Abstract
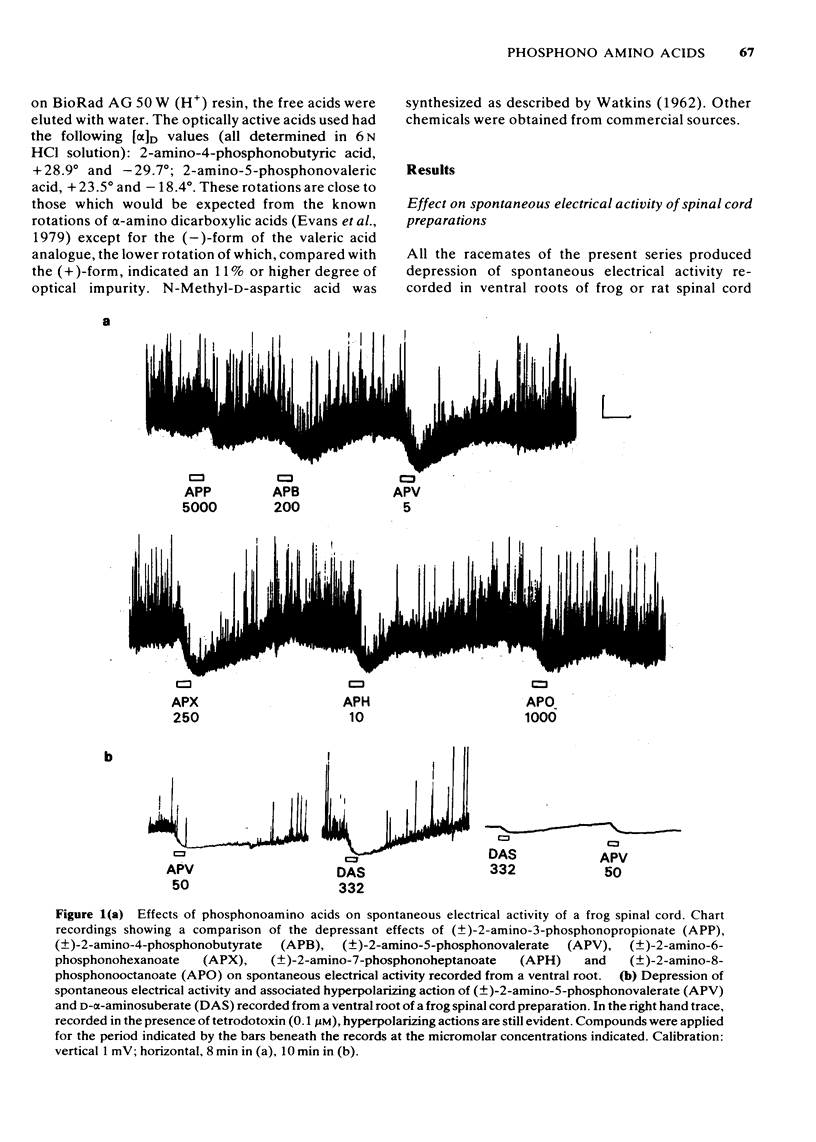
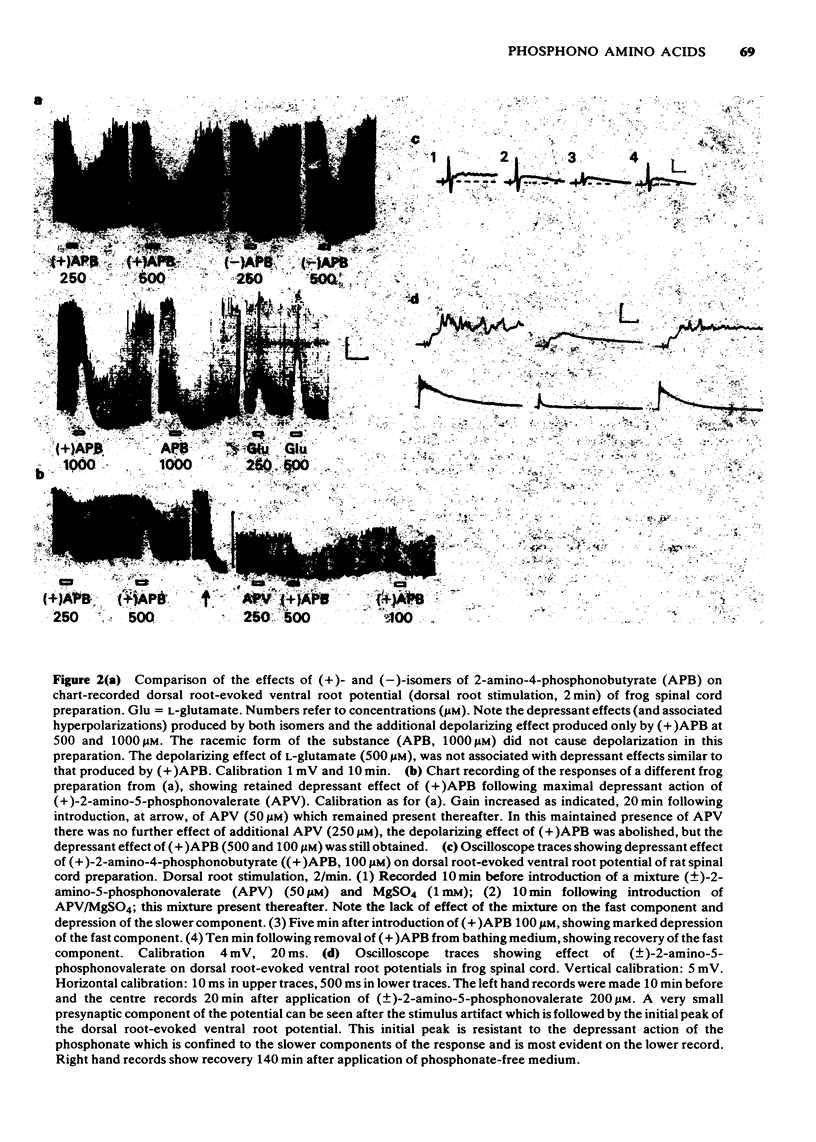
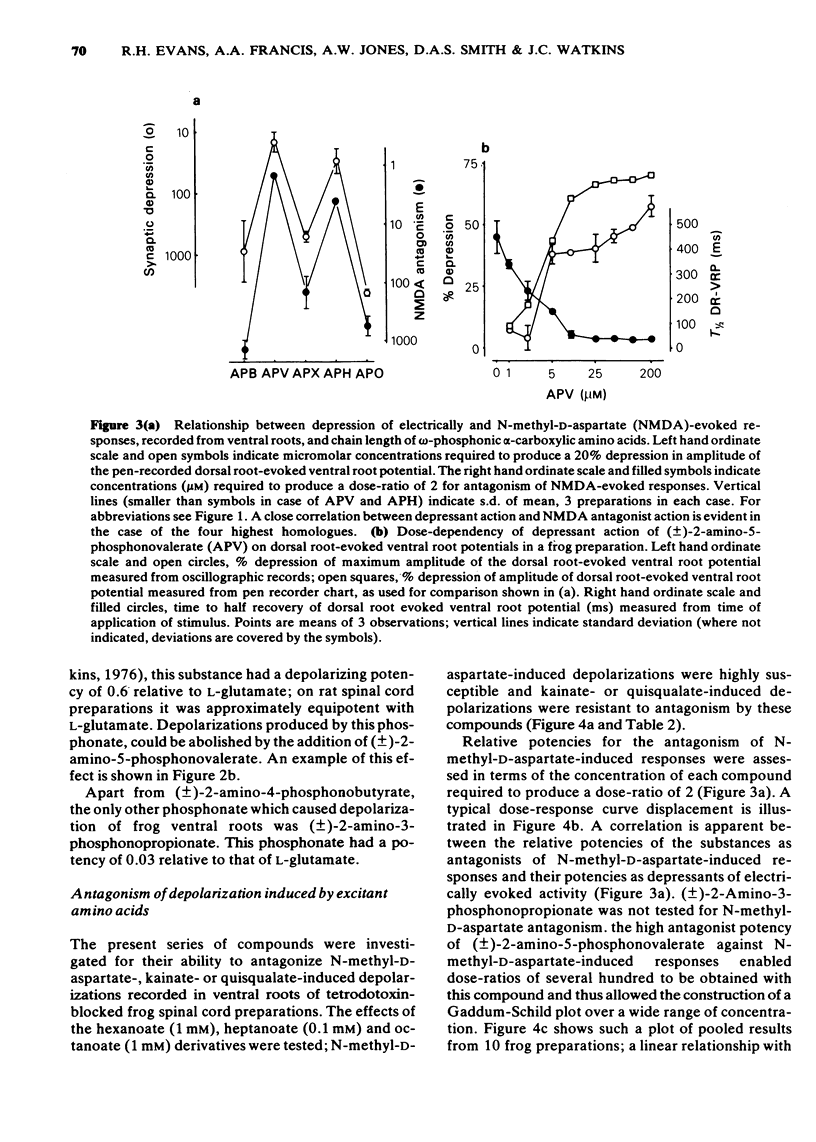
1 The depressant actions on evoked electrical activity and the excitant amino acid antagonist properties of a range of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids have been investigated in the isolated spinal cord preparations of the frog or immature rat. 2 When tested on dorsal root-evoked ventral root potentials, members of the homologous series from 2- amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid to 2-amino-8-phosphonooctanoic acid showed depressant actions which correlated with the ability of the substances to antagonize selectivity motoneuronal depolarizations induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate. 3 2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate was the most potent substance of the series giving an apparent KD of 1.4 microM for the antagonism of responses to N-methyl-D-aspartate. 4 A comparison of the (+)- and (-)-forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate indicated that the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist activity and the neuronal depressant action of this substance were both due mainly to the (-)-isomer. 5 The (-)- and (+)-forms of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate had different actions. The (-)-forms of this substance had a relatively weak and non-selective antagonist action on depolarizations induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate, quisqualate and kainate and a similarly weak depressant effect when tested on evoked electrical activity. The (+)-form was more potent than he (-)-form in depressing electrically evoked activity but did not antagonize responses to amino acid excitants. At concentrations higher than those required to depress electrically evoked activity, the (+)-form produced depolarization. This action was blocked by 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate.
