Abstract
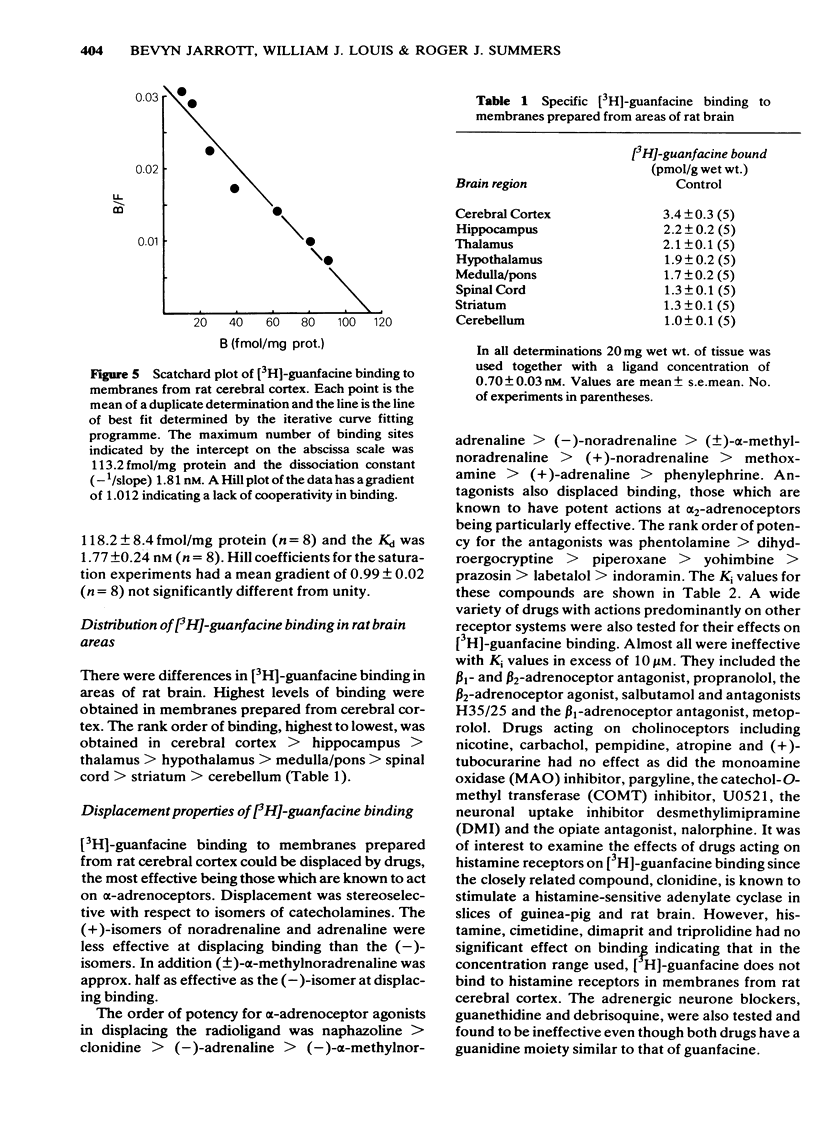
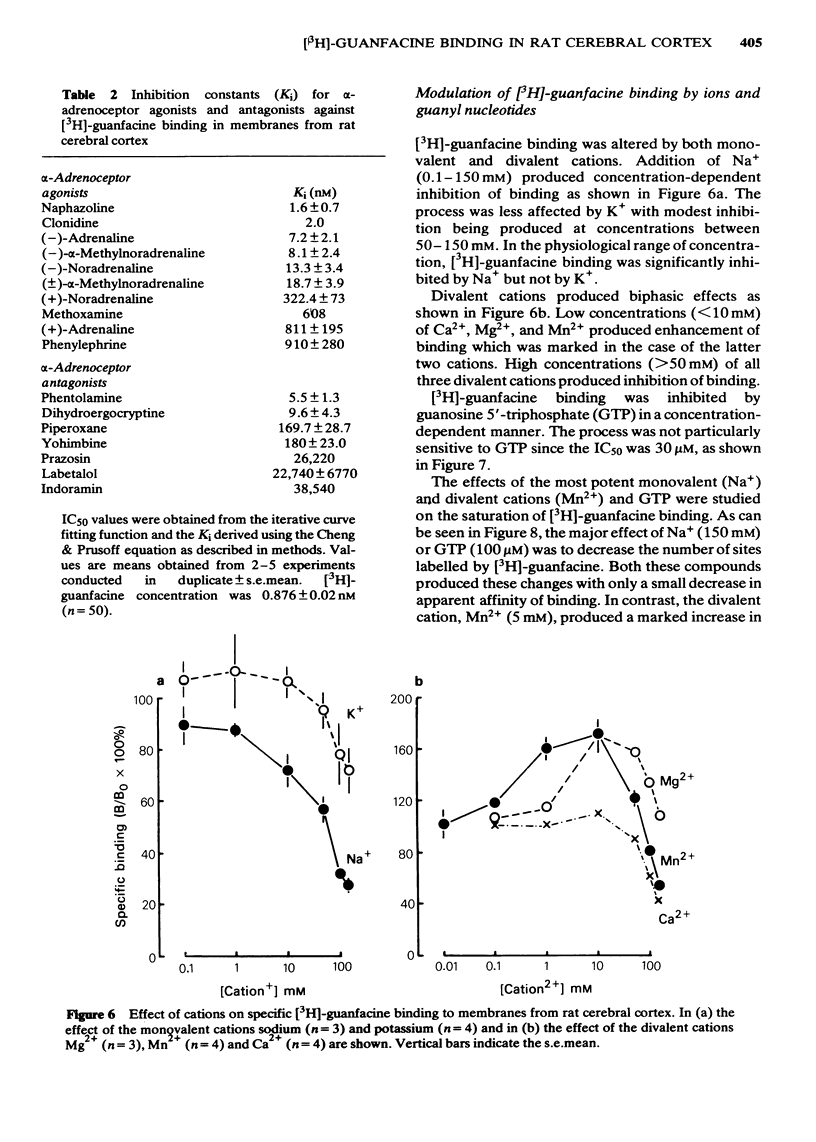
[3H]-guanfacine (N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichloro 3[3H] phenyl) acetamide hydrochloride; 24.2 Ci/mmol) has been used as a radioligand in homogenates of rat cerebral cortex. Specific binding of [3H]-guanfacine was linear with respect to tissue concentration (2.5-15 mg/ml), saturable and not markedly affected in the pH range 6.5-8.0. Analysis of the saturation of [3H]-guanfacine binding using an iterative least squares fitting procedure gave best fits to a single site model. [3H]-guanfacine binding was of high affinity (Kd 1.77 +/- 0.24 nM; n = 8) to a population of non interacting sites (nH 0.99 +/- 0.02; n = 8) with a density of 118.2 +/- 8.4 fmol/mg protein (n = 8). Highest levels of binding were achieved in cerebral cortex followed by thalamus greater than hypothalamus greater than medulla/pons greater than spinal cord greater than striatum greater than cerebellum. Binding was stereoselective with regard to the (-)-isomer of noradrenaline and the order of potency for displacement of [3H]-guanfacine by agonists was naphazoline greater than clonidine greater than (-)-adrenaline greater than (-)-alpha methylnoradrenaline greater than (-)-noradrenaline greater than (+/-)-alpha-methylnoradrenaline greater than (+)-noradrenaline greater than methoxamine greater than (+)-adrenaline greater than phenylephrine and by antagonists was phentolamine greater than dihydroergocryptine greater than piperoxane greater than yohimbine greater than prazosin greater than labetalol greater than indoramin suggested binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors. The monovalent cations Na+ and K+ and also guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP) produced concentration-dependent inhibition whereas the divalent cations Ca2+, Mg2+, and Mn2+ first enhanced, then inhibited [3H]-guanfacine binding. Na+ (150 mM) or GTP (100 microM) produced marked reductions and Mn2+ (5 mM) marked increases in the number of receptor sites labelled by [3H]-guanfacine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-agonists in the anococcygeus muscle of the pithed rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 15;54(1-2):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Presek P. Alpha noradrenergic receptors in brain membranes: sodium, magnesium and guanyl nucleotides modulate agonist binding. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;306(1):67–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00515595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Mullikin-Kilpatrick D., Lefkowitz R. J. Heterogeneity of radioligand binding to alpha-adrenergic receptors. Analysis of guanine nucleotide regulation of agonist binding in relation to receptor subtypes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4645–4652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman R. B., Angwin P., Barchas J. D. Simultaneous determination of indole- and catecholamines in small brain regions in the rat using a weak cation exchange resin. