Abstract
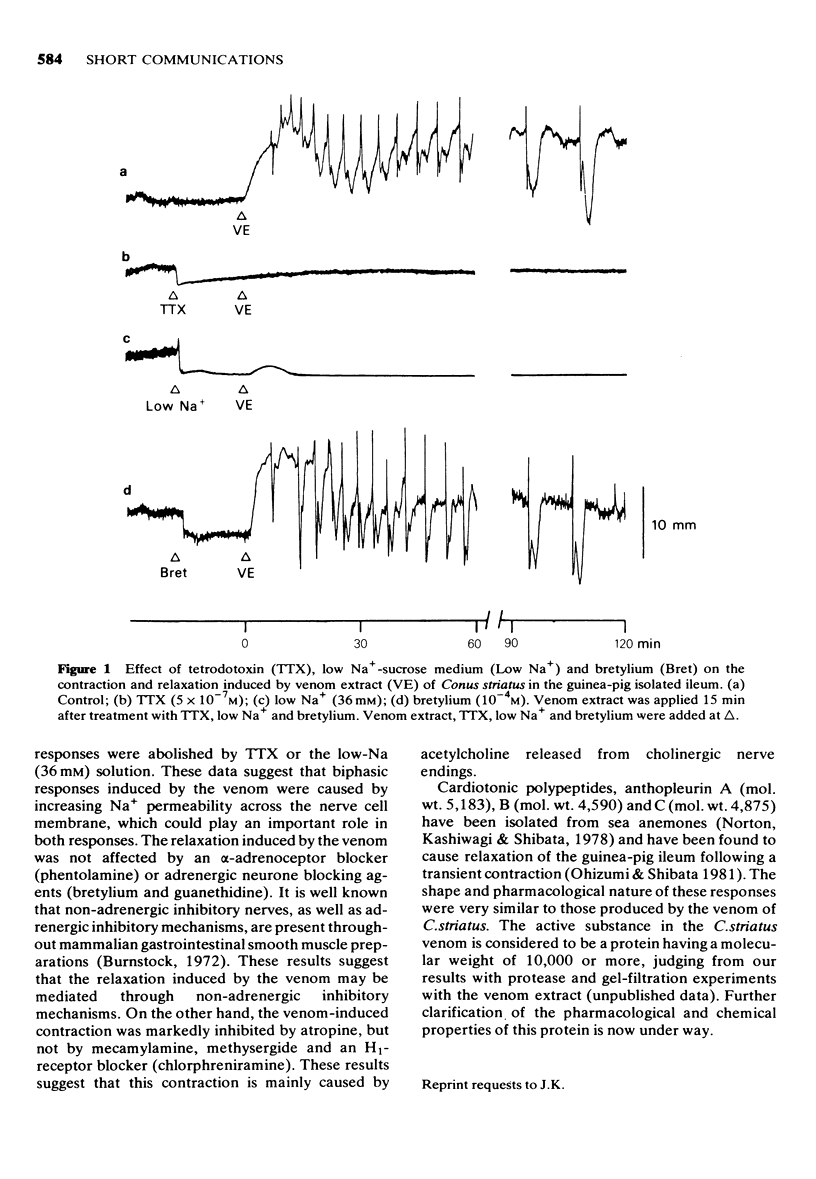
Venom extract of Conus striatus elicited a rhythmic, transient contraction of the guinea-pig isolated ileum followed by a relaxation at concentrations greater than 1 microgram/ml, which was abolished by tetrodotoxin and a low-Na medium. The contraction induced by the venom was inhibited by atropine but not mecamylamine, whereas the relaxation was not affected by bretylium, guanethidine or phentolamine. These results suggest that the contraction of the ileum induced by the venom is due to the excitation of cholinergic nerves, while the relaxation is mediated through non-adrenergic inhibitory nerves.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDEAN R., RUDKIN C. FURTHER STUDIES OF THE VENOMS OF CONIDAE. Toxicon. 1965 May;2:225–249. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(65)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Gyr P., Surridge J. The effects of crude venoms of Conus magus and Conus striatus on the contractile response and electrical activity of guinea-pig cardiac musculature. Toxicon. 1979;17(4):381–395. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Gyr P., Surridge J. The pharmacological actions on guinea-pig ileum of crude venoms from the marine gastropods Conus striatus and Conus magus. Toxicon. 1977;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Surridge J., Gyr P. Some effects of crude venom from the cones Conus striatus and Conus magus on isolated guinea-pig atria. Toxicon. 1977;15(5):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Williams H., Gyr P., Surridge J. Some effects on muscle and nerve of crude venom from the gastropod Conus striatus. Toxicon. 1976;14(4):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(76)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S. E., Turner R. J., Silva S. R. The venom and venom apparatus of the marine gastropod Conus striatus Linne. Toxicon. 1974 Dec;12(6):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Shibata S. Possible mechanism of the dual action of the new polypeptide (anthopleurin-B) from sea anemone in the isolated ileum and taenia caeci of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):239–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


