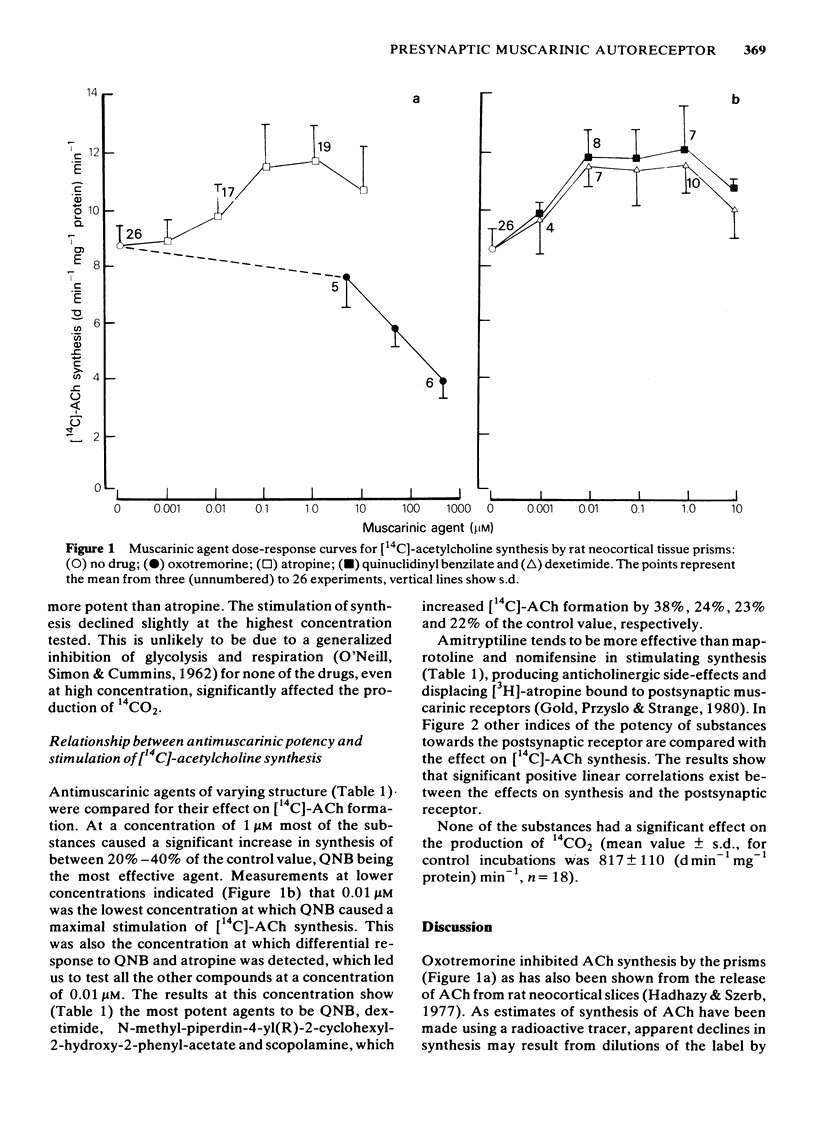
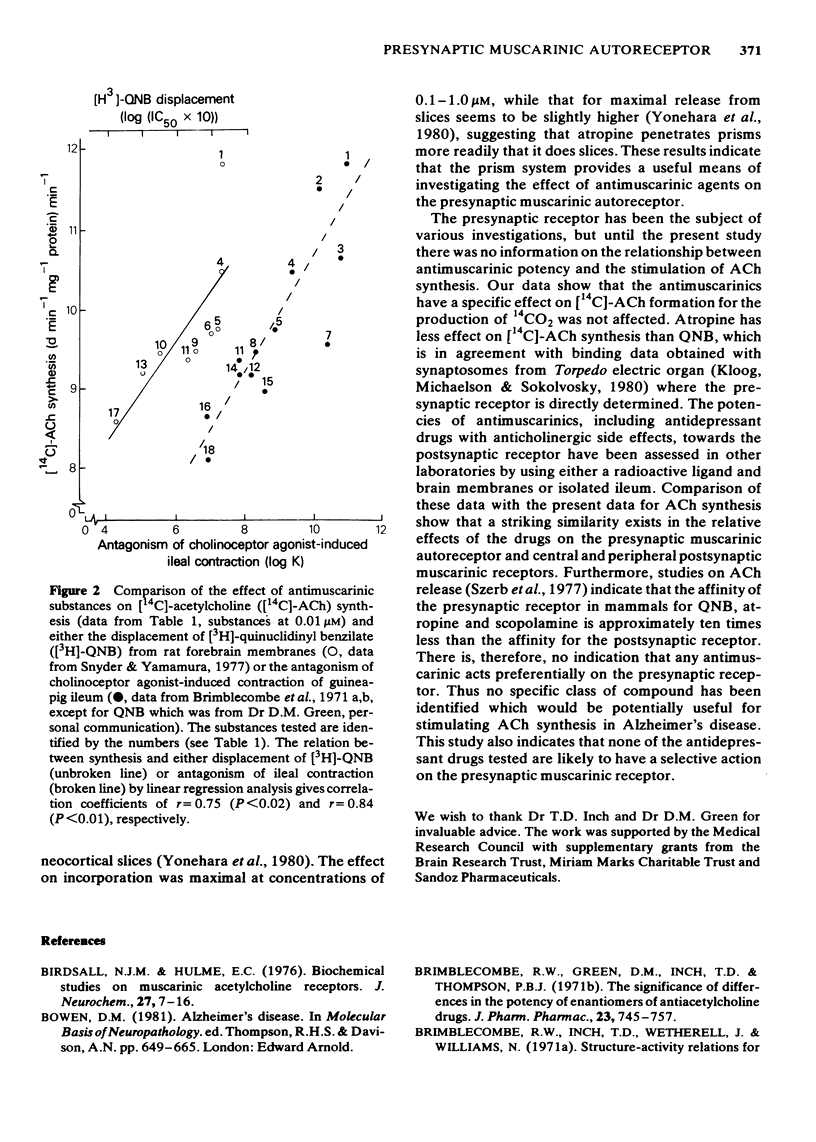
Abstract
Twenty antagonist substances with varying potencies for central and peripheral postsynaptic muscarinic receptors have been examined for effects on the central presynaptic muscarinic autoreceptor. This has been monitored by measuring the stimulating effects of the substances on acetylcholine synthesis by rat neocortical tissue prisms. Dose-response curves for selected agents showed that maximal stimulation of synthesis was to 136-140% of the value without an antagonist. At a concentration of 1 microM, 17 of the substances caused a significant increase in synthesis, whilst at 0.01 microM significant stimulation occurred with only atropine, dexetimide, N-methyl-piperdin-4-yl (R)-2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxyl-2-phenylacetate, quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) and scopolamine. Linear regression analysis between synthesis values obtained with the substances and published data for the effects on either cholinoceptor-agonist induced contraction of guinea-pig ileum or the binding of [3H]-QNB to rat forebrain membranes gave correlation coefficients of r = 0.84 (P less than 0.01), and r = 0.75 (P less than 0.02) respectively. The results provide no indication of a pharmacological difference between the central presynaptic muscarinic autoreceptor and central and peripheral postsynaptic muscarinic receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birdsall N. J., Hulme E. C. Biochemical studies on muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurochem. 1976 Jul;27(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimblecombe R. W., Green D. M., Inch T. D., Thompson P. B. The significance of differences in the potency of enantiomers of anti-acetylcholine drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;23(10):745–757. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning E. T., Schulman M. P. (14C) acetylcholine synthesis by cortex slices of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Dec;15(12):1391–1405. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delini-Stula A., Baumann P., Büch O. Depression of exploratory activity by clonidine in rats as a model for the detection of relative pre- and postsynaptic central noradrenergic receptor selectivity of alpha-adrenolytic drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;307(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00498452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakahany E., Richelson E. Temperature dependence of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation, desensitization, and resensitization. J Neurochem. 1980 May;34(5):1288–1295. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Woodhams P. L., Collins M. J., Balazs R. On the preparation of brain slices: morphology and cyclic nucleotides. Brain Res. 1979 Sep 14;173(2):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Woodhams P. L., Collins M. J., Balázs R. A morphological study of incubated slices of rat cerebellum in relation to postnatal age. Dev Neurosci. 1980;3(2):90–99. doi: 10.1159/000112381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. E., Blass J. P. Inhibition of acetylcholine synthesis and of carbohydrate utilization by maple-syrup-urine disease metabolites. J Neurochem. 1976 Jun;26(6):1073–1078. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golds P. R., Przyslo F. R., Strange P. G. The binding of some antidepressant drugs to brain muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;68(3):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb14570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadházy P., Szerb J. C. The effect of cholinergic drugs on [3H]acetylcholine release from slices of rat hippocampus, striatum and cortex. