Abstract
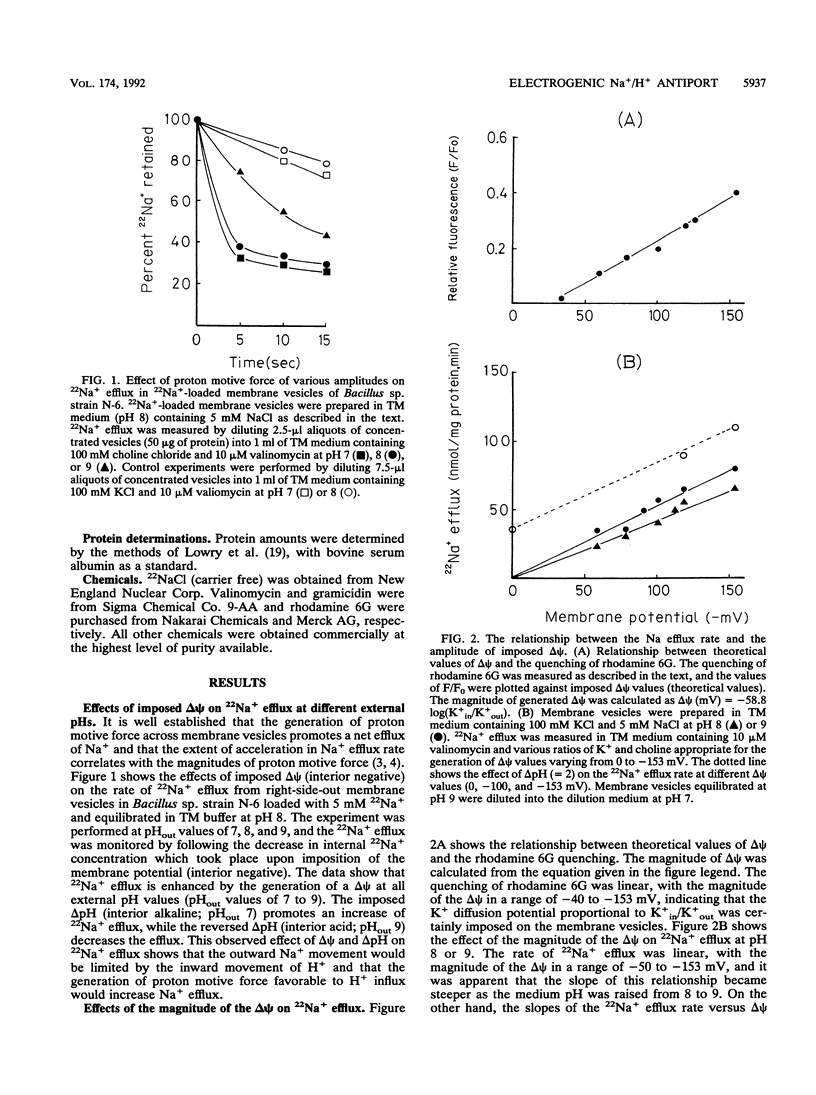
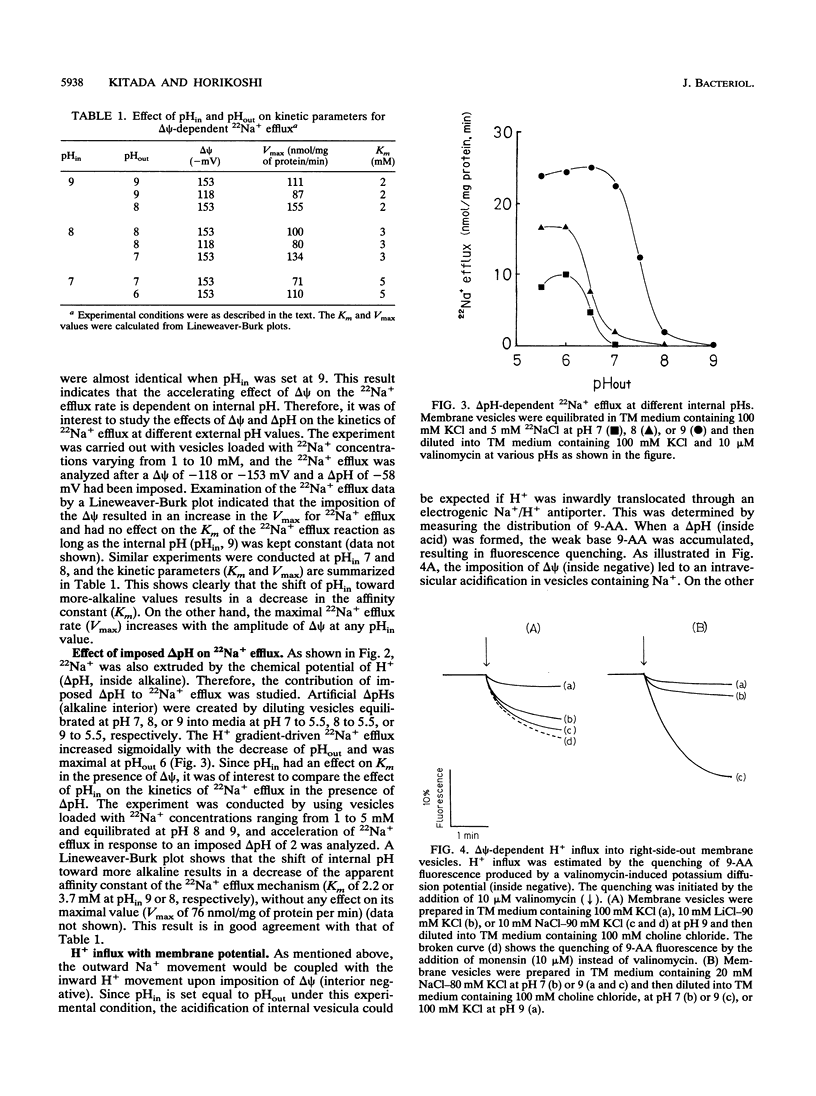
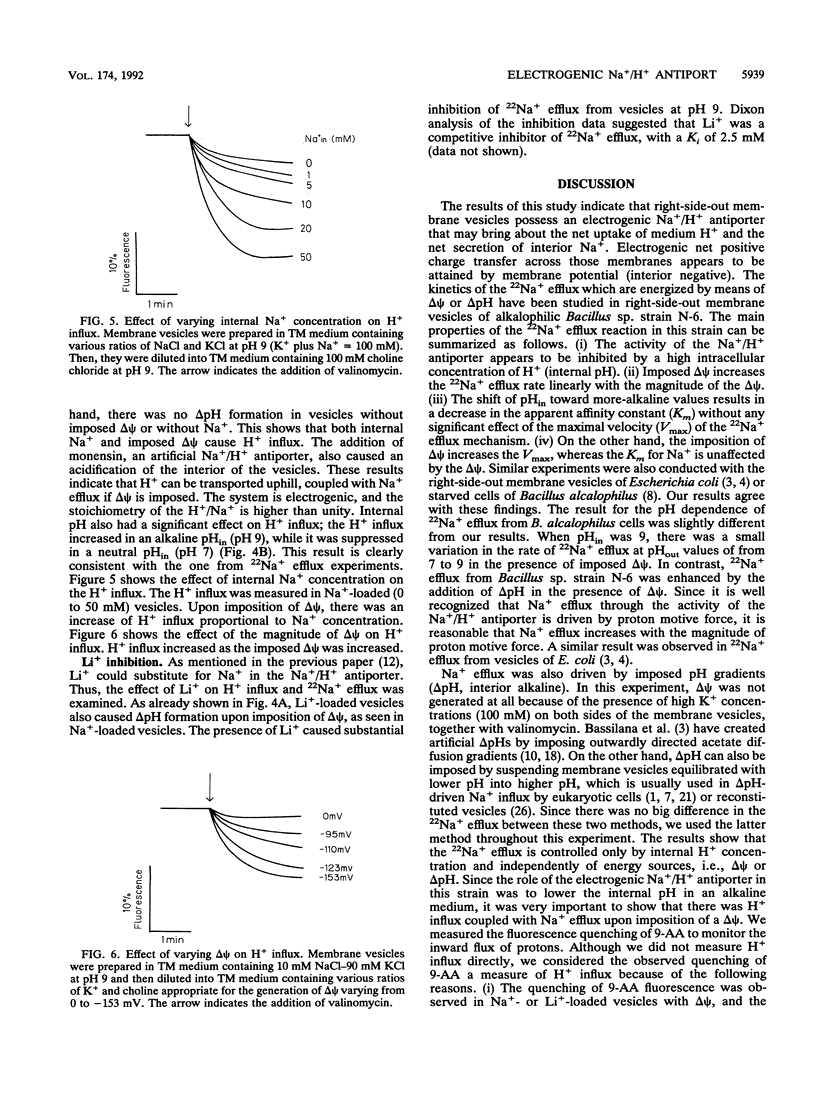
The effects of imposed proton motive force on the kinetic properties of the alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain N-6 Na+/H+ antiport system have been studied by looking at the effect of delta psi (membrane potential, interior negative) and/or delta pH (proton gradient, interior alkaline) on Na+ efflux or H+ influx in right-side-out membrane vesicles. Imposed delta psi increased the Na+ efflux rate (V) linearly, and the slope of V versus delta psi was higher at pH 9 than at pH 8. Kinetic experiments indicated that the delta psi caused a pronounced increase in the Vmax for Na+ efflux, whereas the Km values for Na+ were unaffected by the delta psi. As the internal H+ concentration increased, the Na+ efflux reaction was inhibited. This inhibition resulted in an increase in the apparent Km of the Na+ efflux reaction. These results have also been observed in delta pH-driven Na+ efflux experiments. When Na(+)-loaded membrane vesicles were energized by means of a valinomycin-induced inside-negative K+ diffusion potential, the generated acidic-interior pH gradients could be detected by changes in 9-aminoacridine fluorescence. The results of H+ influx experiments showed a good coincidence with those of Na+ efflux. H+ influx was enhanced by an increase of delta psi or internal Na+ concentration and inhibited by high internal H+ concentration. These results are consistent with our previous contentions that the Na+/H+ antiport system of this strain operates electrogenically and plays a central role in pH homeostasis at the alkaline pH range.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn G. A., Franco P., Clay L. P. Electrogenic 2 Na+/1 H+ exchange in crustaceans. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jul;116(3):215–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01868461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiuchi T., Tanabe H., Kurihara K., Kobatake Y. Fluorescence changes of rhodamine 6G associated with chemotactic responses in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 20;628(3):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassilana M., Damiano E., Leblanc G. Relationships between the Na+-H+ antiport activity and the components of the electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):1015–1022. