Abstract
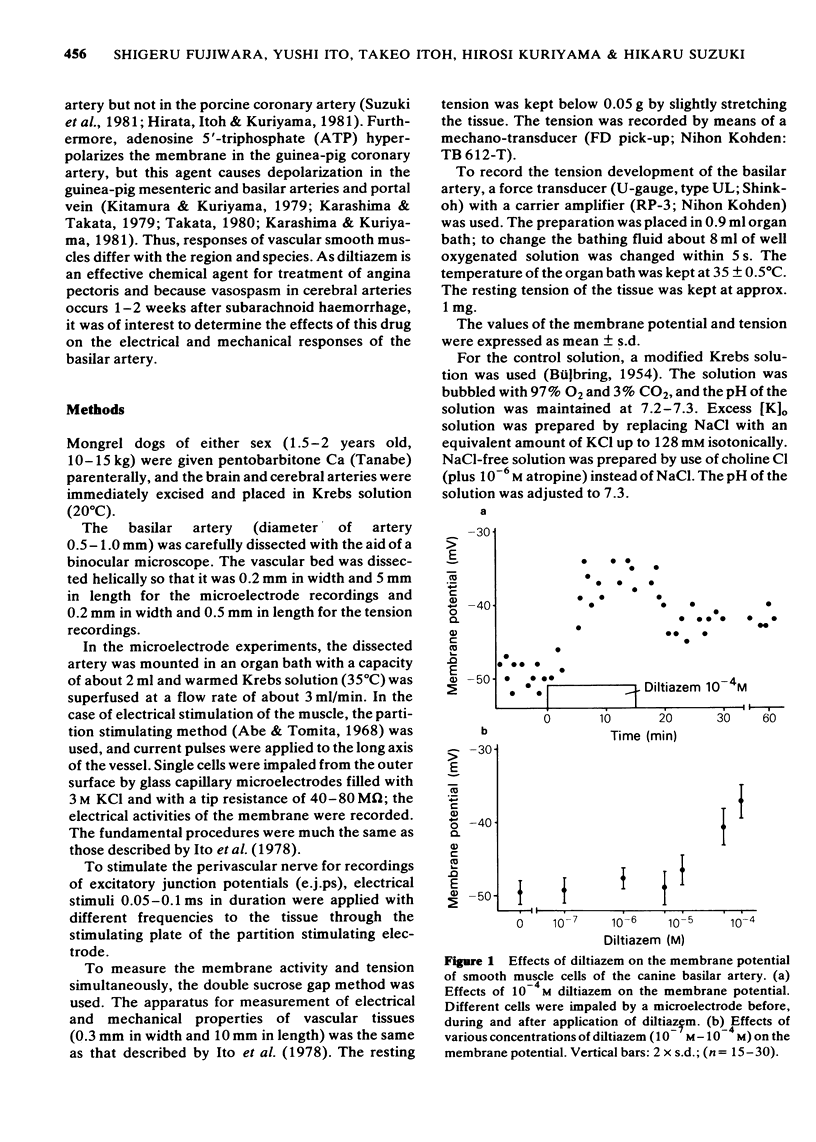
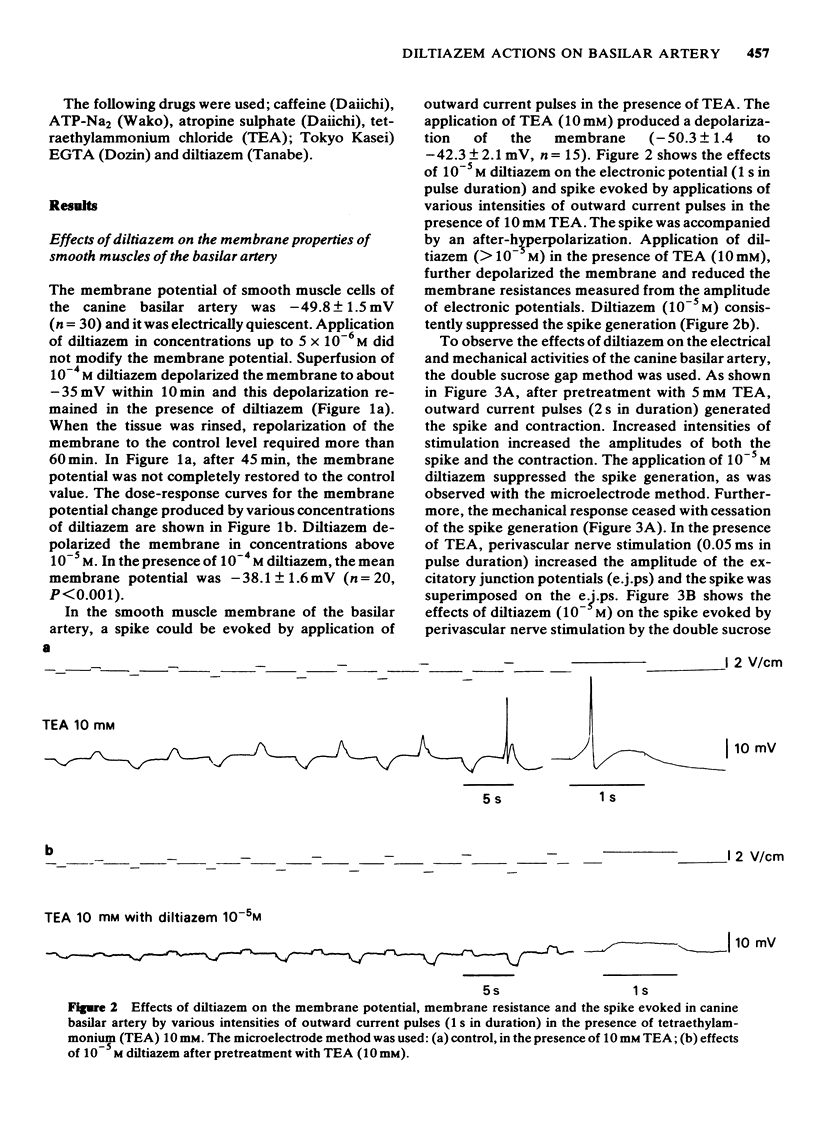
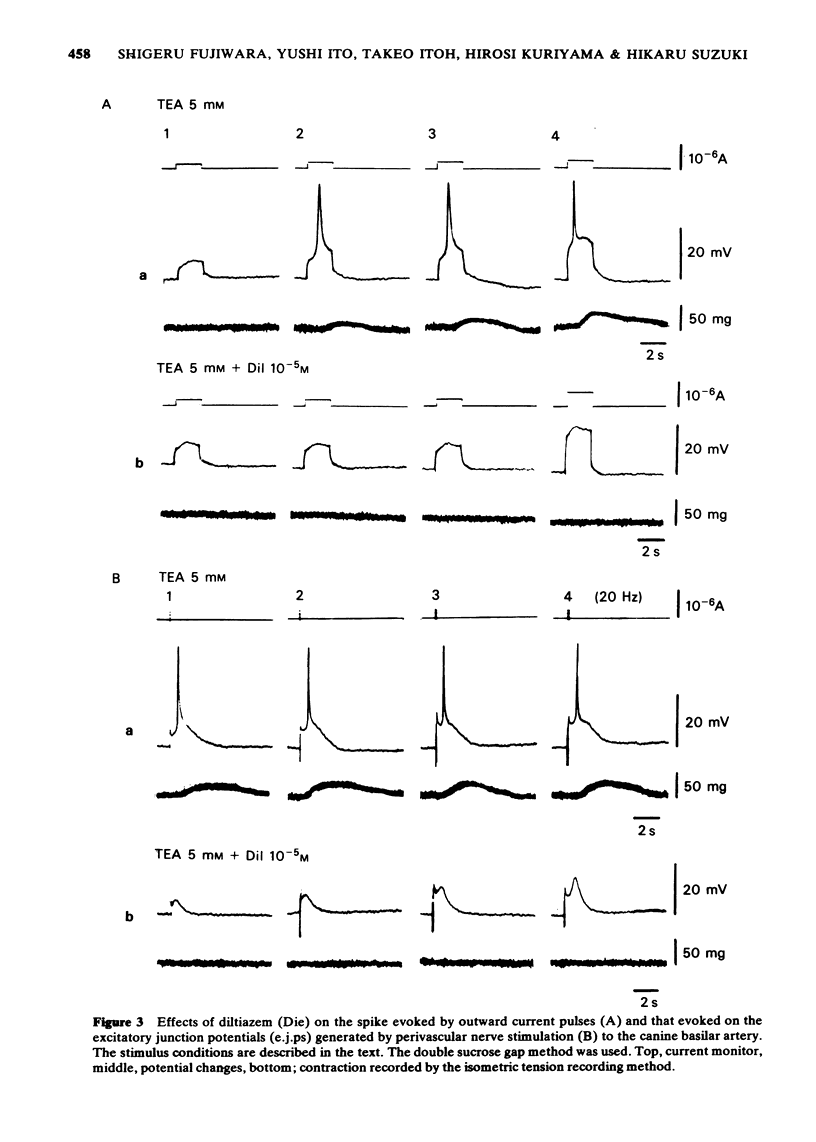
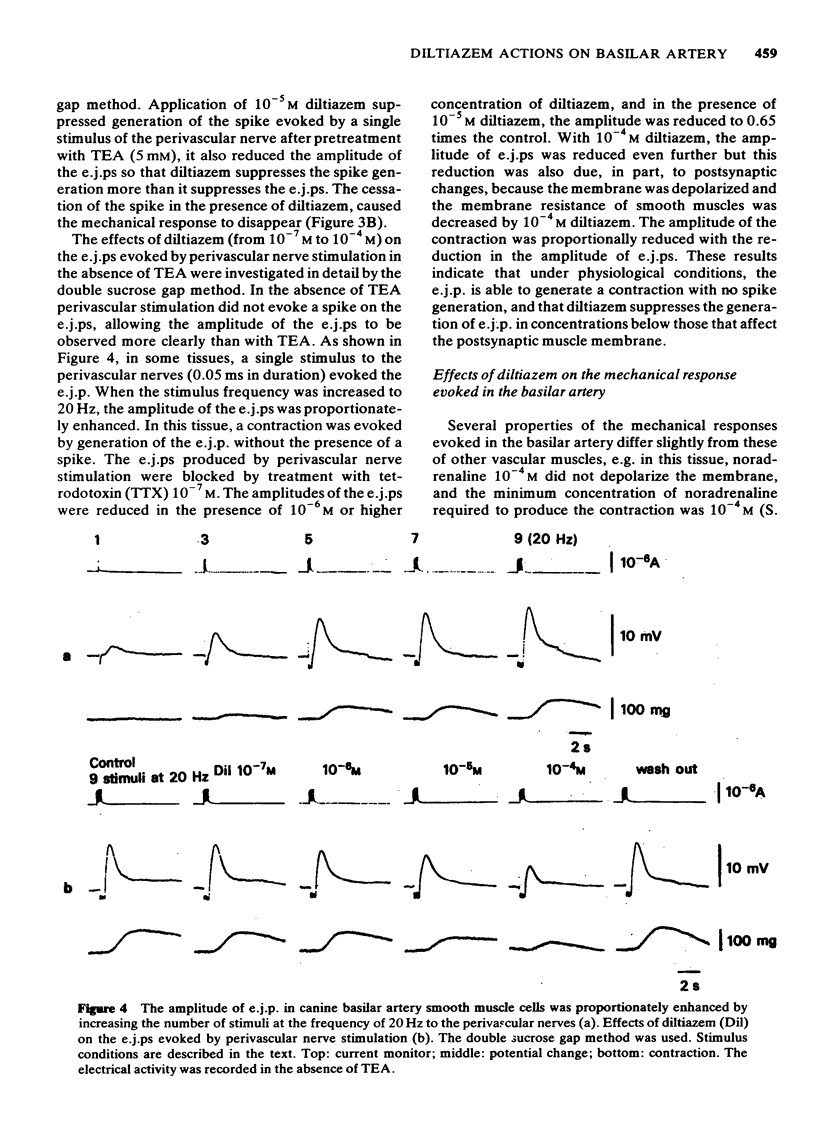
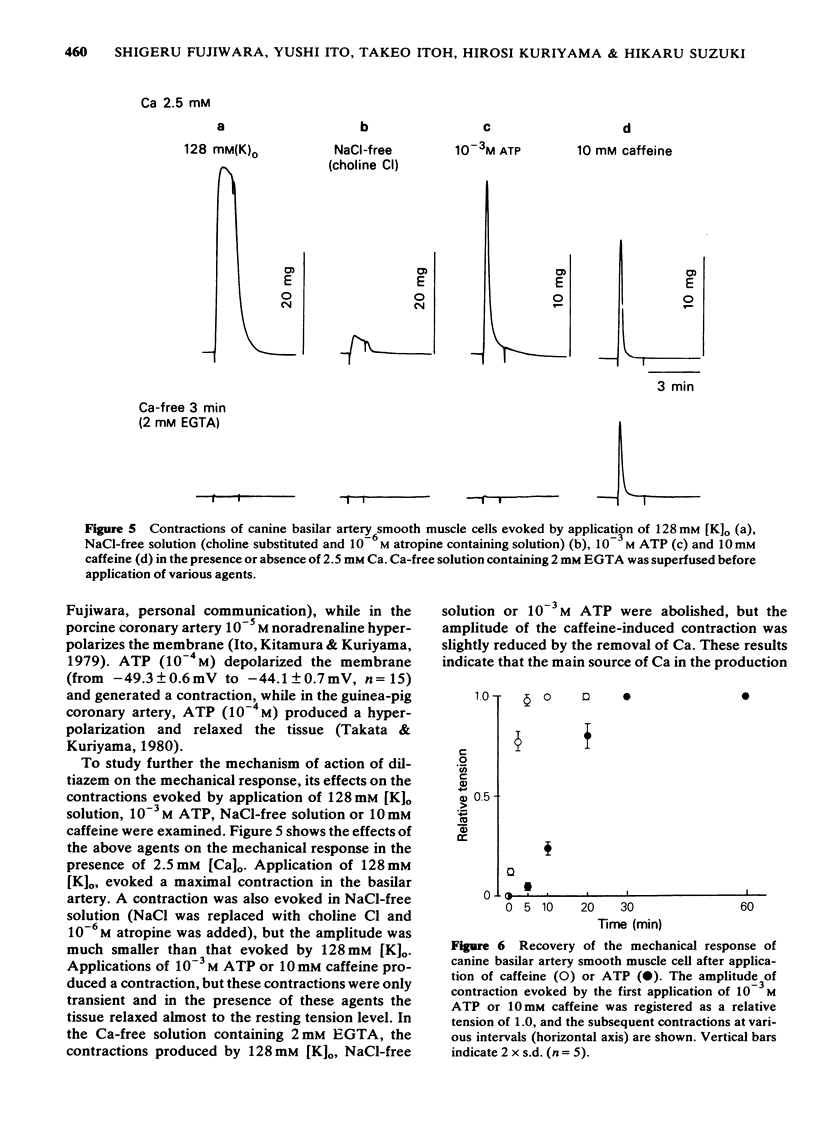
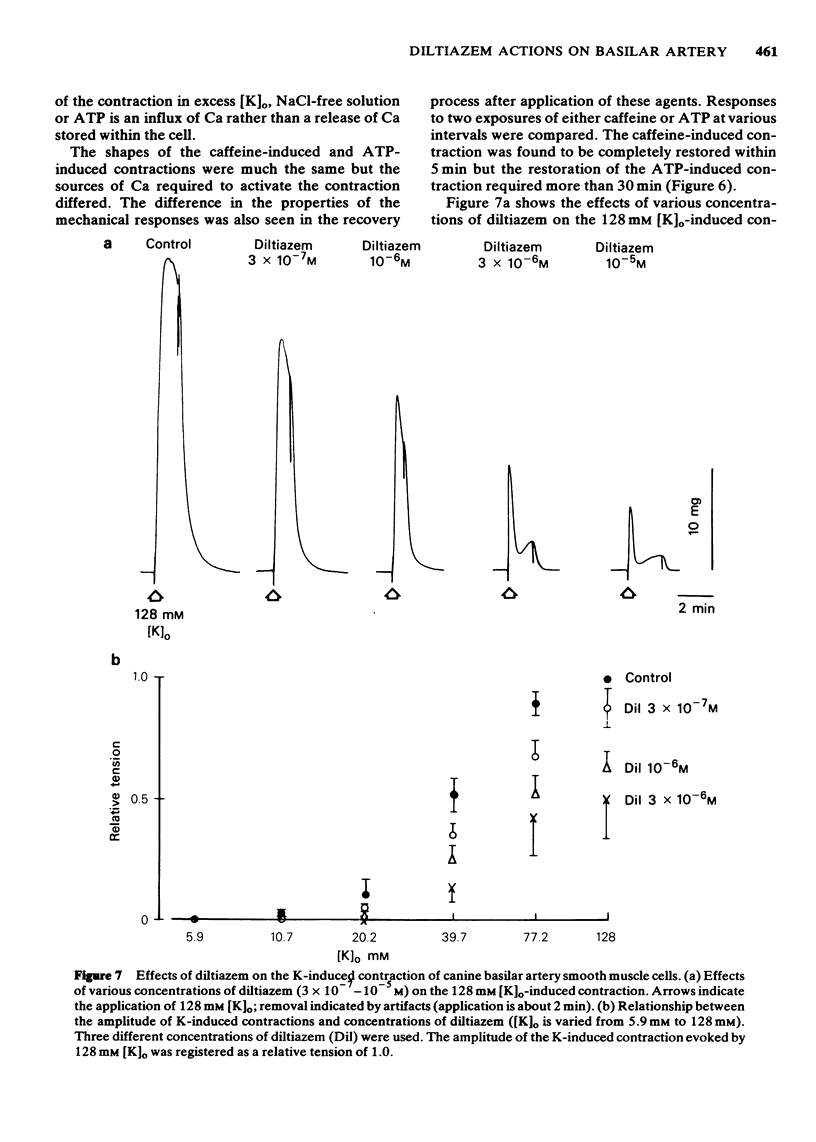
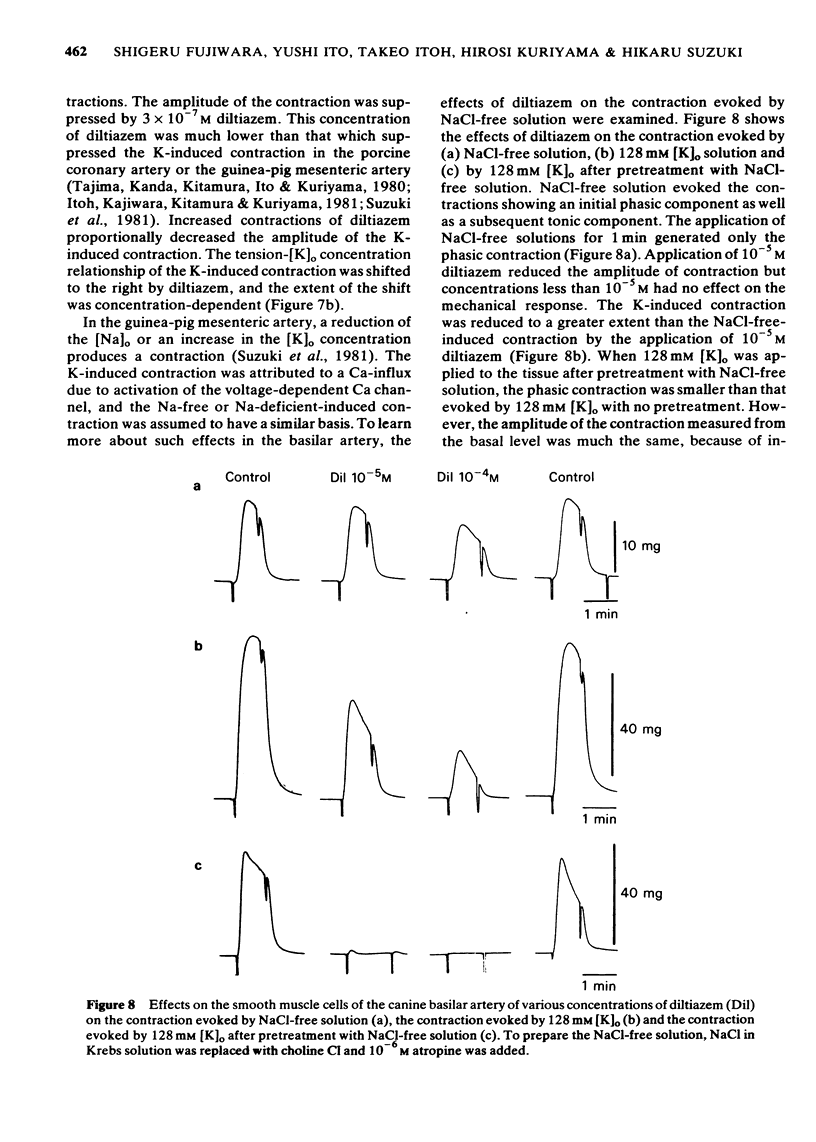
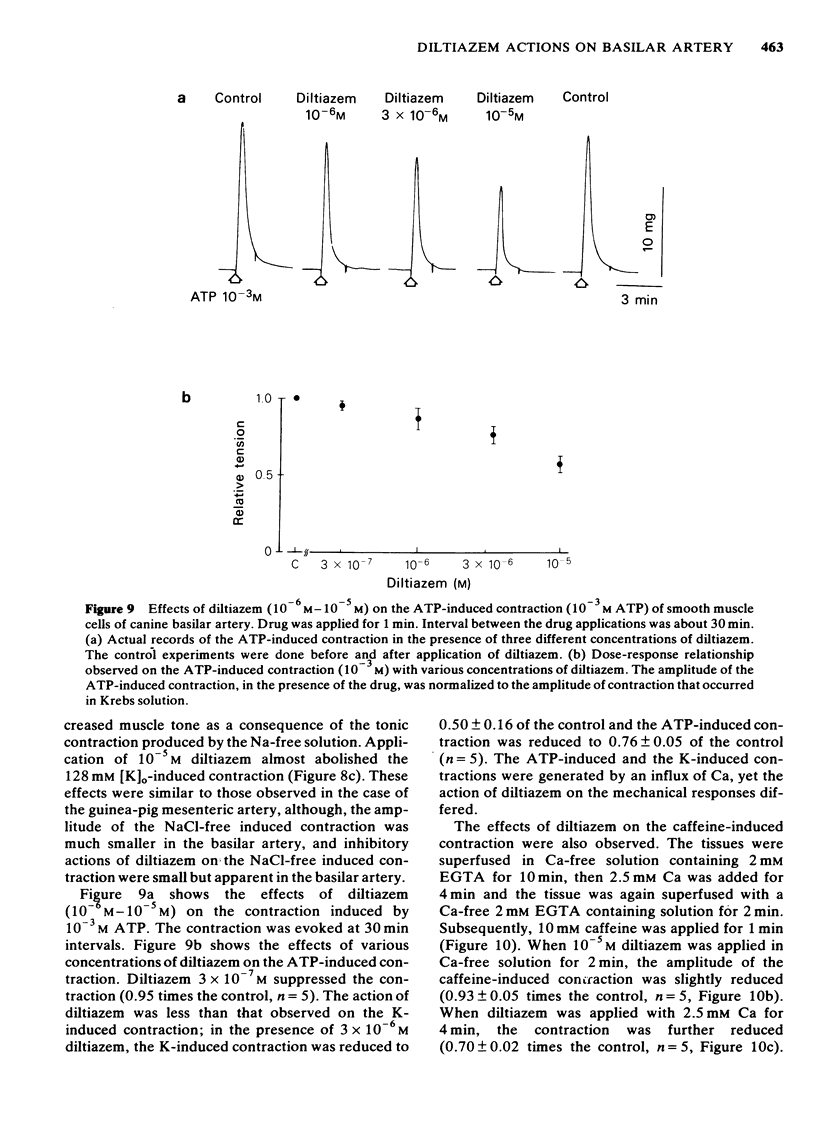
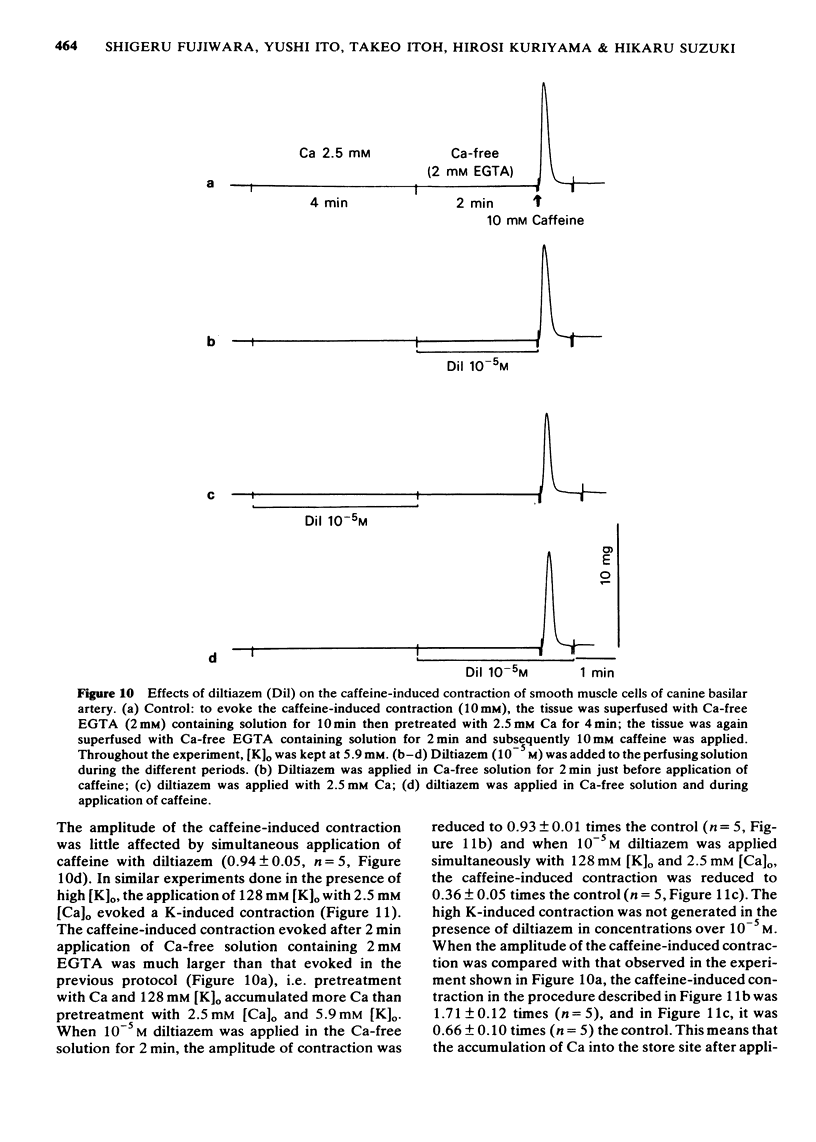
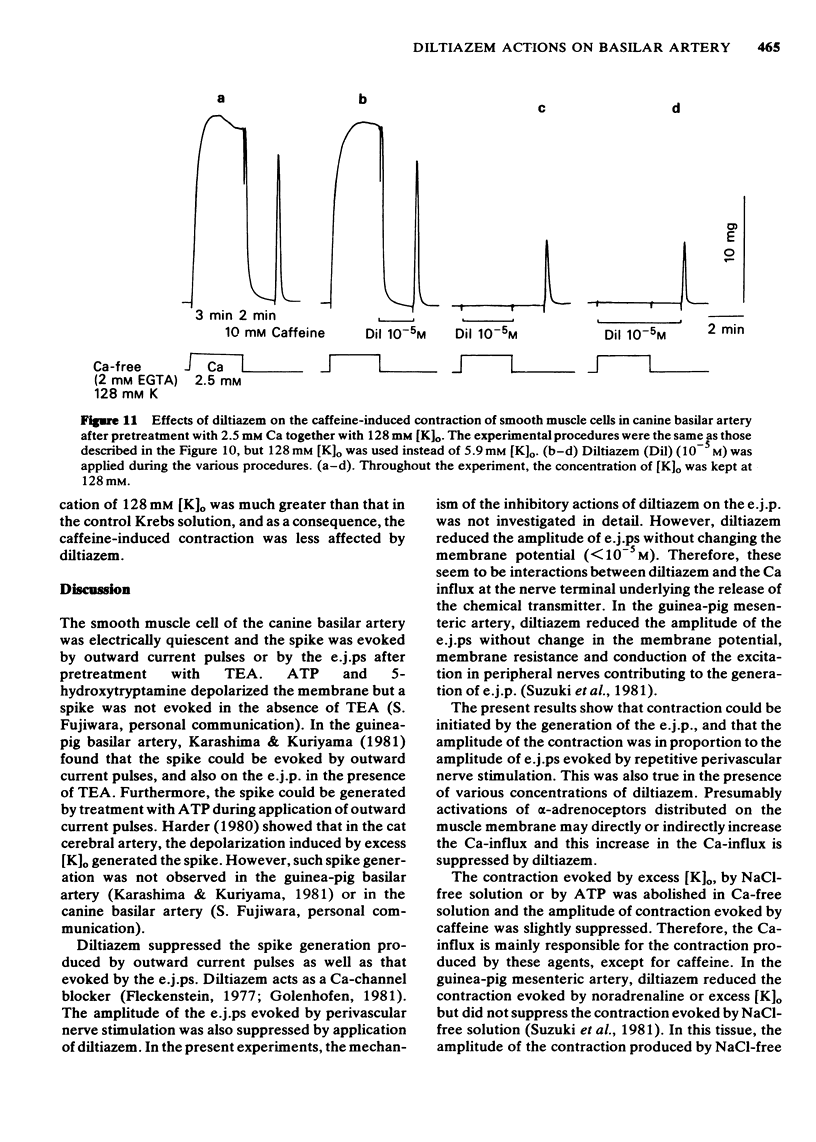
1 The effects of diltiazem on smooth muscle cells of the canine basilar artery were investigated by means of microelectrode, double sucrose gap and isometric tension recording methods. 2 The mean membrane potential of the smooth muscle cells was -49.8 mV and they were electrically quiescent. Diltiazem (over 10(-5) M) depolarized the membrane. After pretreatment with 5 and 10 mM tetraethylammonium (TEA), an outward current pulse (1 and 2 s in duration) produced a spike and this spike was abolished by application of 10(-5) M diltiazem. 