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 11;123(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90482-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Michaelson D. M., Sokolovsky M. Characterization of the presynaptic muscarinic receptor in synaptosomes of Torpedo electric organ by means of kinetic and equilibrium binding studies. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 21;194(1):97–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefresne P., Guyenet P., Glowinski J. Acetylcholine synthesis from (2- 14 C)pyruvate in rat striatal slices. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):1083–1097. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefresne P., Rospars J. P., Beaujouan J. C., Westfall T. C., Glowinski J. Effects of acetylcholine and atropine on the release of 14C-acetylcholine formed from U-14C-glucose in rat brain cortical and striatal prisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;303(3):279–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00498055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar P. C., Polak R. L. Stimulation by atropine of acetylcholine release and synthesis in cortical slices from rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):406–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10622.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rospars J. P., Lefresne P., Beaujouan J. C., Glowinski J. Effect of external ACh and of atropine on 14C-ACh synthesis and release in rat cortical slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;300(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00505046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims N. R., Bowen D. M., Davison A. N. [14C]acetylcholine synthesis and [14C]carbon dioxide production from [U-14C]glucose by tissue prisms from human neocortex. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 15;196(3):867–876. doi: 10.1042/bj1960867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims N. R., Bowen D. M., Smith C. C., Flack R. H., Davison A. N., Snowden J. S., Neary D. Glucose metabolism and acetylcholine synthesis in relation to neuronal activity in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1980 Feb 16;1(8164):333–336. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90884-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Yamamura H. I. Antidepressants and the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Feb;34(2):236–239. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770140126014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C., Hadházy P., Dudar J. D. Release of [3H]acetylcholine from rat hippocampal slices: effect of septal lesion and of graded concentrations of muscarnic agonists and antagonists. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 10;128(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90995-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C., Somogyi G. T. Depression of acetylcholine release from cerebral cortical slices by cholinesterase inhibition and by oxotremorine. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 24;241(108):121–122. doi: 10.1038/newbio241121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonehara N., Matsuda T., Saito K., Ishida H., Yoshida H. Effect of cyclic nucleotide derivatives on the release of ACh from cortical slices of the rat brain. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 20;182(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90836-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


