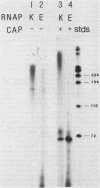
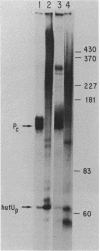
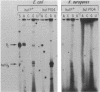
Abstract
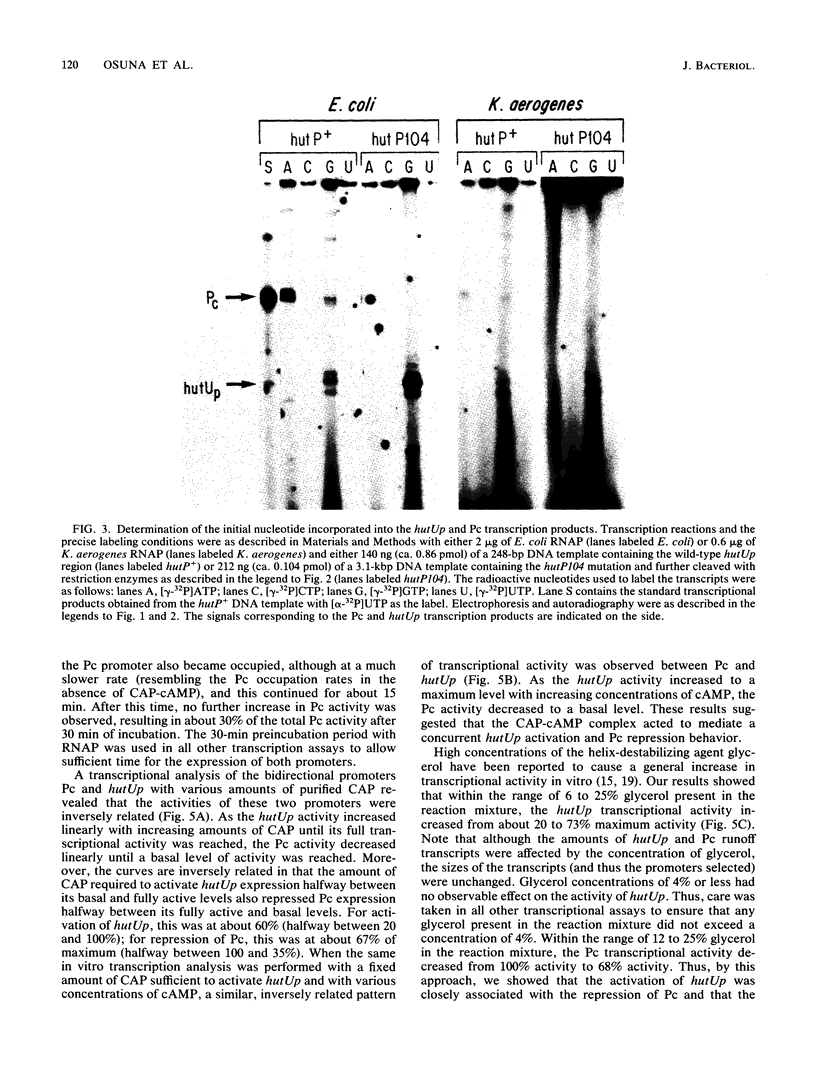
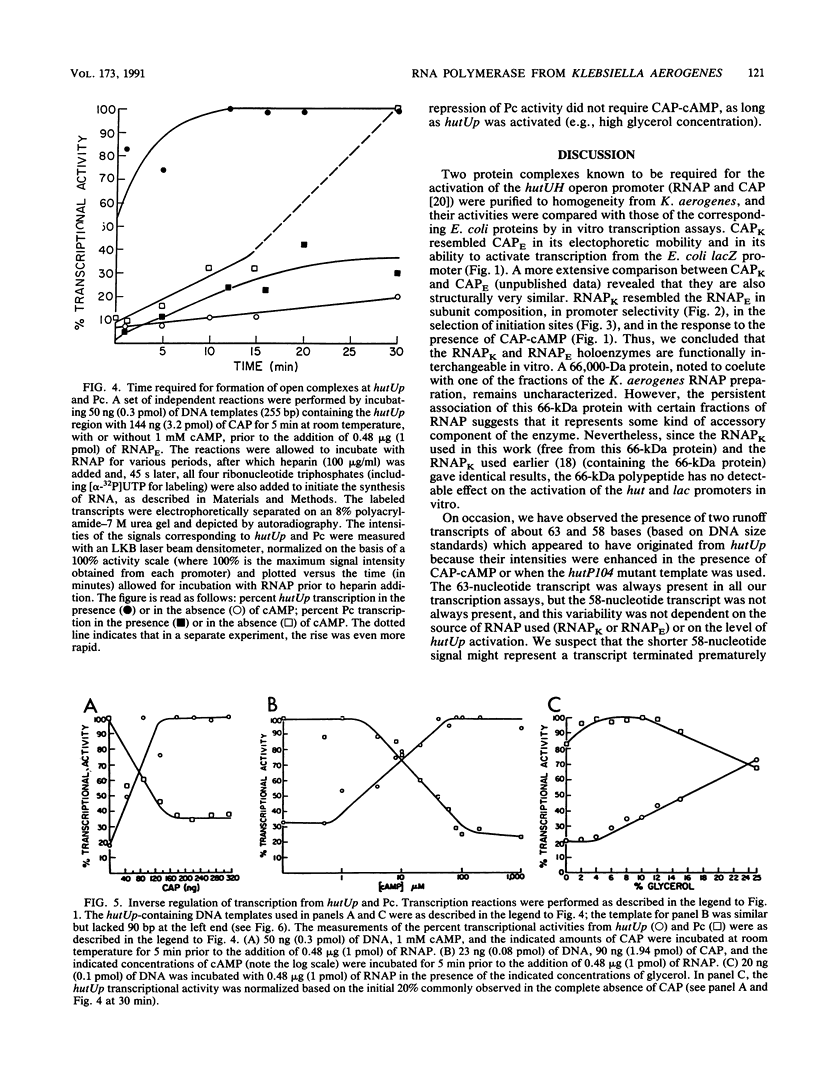
The promoter region preceding the hutUH operon in Klebsiella aerogenes contains two oppositely oriented, overlapping promoters. In the absence of catabolite gene activator protein-cyclic AMP (CAP-cAMP), transcription proceeds primarily from the backward-oriented promoter (Pc), whose function has not yet been determined, and only very weakly from the forward hutUH promoter, hutUp. In the presence of CAP-cAMP, Pc is repressed and transcription from hutUp is favored. Two protein components required for this in vitro transcription system, RNA polymerase (RNAP) and CAP, were purified from K. aerogenes and were shown to be functionally interchangeable with the corresponding proteins from Escherichia coli, suggesting that E. coli RNAP could be used to study some aspects of hut transcription. We showed that a gradual activation of hutUp (by increasing concentrations of CAP, cAMP, or glycerol) resulted in a parallel repression of Pc, arguing in favor of a direct competition between the two promoters. The presence of a DNA sequence resembling the consensus for CAP-binding sites and centered at nucleotide -82 (relative to hutUp) initially suggested that a primary role of CAP was to repress Pc, thereby indirectly activating hutUp. However, the relatively slow formation of open complexes at Pc, even in the absence of CAP-cAMP, showed that Pc is a weak promoter and likely to be a poor competitor for RNAP. The observed dominance of Pc over hutUp suggested that the latter is an even weaker promoter. Thus, repression of Pc would not be sufficient to cause the observed increase in hutUp activity, and the CAP-cAMP complex must play a direct role in the activation of hutUp.