Full text
PDF


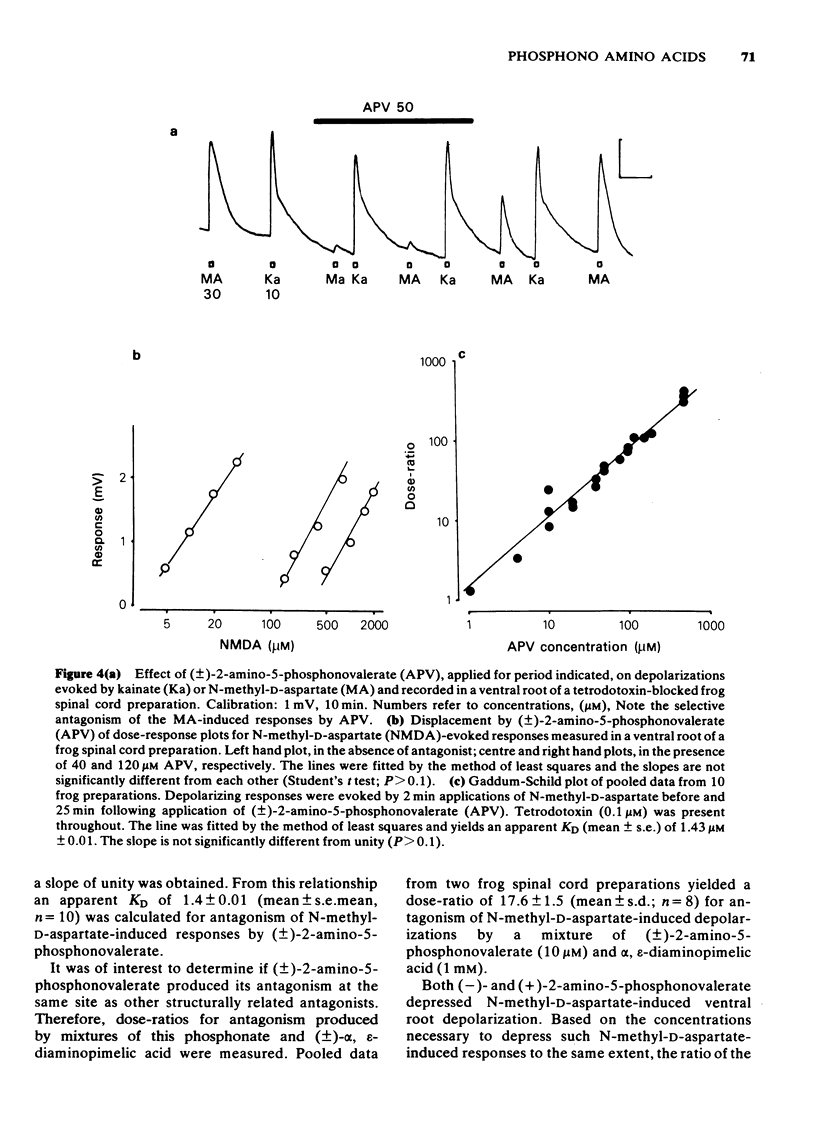




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan R. D., Evans R. H., Johnston G. A. gamma-Aminobutyric acid agonists: an in vitro comparison between depression of spinal synaptic activity and depolarization of spinal root fibres in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec;70(4):609–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb09779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:413–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron D. H., Matthews B. H. The interpretation of potential changes in the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1938 Apr 14;92(3):276–321. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey G. K., Martin M. R., Hermes M. Effects of D,L-alpha-aminoadipate on postsynaptic amino acid responses in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 7;193(1):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90957-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Evans R. H., Headley P. M., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C. Structure-activity relations of excitatory amino acids on frog and rat spinal neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):373–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Donnellan J. F., James R. W., Lunt G. G. 2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid as a glutamate antagonist on locust muscle. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):408–409. doi: 10.1038/262408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Watkins J. C. The pharmacology of amino acids related to gamma-aminobutyric acid. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Dec;17(4):347–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. 