Abstract
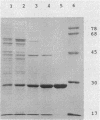
An enzyme capable of dehalogenating vicinal haloalcohols to their corresponding epoxides was purified from the 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol-utilizing bacterium Arthrobacter sp. strain AD2. The inducible haloalcohol dehalogenase converted 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol, 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol, 1-chloro-2-propanol, and their brominated analogs, 2-bromoethanol, as well as chloroacetone and 1,3-dichloroacetone. The enzyme possessed no activity for epichlorohydrin (3-chloro-1,2-epoxypropane) or 2,3-dichloro-1-propanol. The dehalogenase had a broad pH optimum at about 8.5 and a temperature optimum of 50 degrees C. The enzyme followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and the Km values for 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol and 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol were 8.5 and 48 mM, respectively. Chloroacetic acid was a competitive inhibitor, with a Ki of 0.50 mM. A subunit molecular mass of 29 kDa was determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. With gel filtration, a molecular mass of 69 kDa was found, indicating that the native protein is a dimer. The amino acid composition and N-terminal amino acid sequence are given.
Full text
PDF


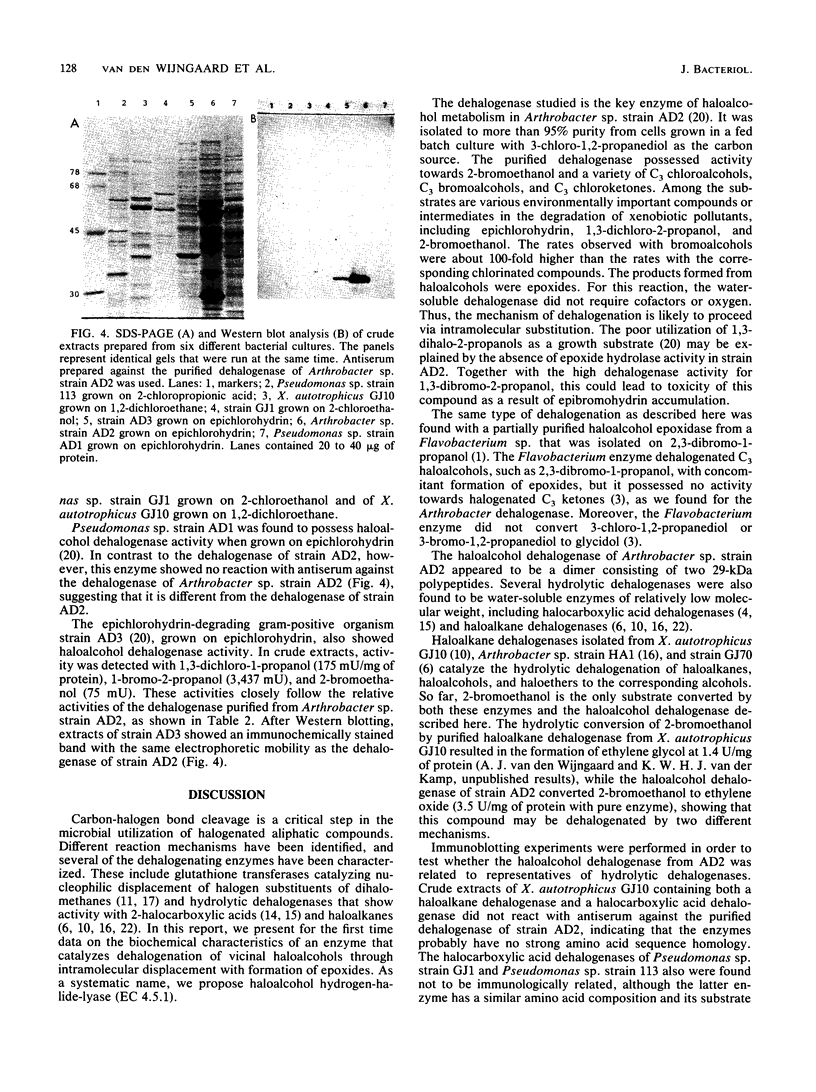

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartnicki E. W., Castro C. E. Biodehalogenation. The pathway for transhalogenation and the stereochemistry of epoxide formation from halohydrins. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4677–4680. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro C. E., Bartnicki E. W. Biodehalogenation. Epoxiation of halohydrins, epoxide opening, and transhalogenation by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3213–3218. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Gerritse J., Brackman J., Kalk C., Jager D., Witholt B. Purification and characterization of a bacterial dehalogenase with activity toward halogenated alkanes, alcohols and ethers. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):67–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Jager D., Witholt B. Degradation of n-haloalkanes and alpha, omega-dihaloalkanes by wild-type and mutants of Acinetobacter sp. strain GJ70. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):561–566. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.561-566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Scheper A., Dijkhuizen L., Witholt B. Degradation of halogenated aliphatic compounds by Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):673–677. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.673-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keuning S., Janssen D. B., Witholt B. Purification and characterization of hydrolytic haloalkane dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.635-639.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler-Staub D., Leisinger T. Dichloromethane dehalogenase of Hyphomicrobium sp. strain DM2. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):676–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.676-681.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motosugi K., Esaki N., Soda K. Purification and properties of a new enzyme, DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase, from Pseudomonas sp. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):522–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.522-527.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motosugi K., Soda K. Microbial degradation of synthetic organochlorine compounds. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1214–1220. doi: 10.1007/BF01990358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz R., Leisinger T., Suter F., Cook A. M. Characterization of 1-chlorohexane halidohydrolase, a dehalogenase of wide substrate range from an Arthrobacter sp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5016–5021. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5016-5021.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz R., Wackett L. P., Egli C., Cook A. M., Leisinger T. Dichloromethane dehalogenase with improved catalytic activity isolated from a fast-growing dichloromethane-utilizing bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5698–5704. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5698-5704.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srám R. J., Tomatis L., Clemmesen J., Bridges B. A. An evaluation of the genetic toxicity of epichlorohydrin. A report of an expert group of the International Commission for Protection against Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens. Mutat Res. 1981 Nov;87(3):299–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
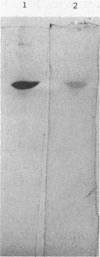
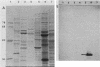
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Omori T., Kodama T. Purification and properties of haloalkane dehalogenase from Corynebacterium sp. strain m15-3. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4049–4054. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4049-4054.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]