 10.1515/znc-1973-11-1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. A multifunctional fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase from the strict aerobe Alcaligenes eutrophus: purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):555–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Lewis H. M., Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. S., Wand A. J., Templeton D. M., Weiss P. M. Multifunctionality of lipoamide dehydrogenase promotion of electron transferase reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):554–561. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. L., Oliver D. J. Glycine decarboxylase multienzyme complex. Purification and partial characterization from pea leaf mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2214–2221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdel F., Pfennig N. Studies on dissimilatory sulfate-reducing bacteria that decompose fatty acids. I. Isolation of new sulfate-reducing bacteria enriched with acetate from saline environments. Description of Desulfobacter postgatei gen. nov., sp. nov. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jul;129(5):395–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00406470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]