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrott B., Louis W. J., Summers R. J. The effect of a series of clonidine analogues on [3H] clonidine binding in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirch W., Distler A. Antihypertensive effect of N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl) acetamide hydrochloride. A double-blind cross-over trial versus clonidine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1978 Mar;16(3):132–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger Central alpha-adrenergic systems as targets for hypotensive drugs. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;81:39–100. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacha W., Salzmann R., Scholtysik G. Inhibitory effects of clonidine and BS 100-141 on responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in cats and rabbits. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;53(4):513–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouot B. M., U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Multiple alpha 2-noradrenergic receptor sites in rat brain: selective regulation of high-affinity [3H]clonidine binding by guanine nucleotides and divalent cations. J Neurochem. 1980 Feb;34(2):374–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saameli K., Scholtysik G., Waite R. Pharmacology of BS 100-141, a centrally acting antihypertensive drug. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1975;Suppl 2:207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtysik G., Lauener H., Eichenberger E., Bürki H., Salzmann R., Müller-Schweinitzer E., Waite R. Pharmacological actions of the antihypertensive agent N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide hydrochloride (BS 100-141). Arzneimittelforschung. 1975 Oct;25(10):1483–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J., Jarrott B., Louis W. J. Comparison of [3H]clonidine and [3H]guanfacine binding to alpha 2 adrenoceptors in membranes from rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Aug 7;25(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J., Jarrott B., Louis W. J. Displacement of [3H]clonidine binding by clonidine analogues in membranes from rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 29;66(2-3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J., Jarrott B., Louis W. J. Selectivity of a series of clonidine-like drugs for alpha 1 and alpha 2 adrenoceptors in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Dec;20(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Bechtel W. D., Rouot B. M., Snyder S. H. Multiple apparent alpha-noradrenergic receptor binding sites in rat brain: effect of 6-hydroxydopamine. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):47–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Greenberg D. A., Snyder S. H. Binding characteristics of a radiolabeled agonist and antagonist at central nervous system alpha noradrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):454–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


