Abstract
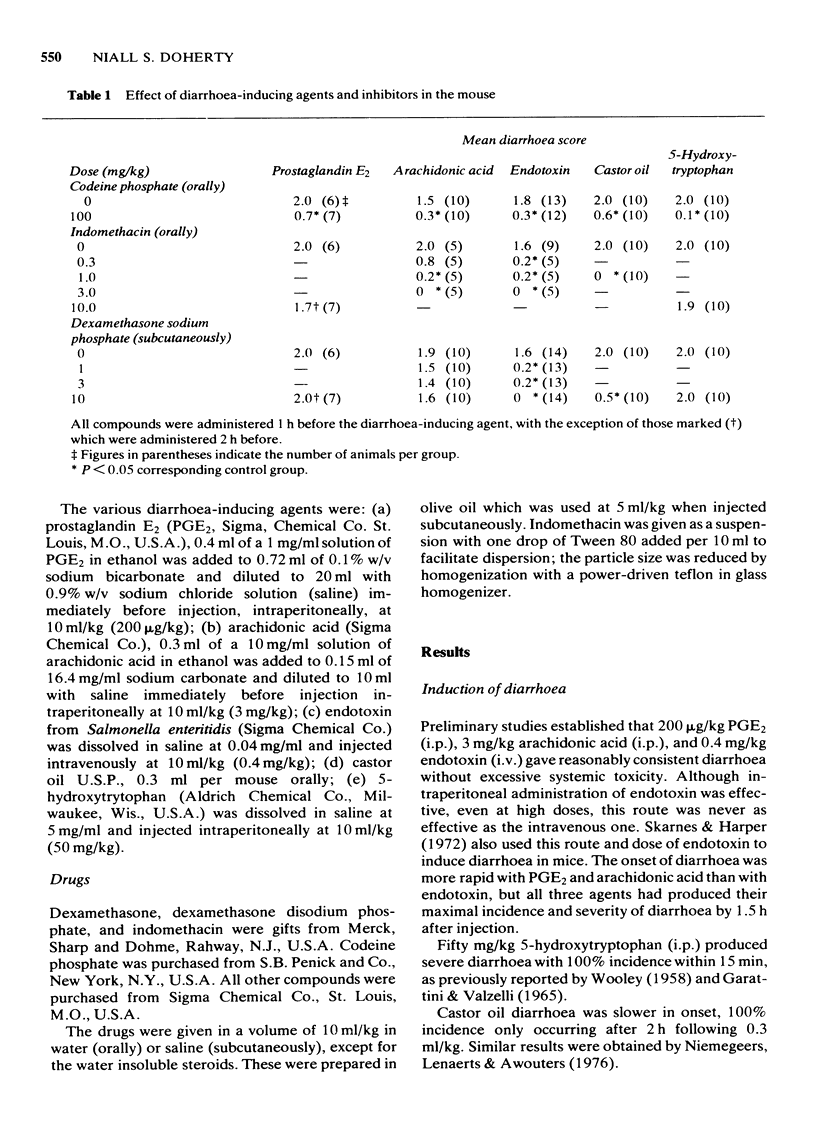
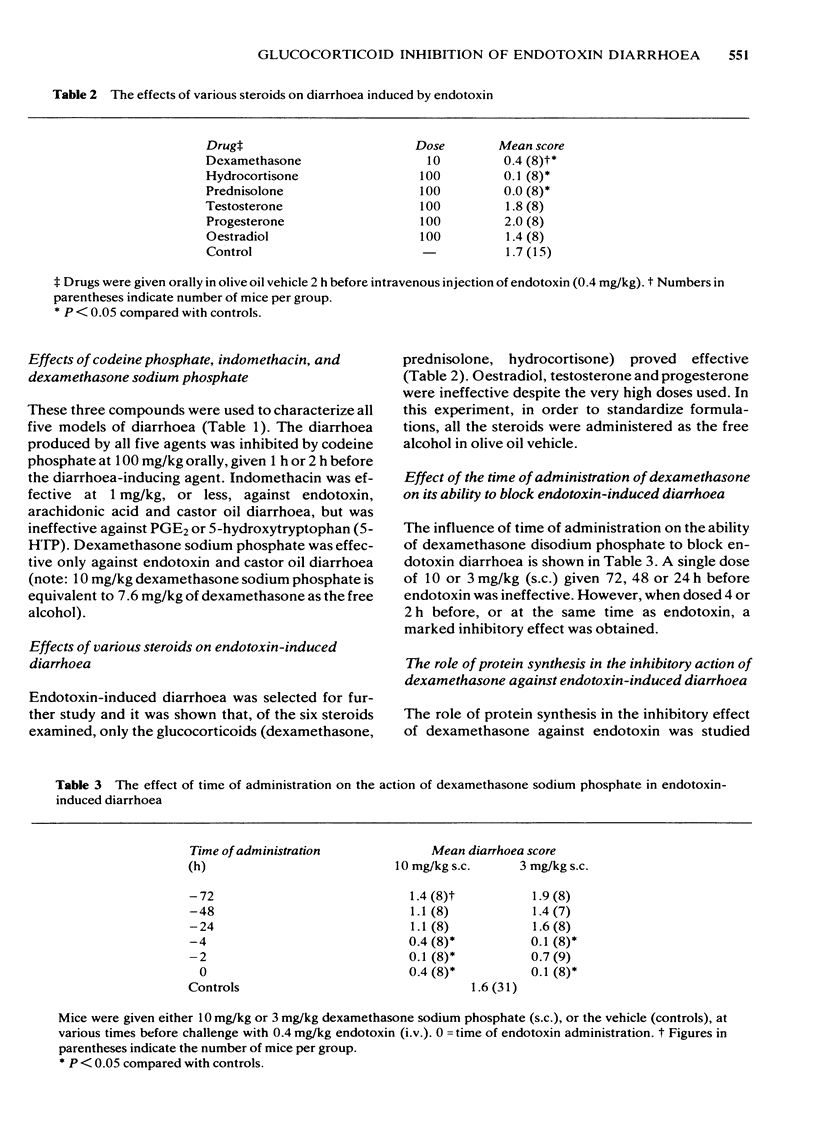
1 Dexamethasone blocked endotoxin-induced diarrhoea in mice, but not that induced by arachidonic acid or prostaglandin E2. 2 Indomethacin blocked endotoxin and arachidonic acid-induced diarrhoea, but not that induced by prostaglandin E2. 3 Codeine blocked all three forms of diarrhoea. 4 The above data, when considered in relation to literature reports that endotoxin induces prostaglandin synthesis, suggest that dexamethasone blocks diarrhoea by preventing the release of arachidonic acid, the substrate for prostaglandin biosynthesis. 5 The activities of indomethacin and dexamethasone in castor oil diarrhoea support the above conclusion and their inactivity in 5-hydroxytryptophan-induced diarrhoea confirms the absence of 'codeine-like' direct effects on the gut. 6 Other glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone, prednisolone) were also able to block endotoxin diarrhoea, but oestradiol, testosterone and progesterone did not. 7 The inhibitory action of dexamethasone on endotoxin diarrhoea could not be blocked by the protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide, nor by the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, progesterone. Thus, involvement of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated gene activation could not be demonstrated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awouters F., Niemegeers C. J., Lenaerts F. M., Janssen P. A. Delay of castor oil diarrhoea in rats: a new way to evaluate inhibitors of prostaglandin biosynthesis. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;30(1):41–45. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Beetens J., Herman A. G. Blood levels of 6-oxo-prostaglandin F 1 alpha during endotoxin-induced hypotension in rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 11;63(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Rampart M., Van Hove C., Herman A. G. Effects of endotoxin on biosynthesis of prostacyclin by isolated rabbit peritoneum. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Dec;242(2):288–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Persico P. Hydrocortisone-induced inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis in rat leucocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;68(1):14–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10691.