3 The spike could also be generated by the excitatory junction potential (e.j.p.) evoked by perivascular nerve stimulation (0.05 ms in pulse duration) in the presence of 5 mM TEA. Diltiazem (greater than 10(-6) M) suppressed both the spike and the e.j.ps, the suppression being more apparent for spike generation. The amplitude of the e.j.ps was reduced by diltiazem in concentrations greater than 10(-6) M. The effects were dose-dependent: when the amplitude of e.j.ps was reduced by application of diltiazem, the resulting mechanical response was also proportionally smaller. 4 The contractions evoked by 128 mM [K]o, 10(-3) M adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) or, NaCl-free solution were abolished in Ca-free solutions containing 2 mM EGTA, but the amplitude of caffeine-induced contraction (10 mM) was only slightly reduced. Diltiazem, in concentrations above 3 X 10(-7) M suppressed the contraction evoked by excess [K]o, ATP or caffeine, but the inhibitory action of diltiazem on the K-induced contraction was greatest. 5 Following pretreatment with 2.5 mM [Ca]o, a contraction was evoked by caffeine in Ca-free solution. The amplitude of the caffeine-induced contraction was increased by simultaneous application of 2.5 mM [Ca]o with 128 mM [K]o and to a lesser extent by simultaneous application of 2.5 mM [Ca]o with 5.9 mM [K]o. The amplitude of the caffeine-induced contraction generated in the presence of 5.9 mM or 128 mM [K]o was suppressed to the same extent by application of diltiazem [10(-5) M) during preincubation in [Ca]o. This result suggests that the Ca stored in cell is replenished by Ca-influx from [Ca]o during the resting and active states of the membrane, and