Abstract
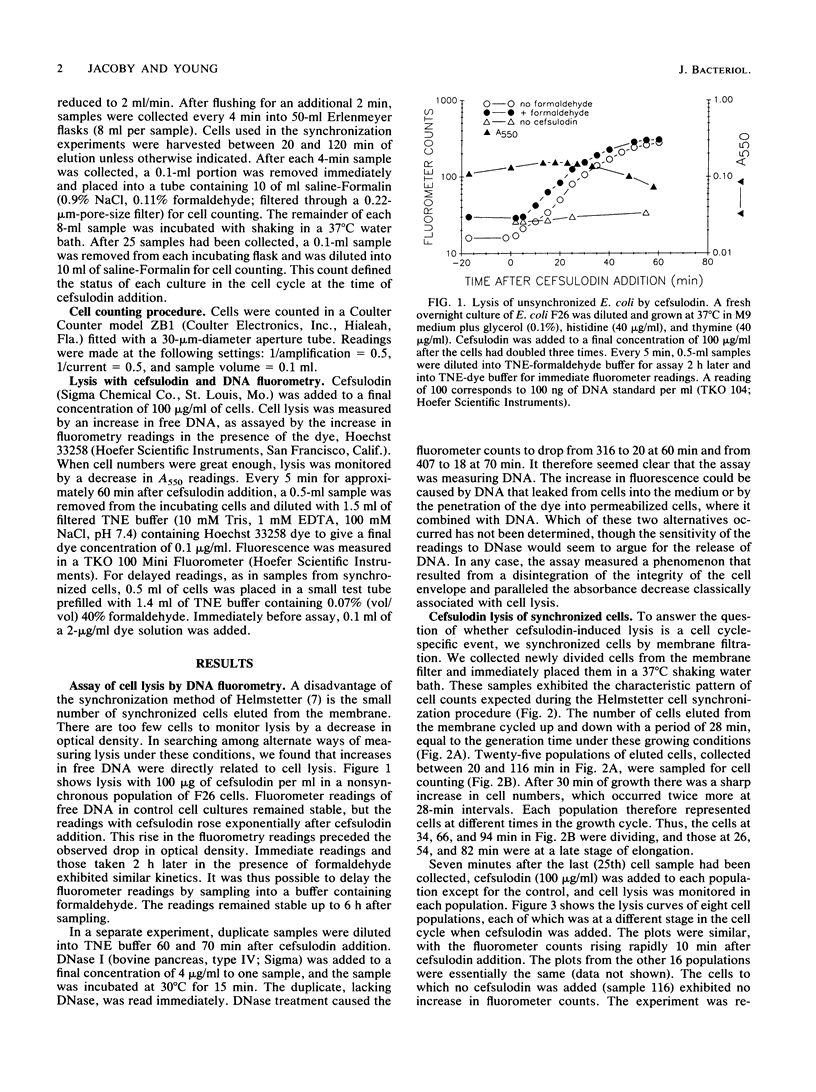
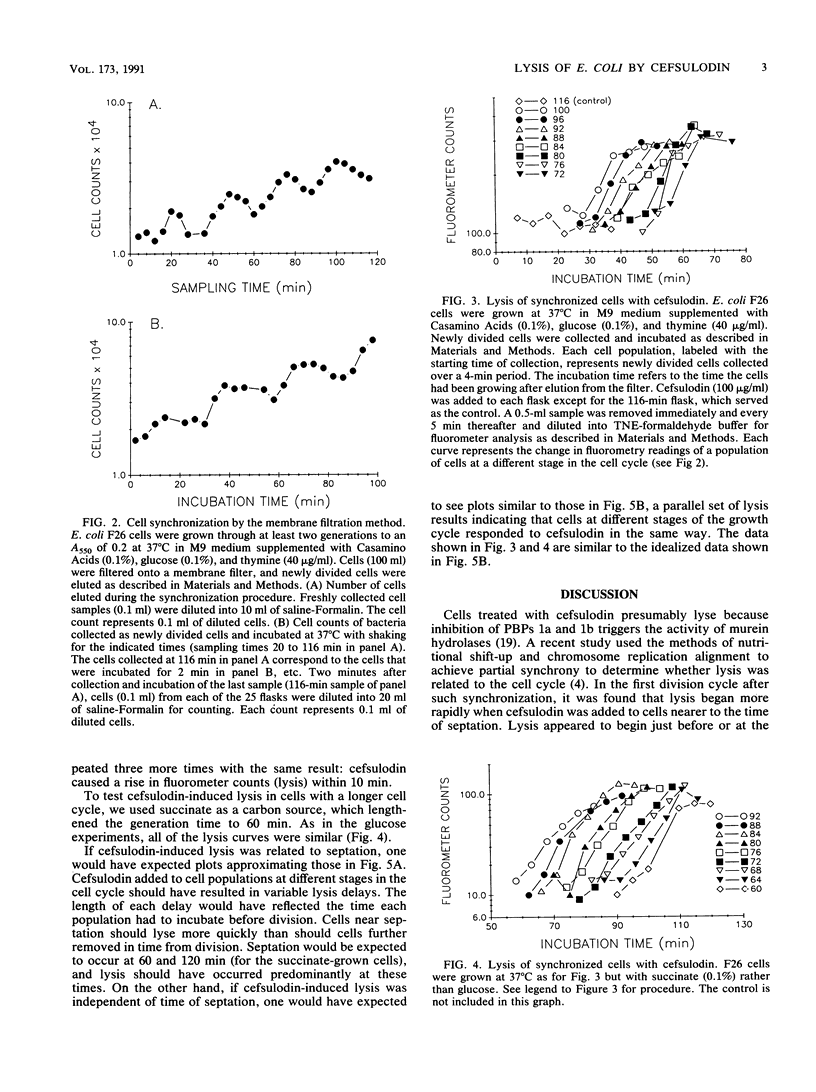
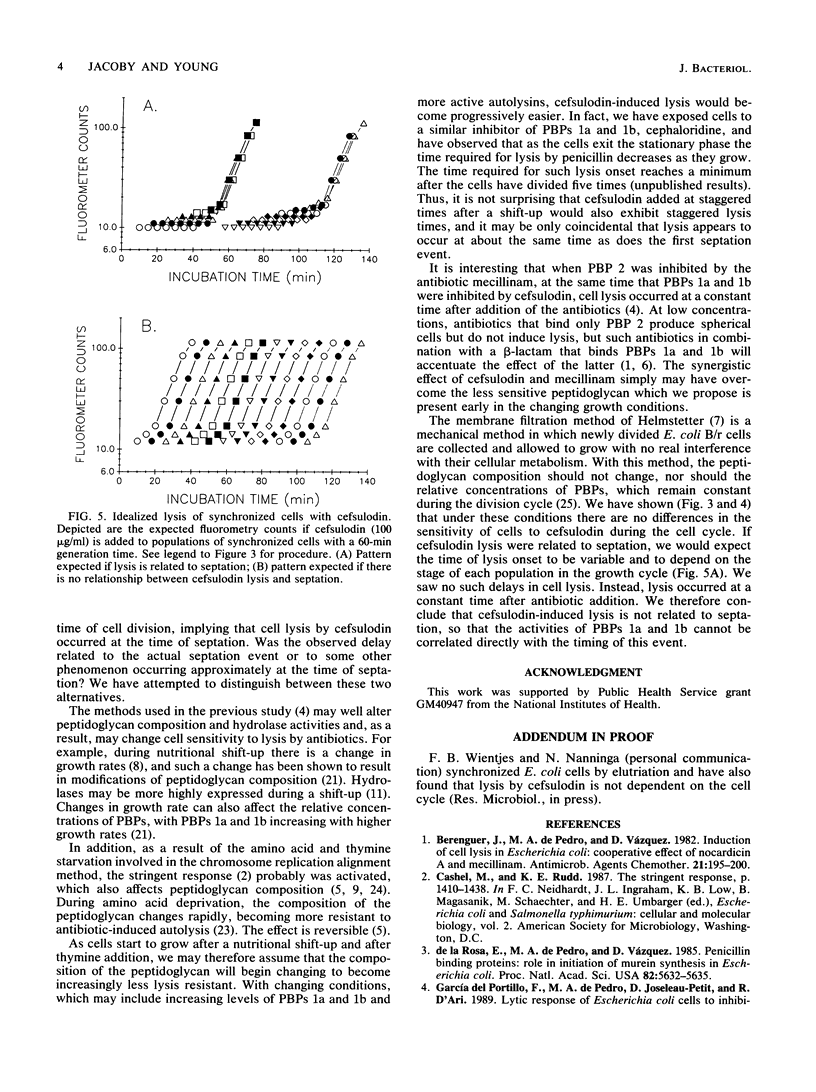
Cefsulodin lyses actively growing Escherichia coli by binding specifically to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) 1a and 1b. Recent findings (F. García del Portillo, M. A. de Pedro, D. Joseleau-Petit, and R. D'Ari, J. Bacteriol. 171:4217-4221, 1989) have linked cefsulodin-induced lysis to septation during the first division cycle after a nutritional shift-up or chromosome replication realignment. We synchronized cells by membrane filtration to determine whether cefsulodin-induced lysis depended on septation in normally growing cells. Populations of newly divided cells were allowed to grow for variable lengths of time. Cefsulodin was added to these synchronous cultures, which represented points in two to three rounds of the cell cycle. Since the cell numbers were small, a new lysis assay was developed that was based on the release of DNA measured by fluorometry. Lysis occurred at a constant time after addition of the antibiotic, regardless of the time in the cell cycle at which the addition was made. Thus, cefsulodin-induced lysis is not linked to septation or to any other cell cycle-related event.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berenguer J., de Pedro M. A., Vázquez D. Induction of cell lysis in Escherichia coli: cooperative effect of nocardicin A and mecillinam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):195–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell W., Tomasz A. Alteration of Escherichia coli murein during amino acid starvation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1009-1016.