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Characterization of the Na+/H+ antiporter of alkalophilic bacilli in vivo: delta psi-dependent 22Na+ efflux from whole cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1151–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1151-1157.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Robertson D. E., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 2. Effect of imposed delata psi, delta pH, and Delta mu H+. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3697–3704. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Bioenergetic properties and viability of alkalophilic Bacillus firmus RAB as a function of pH and Na+ contents of the incubation medium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1096–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1096-1104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Onda K., Horikoshi K. The sodium/proton antiport system in a newly isolated alkalophilic Bacillus sp. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1879–1884. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1879-1884.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Murakami N., Unemoto T. Regulation of the cytoplasmic pH in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13246–13252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Bioenergetics of alkalophilic bacteria. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01869707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Hoffstein J. A sodium requirement for growth, solute transport, and pH homeostasis in Bacillus firmus RAB. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1885–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Hino M., Kitada M., Horikoshi K. DNA sequences required for the alkalophily of Bacillus sp. strain C-125 are located close together on its chromosomal DNA. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7282–7283. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7282-7283.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hinkle P. C. Studies of the beta-galactoside transporter in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. I. Symmetrical facilitated diffusion and proton gradient-coupled transport. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7657–7661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Monovalent cation/proton antiporters in membrane vesicles from Bacillus alcalophilus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7391–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K., Canessa M. Interactions of external and internal H+ and Na+ with Na+/Na+ and Na+/H+ exchange of rabbit red cells: evidence for a common pathway. J Membr Biol. 1990 Dec;118(3):193–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01868604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plack R. H., Jr, Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Absence of potassium/proton antiporter activity in a pH-sensitive mutant. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3824–3825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reenstra W. W., Warnock D. G., Yee V. J., Forte J. G. Proton gradients in renal cortex brush-border membrane vesicles. Demonstration of a rheogenic proton flux with acridine orange. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11663–11666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H. Sodium-proton antiport in isolated membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):706–711. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Takeda K. Calcium/proton and sodium/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1979 Apr;85(4):943–951. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Dubinsky W. P. Solubilization and reconstitution of renal brush border Na+-H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1988;101(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF01872814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. The sodium/proton antiporter is part of the pH homeostasis mechanism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3687–3691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



