Abstract
1 Noradrenaline and 28 imidazolidine (clonidine-like) and imidazoline (oxymetazoline-like) compounds with various phenyl ring substituents have been examined for their ability to inhibit responses to transmural stimulation and exogenous acetylcholine in ileal preparations from reserpine-treated guinea-pigs.
2 The bathing solution contained propranolol, mepyramine, cimetidine and desipramine to preclude interference with the responses by other than the α-receptor-mediated actions of the compounds.
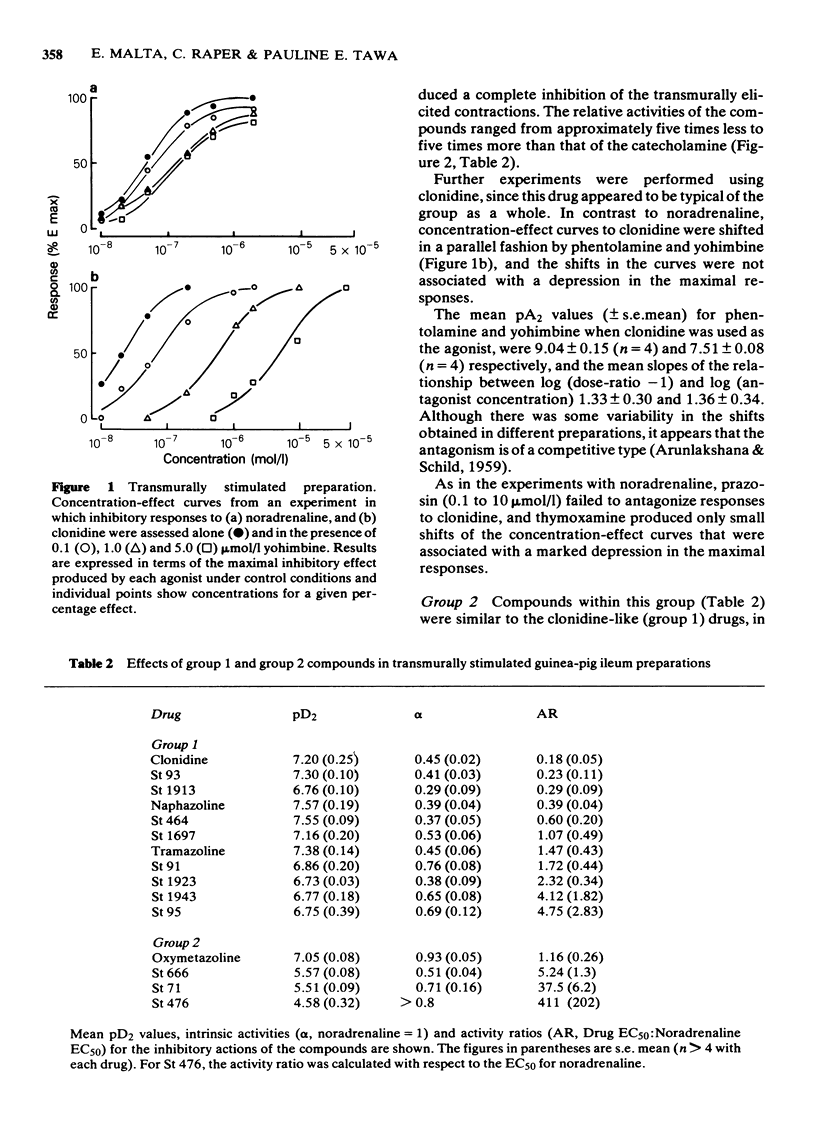
3 In transmurally stimulated preparations the inhibitory response to noradrenaline is due to a combination of prejunctional α-adrenoceptor stimulation and a postjunctional depressant effect that does not involve adrenoceptor activation.