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Vincent S., Billot-Klein D., Acar J. F., Mrèna E., Williamson R. Involvement of penicillin-binding protein 2 with other penicillin-binding proteins in lysis of Escherichia coli by some beta-lactam antibiotics alone and in synergistic lytic effect of amdinocillin (mecillinam). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):906–912. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano K., Tomasz A. Triggering of autolytic cell wall degradation in Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):838–848. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengin-Lecreulx D., van Heijenoort J. Effect of growth conditions on peptidoglycan content and cytoplasmic steps of its biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):208–212. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.208-212.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Bouloc P., Niki H., D'Ari R., Hiraga S., Jaffé A. Penicillin-binding protein 2 is essential in wild-type Escherichia coli but not in lov or cya mutants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3025–3030. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3025-3030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisabarro A. G., de Pedro M. A., Vázquez D. Structural modifications in the peptidoglycan of Escherichia coli associated with changes in the state of growth of the culture. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):238–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.238-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins and the antibacterial effectiveness of beta-lactam antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 3):S260–S278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Cozens R. Changes in peptidoglycan composition and penicillin-binding proteins in slowly growing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5308–5310. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5308-5310.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Cozens R., Tosch W., Zak O., Tomasz A. The rate of killing of Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics is strictly proportional to the rate of bacterial growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Markiewicz Z., Tomasz A. Autolysis-resistant peptidoglycan of anomalous composition in amino-acid-starved Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1373-1376.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes F. B., Olijhoek T. J., Schwarz U., Nanninga N. Labeling pattern of major penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli during the division cycle. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1287–1293. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1287-1293.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousif S. Y., Broome-Smith J. K., Spratt B. G. Lysis of Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics: deletion analysis of the role of penicillin-binding proteins 1A and 1B. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2839–2845. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa E. J., de Pedro M. A., Vázquez D. Penicillin binding proteins: role in initiation of murein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5632–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