that diltiazem has no effect on the mobilization of Ca stored in the cell. 6 Thus, diltiazem acts on the canine basilar artery suppressing the Ca-influx during the active condition as a Ca-spike suppressor and the voltage-dependent Ca-influx induced by excess [K]o or by chemical depolarization. Diltiazem has no effect on the Ca mobilization from the store site. This agent also suppresses the amplitude of e.j.ps due to inhibition of the release of chemical transmitter from nerve terminals following the suppression of the Ca-influx. Diltiazem appears to act as a vasodilator on the canine basilar artery.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y., Tomita T. Cable properties of smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):87–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E. Membrane potentials of smooth muscle fibres of the taenia coli of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1954 Aug 27;125(2):302–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic modulation of cholinergic transmission. Gen Pharmacol. 1980;11(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(80)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Review lecture. Neurotransmitters and trophic factors in the autonomic nervous system. J Physiol. 1981;313:1–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. Chest. 1980 Jul;78(1 Suppl):150–156. doi: 10.1378/chest.78.1_supplement.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R. Comparison of electrical properties of middle cerebral and mesenteric artery in cat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):C23–C26. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.239.1.C23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Itoh T., Kuriyama H. Effects of external cations on calcium efflux from single cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli and porcine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:321–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. The effects of diltiazem (CRD-401) on the membrane and mechanical properties of vascular smooth muscles of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;64(4):503–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima T., Kuriyama H. Electrical properties of smooth muscle cell membrane and neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig basilar artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;74(2):495–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima T., Takata Y. The effects of ATP related compounds on the electrical activity of the rat portal vein. Gen Pharmacol. 1979;10(6):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(79)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Effects of acetylcholine on the smooth muscle cell of isolated main coronary artery of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:119–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magaribuchi T., Nakajima H., Kiyomoto A. Effects of diltiazem and lanthanum ion on the potassium contracture of isolated guinea pig smooth muscle. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;27(3):333–339. doi: 10.1254/jjp.27.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magaribuchi T., Nakajima H., Kiyomoto A. Effects of diltiazem on electrical and mechanical activities of isolated guinea pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;27(3):361–369. doi: 10.1254/jjp.27.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Blaustein M. P., Haeusler G. Na-Ca exchange and tension development in arterial smooth muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):87–94. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima K., Kanda S., Kitamura K., Ito Y., Kuriyama H. Diltiazem actions on smooth muscle cells of the porcine coronary artery and on neuromuscular junctions of the guinea-pig vas deferens. Gen Pharmacol. 1980;11(6):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(80)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y., Kuriyama H. ATP-induced hyperpolarization of smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig coronary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Mar;212(3):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y. Regional differences in electrical and mechanical properties of guinea-pig mesenteric vessels. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(5):709–728. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