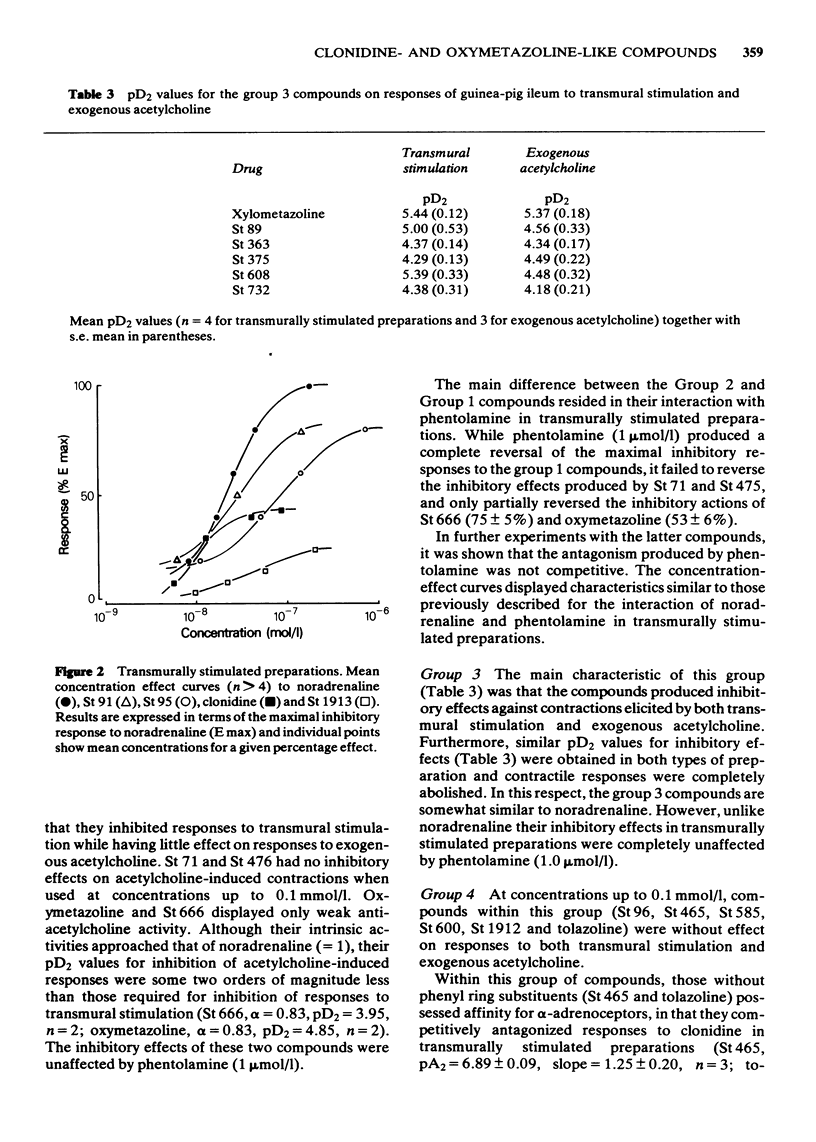
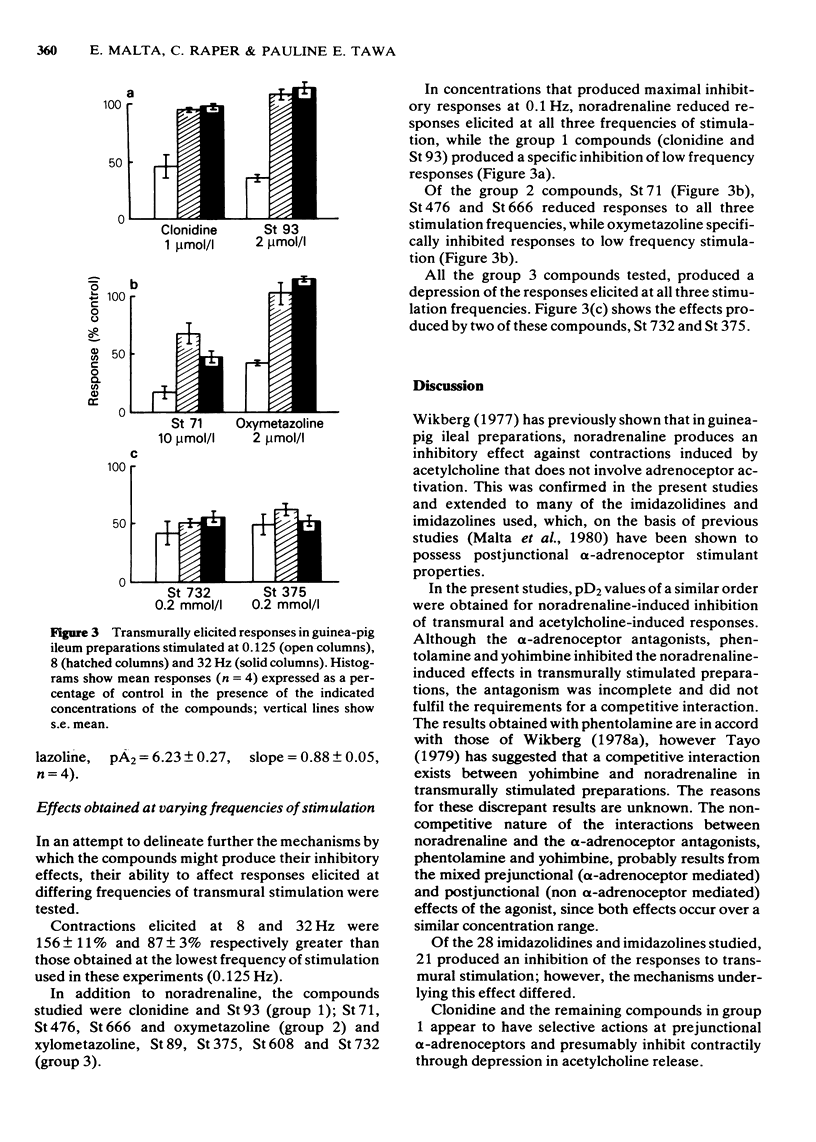
4 Of the 28 imidazolidines and imidazolines studied, 21 inhibited transmurally elicited responses. In the various compounds studied this effect involved actions at pre- or postjunctional sites as indicated by (a) the frequency-dependence of the inhibitory response, (b) its susceptibility to blockade by α-receptor antagonists and (c) the relative concentrations required to inhibit responses to transmural stimulation and exogenous acetylcholine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Crema A. The effect of catecholamines and sympathetic stimulation on the release of acetylcholine from the guinea-pig colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 May;36(1):1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterization of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors regulating cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;64(2):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J., Vizi E. S. Effect of frequency of stimulation on the inhibition by noradrenaline of the acetylcholine output from parasympathetic nerve terminals. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;42(2):263–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malta E., Ong J. S., Raper C., Tawa P. E., Vaughan G. N. Structure-activity relationships of clonidine- and tolazoline-like compounds at histamine and alpha-adrenoceptor sites. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;69(4):679–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle strip. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):10–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tayo F. M. Prejunctional inhibitory alpha-adrenoceptors and dopaminoceptors of the rat vas deferens and the guinea-pig ileum in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;58(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Knoll J. The effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation and guanethidine on parasympathetic neuroeffector transmission; the inhibition of acetylcholine release. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;23(12):918–925. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb09893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological classification of adrenergic alpha receptors in the guinea pig. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):164–166. doi: 10.1038/273164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E. The pharmacological classification of adrenergic alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors and their mechanisms of action. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1979;468:1–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Differentiation between pre- and postjunctional alpha-receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit aorta. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):225–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Localization of adrenergic receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit jejunum to cholinergic neurons and to smooth muscle cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Feb;99(2):190–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