Full text
PDF

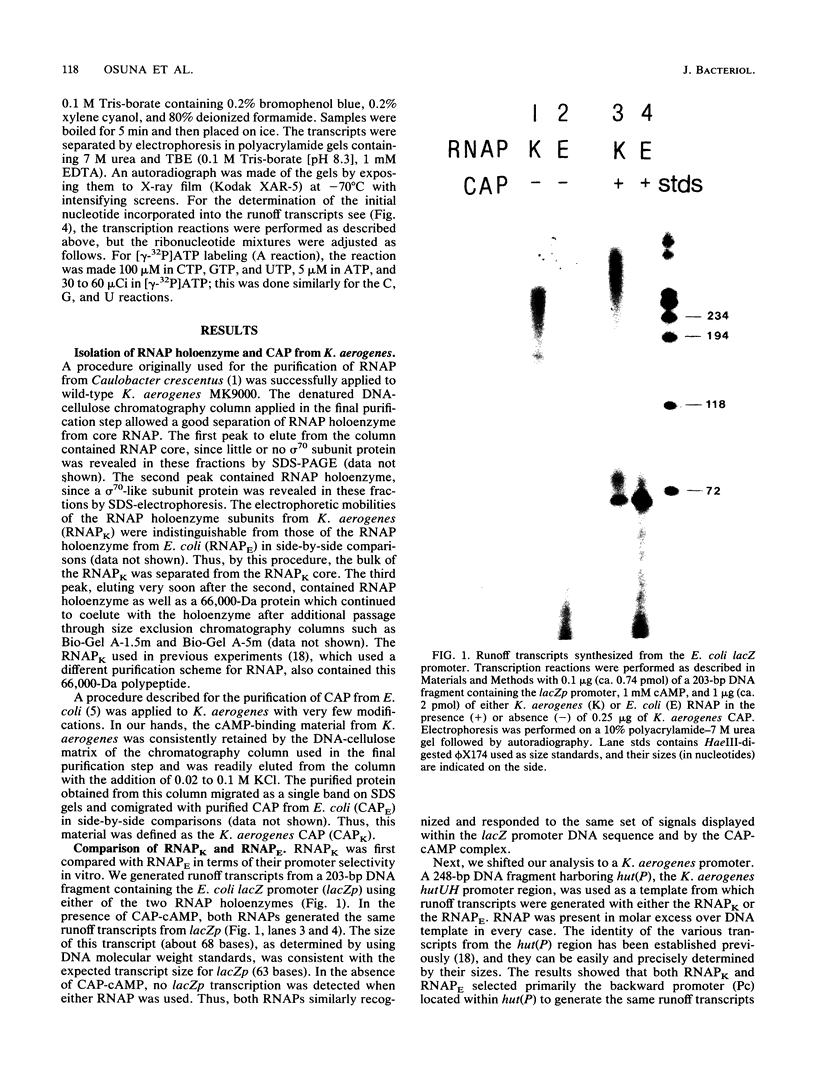



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amemiya K., Wu C. W., Shapiro L. Caulobacter crescentus RNA polymerase. Purification and characterization of holoenzyme and core polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4157–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter-Gabbard K. L. A simple method for the large-scale preparation of sucrose gradients. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):117–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone T., Wilcox G. A rapid high-yield purification procedure for the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor protein from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 17;541(4):528–534. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Reznikoff W. S. In vitro analysis of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase interaction with wild-type and mutant lactose promoters. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 15;125(4):467–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Gel protein stains: silver stain. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Adhya S., Gottesman M., Pastan I. Activation of transcription at specific promoters by glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4050–4056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop A. J., Baldauf S. A., Hudspeth M. E., Bender R. A. Bidirectional promoter in the hut(P) region of the histidine utilization (hut) operons from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2240–2246. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2240-2246.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop A. J., Bender R. A. RNA polymerase as a repressor of transcription in the hut(P) region of mutant Klebsiella aerogenes histidine utilization operons. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4986–4990. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4986-4990.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop A. J., Boylan S. A., Bender R. A. Regulation of hutUH operon expression by the catabolite gene activator protein-cyclic AMP complex in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):934–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.934-939.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S. L., Bender R. A., Magasanik B. Genetic control of glutamine synthetase in Klebiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.320-331.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]