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde G., Garcia-Barreno P., Suarez A. Arachidonate release from rat liver mitochondria in endotoxin shock. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 24;112(1):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Weinstock M. The effect of analgesic drugs on the release of acetylcholine from electrically stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferluga J., Kaplun A., Allison A. C. Protection of mice against endotoxin-induced liver damage by anti-inflammatory drugs. Agents Actions. 1979 Dec;9(5-6):566–574. doi: 10.1007/BF01968129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):456–459. doi: 10.1038/278456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. Steroidal antiinflammatory drugs as inhibitors of phospholipase A2. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Nezamis J. E., Lancaster C., Hanchar A. J., Klepper M. S. Enteropooling assay: a test for diarrhea produced by prostaglandins. Prostaglandins. 1976 May;11(5):809–828. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Glucocorticoid receptors: relations between steroid binding and biological effects. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):99–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C., Harper M. J. Relationship between endotoxin-induced abortion and the synthesis of prostaglandin F. Prostaglandins. 1972 Mar;1(3):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K. M., Müller R. K. Relation between ulcerogenic activity of various NSAID and their potency as inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in vivo. Agents Actions Suppl. 1979;(4):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurufuji S., Sugio K., Takemasa F. The role of glucocorticoid receptor and gene expression in the anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):408–410. doi: 10.1038/280408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurufuji S., Sugio K., Takemasa F., Yoshizawa S. Blockade by antiglucocorticoids, actinomycin D and cycloheximide of anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone against bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Feb;212(2):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin T. O., Buck S. H., Sperow J. W. Inhibition of the diarrheal and cardiac actions of arachidonic acid by fenclorac, a new anti-inflammatory agent. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1211–1216. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


