Abstract
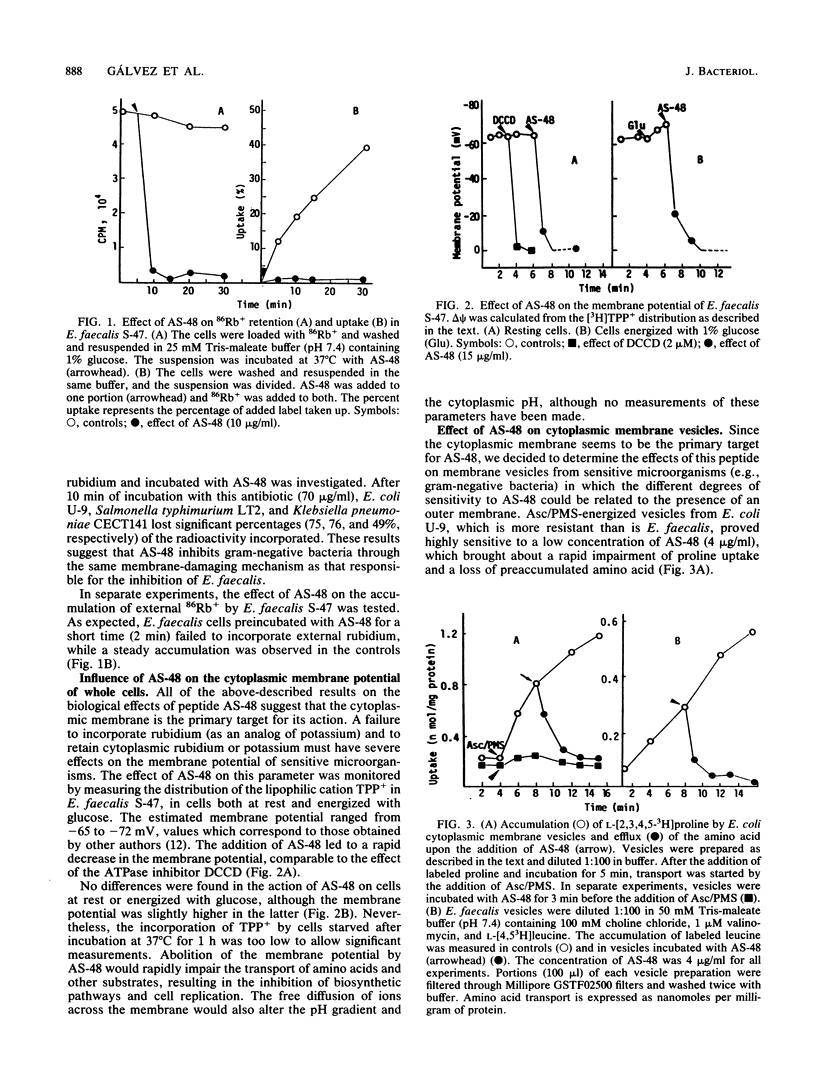
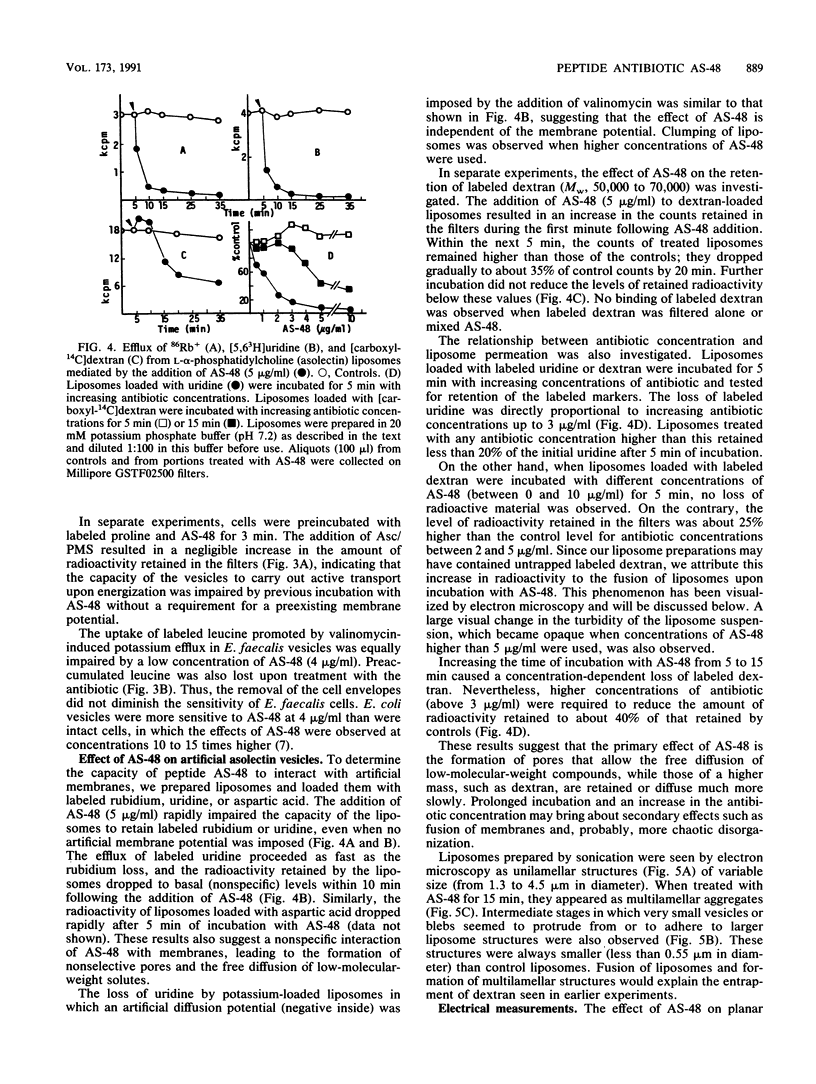
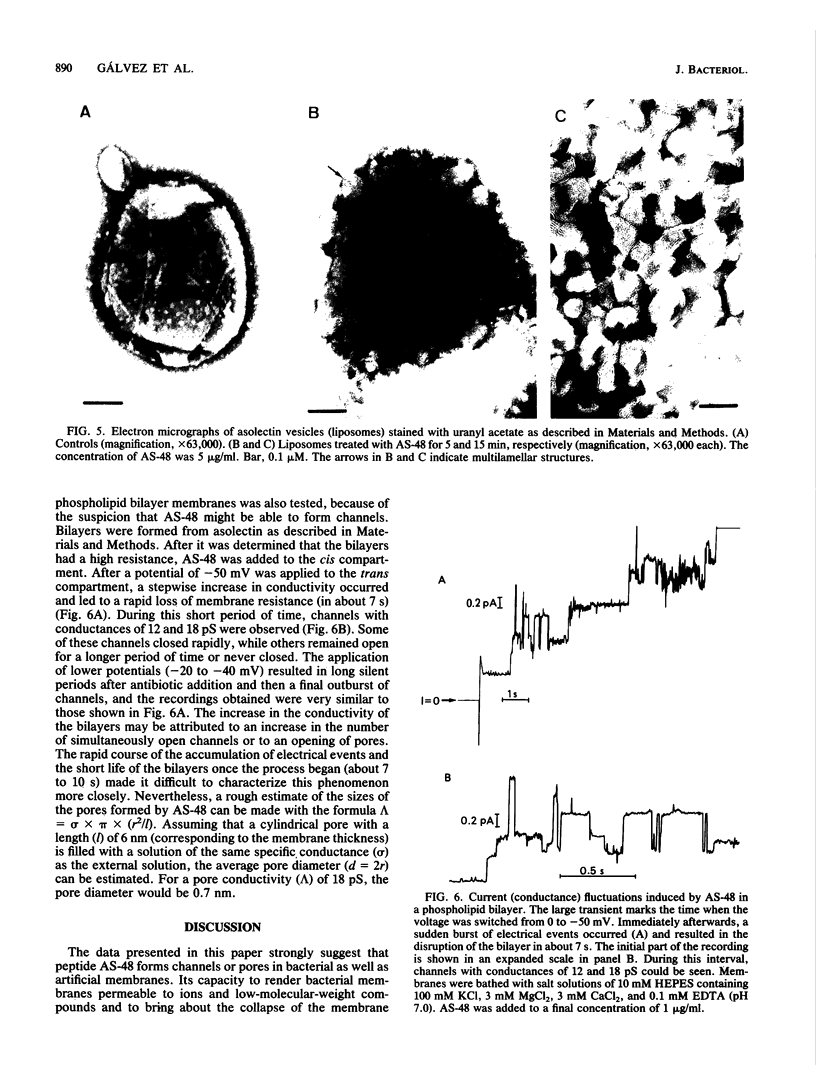
Peptide AS-48 induces ion permeation, which is accompanied by the collapse of the cytoplasmic membrane potential, in sensitive bacteria. Active transport by cytoplasmic membrane vesicles is also impaired by AS-48. At low concentrations, this peptide also causes permeability of liposomes to low-molecular-weight compounds without a requirement for a membrane potential. Higher antibiotic concentrations induce severe disorganization, which is visualized under electron microscopy as aggregation and formation of multilamellar structures. Electrical measurements suggest that AS-48 can form channels in lipid bilayers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCK T. D., PEACHER B., PIERSON D. SURVEY OF THE BACTERIOCINES OF ENTEROCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.702-707.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisschop A., Konings W. N. Reconstitution of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidase activity with menadione in membrane vesicles from the menaquinone-deficient Bacillus subtilis aro D. Relation between electron transfer and active transport. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):357–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvez A., Valdivia E., Maqueda M., Montoya E. Production of bacteriocin-like substances by group D streptococci of human origin. Microbios. 1985;43(176S):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvez A., Valdivia E., Martinez M., Maqueda M. Effect of peptide AS-48 on Enterococcus faecalis subsp. liquefaciens S-47. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):641–645. