Abstract
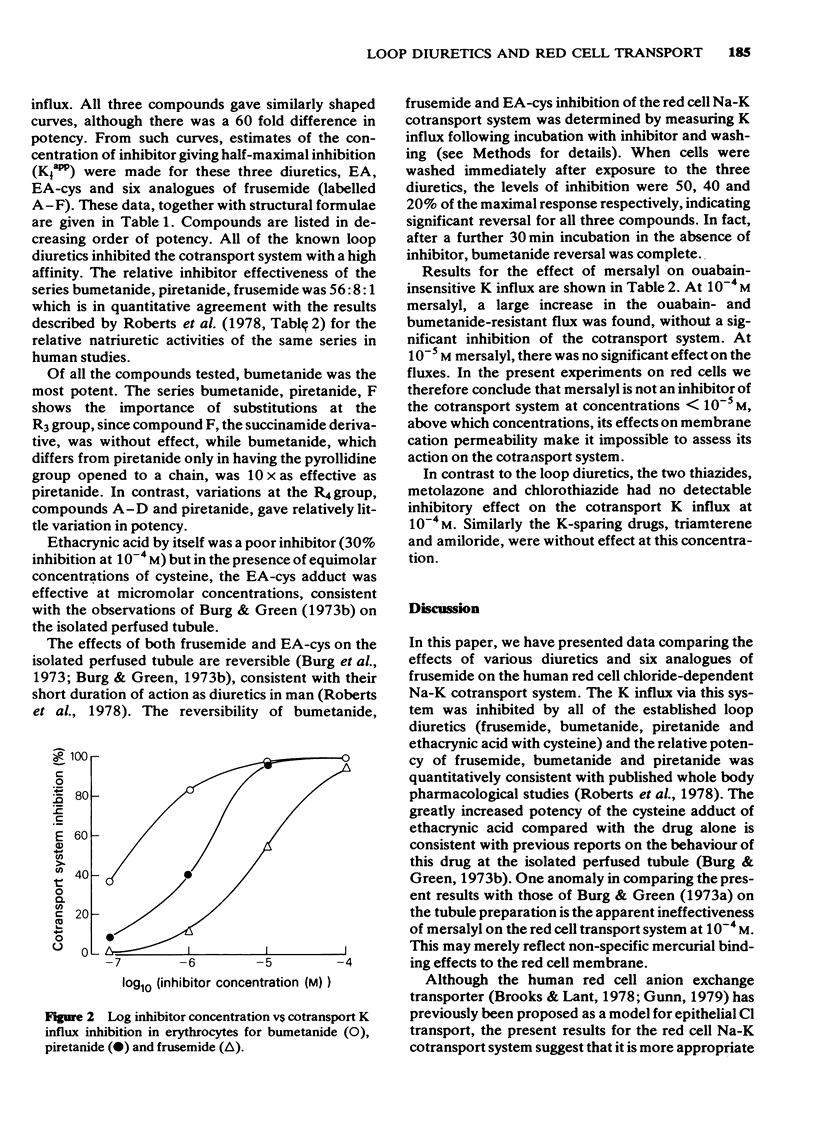
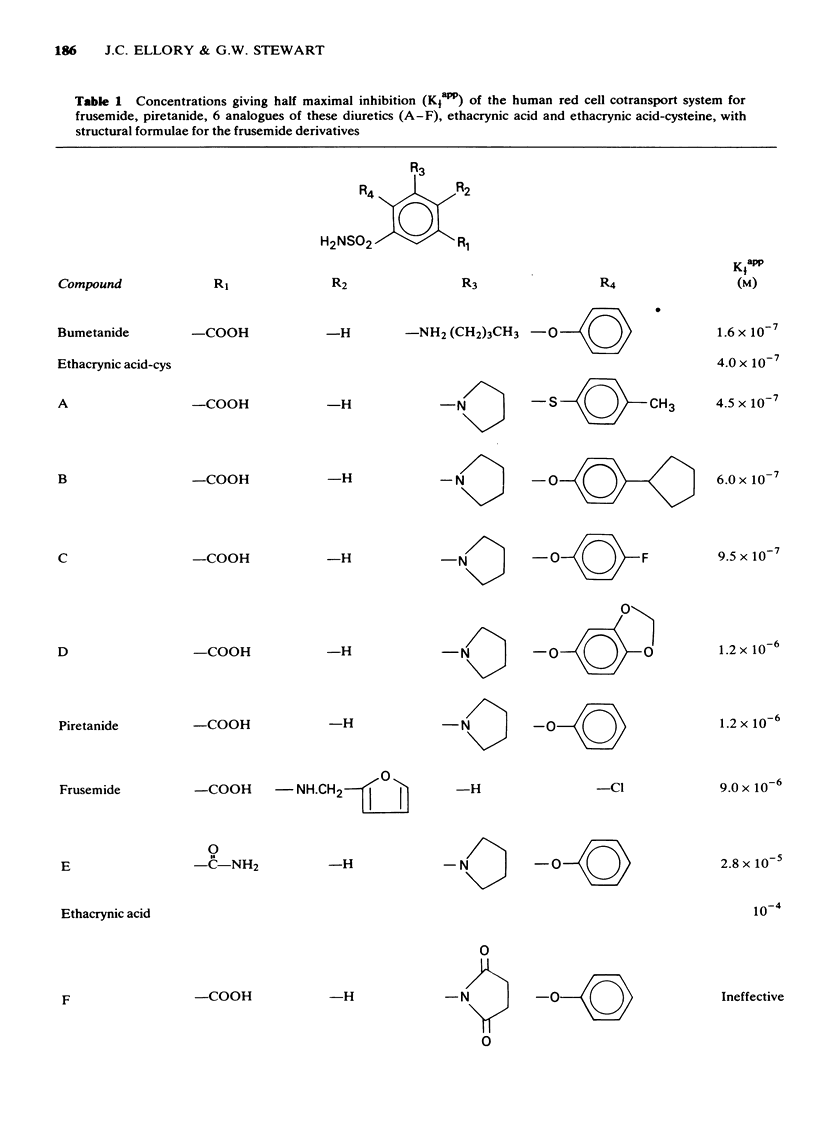
1 The recent demonstration of the chloride-dependence of the red cell Na-K cotransport system suggests an analogy between this process and the active Cl- absorption in the ascending loop of Henle, which is the target transport system for loop diuretics. 2 Using red cell K influx, four known loop diuretics, six experimental frusemide analogues, two thiazides, two K-retaining diuretics and one organomercurial were compared for inhibitory potency on the red cell Na-K cotransport system. 3 Except for mersalyl, whose exact mode of action in the kidney is still in doubt, the inhibition of the red cell system by various loop diuretics was consistent with both published whole body diuretic data and isolated perfused tubule studies, while the system did not respond to the thiazides or the K-retaining diuretics. 4 It is concluded that the human red cell Na-K cotransport system is a possible valid model process on which to study the activity of loop diuretics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brading A. F. Maintenance of ionic composition. Br Med Bull. 1979 Sep;35(3):227–234. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazy P. C., Gunn R. B. Furosemide inhibition of chloride transport in human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Dec;68(6):583–599. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.6.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. A., Lant A. F. The use of the human erythrocyte as a model for studying the action of diuretics on sodium and chloride transport. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1978 Jun;54(6):679–683. doi: 10.1042/cs0540679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Green N. Effect of ethacrynic acid on the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Kidney Int. 1973 Nov;4(5):301–308. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Green N. Effect of mersalyl on the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Kidney Int. 1973 Oct;4(4):245–251. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Stoner L., Cardinal J., Green N. Furosemide effect on isolated perfused tubules. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jul;225(1):119–124. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Stoner L. Renal tubular chloride transport and the mode of action of some diuretics. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:37–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafruny E. J. The site and mechanism of action of mercurial diruetics. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Jun;20(2):89–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Ellory J. C. Stimulation of the sodium-potassium pump by trypsin in low potassium type erythrocytes of goats. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:25–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Stewart G. W., Ellory J. C. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Field M., Schultz S. G. Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):F1–F8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C., Feit P. W., Greengard P. cAMP-stimulated cation cotransport in avian erythrocytes: inhibition by "loop" diuretics. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):C139–C148. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.238.3.C139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Homeida M., Roberts F., Bogie W. Effects of piretanide, bumetanide and frusemide on electrolyte and urate excretion in normal subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;6(2):129–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb00837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M. Chloride and sodium influx: a coupled uptake mechanism in the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jun;73(6):801–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEED R., EBER J., ROTHSTEIN A. Interaction of mercury with human erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jan;45:395–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.3.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