2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate (2APV), a potent and selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jan 1;21(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Aspartate and other inhibitors of excitatory synaptic transmission in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1977 May 6;369(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00580803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H. Evidence supporting the indirect depolarization of primary afferent terminals in the frog by excitatory amino acids. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:25–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Hunt K., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced responses and of synaptic excitation in the isolated spinal cord of the frog. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;67(4):591–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H. The effects of amino acids and antagonists on the isolated hemisected spinal cord of the immature rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;62(2):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb08442.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Watkins J. C. Pharmacological antagonists of excitant amino acid action. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 23;28(12):1303–1308. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90401-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Watkins J. C. Specific antagonism of excitant amino acids in the isolated spinal cord of the neonatal rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul 15;50(2):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. Dipeptide antagonists of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the frog spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1980 Dec;35(6):1458–1460. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner J. F., Cotman C. W. Micromolar L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid selectively inhibits perforant path synapses from lateral entorhinal cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 6;216(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo Y. The pharmacology of the amphibian spinal cord. Prog Neurobiol. 1978;11(1):1–76. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(78)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Lodge D. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitation of spinal neurones in the cat. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 15;169(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Electrophysiology of mammalian spinal cord in vitro. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):733–734. doi: 10.1038/252733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. The actions of glutamic acid on neurons in the rat hippocampal slice. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.6255566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS J. C. THE SYNTHESIS OF SOME ACIDIC AMINO ACIDS POSSESSING NEUROPHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITY. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 Nov;91:1187–1199. doi: 10.1021/jm01241a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Curtis D. R., Brand S. S. Phosphonic analogues as antagonists of amino acid excitants. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1977 May;29(5):324–324. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1977.tb11328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Nadler J. V., Cotman C. W. The effect of acidic amino acid antagonists on synaptic transmission in the hippocampal formation in vitro. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 23;164:177–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Nadler J. V., Hamberger A., Cotman C. W., Cummins J. T. Glutamate as transmitter of hippocampal perforant path. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):356–357. doi: 10.1038/270356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