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gálvez A., Giménez-Gallego G., Maqueda M., Valdivia E. Purification and amino acid composition of peptide antibiotic AS-48 produced by Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecalis subsp. liquefaciens S-48. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gálvez A., Valdivia E., Martínez M., Maqueda M. Bactericidal action of peptide antibiotic AS-48 against Escherichia coli K-12. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Feb;35(2):318–321. doi: 10.1139/m89-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Iwanami T., Hirasawa M., Watanabe C., McGhee J. R., Shiota T. Purification and certain properties of a bacteriocin from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):861–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.861-868.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJEMS E. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. I. Technique of isolating phage-producing strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(5):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Murakami N., Unemoto T. Regulation of the cytoplasmic pH in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13246–13252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Unemoto T. Streptococcus faecalis mutants defective in regulation of cytoplasmic pH. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1187–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1187-1193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordel M., Benz R., Sahl H. G. Mode of action of the staphylococcinlike peptide Pep 5: voltage-dependent depolarization of bacterial and artificial membranes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):84–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.84-88.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Bueno M., Gálvez A., Valdivia E., Maqueda M. A transferable plasmid associated with AS-48 production in Enterococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2817–2818. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2817-2818.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattus F., Cavard D., Crozel V., Baty D., Adrian M., Lazdunski C. pH-dependent membrane fusion is promoted by various colicins. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2469–2474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhr E., Sahl H. G. Mode of action of the peptide antibiotic nisin and influence on the membrane potential of whole cells and on cytoplasmic and artificial membrane vesicles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):841–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl H. G., Brandis H. Production, purification and chemical properties of an antistaphylococcal agent produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):377–384. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl H. G. Influence of the staphylococcinlike peptide Pep 5 on membrane potential of bacterial cells and cytoplasmic membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):833–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.833-836.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield J. B., Graff D., Li H. P. A solid-phase method for the quantitation of protein in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate and other interfering substances. Anal Biochem. 1987 Oct;166(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90544-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Effect of colicins Ia and E1 on ion permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Boulnois G. J. Analysis of a cloned colicin Ib gene: complete nucleotide sequence and implications for regulation of expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6727–6739. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



