Abstract
1 Intracellular recordings were made from neurones in the myenteric plexus of the ileum removed from guinea-pigs. The effects of clonidine and adrenaline on membrane potential and resistance were observed.
2 Clonidine (100 pM—30 nM) caused a concentration-dependent membrane hyperpolarization associated with a fall in neurone input resistance.
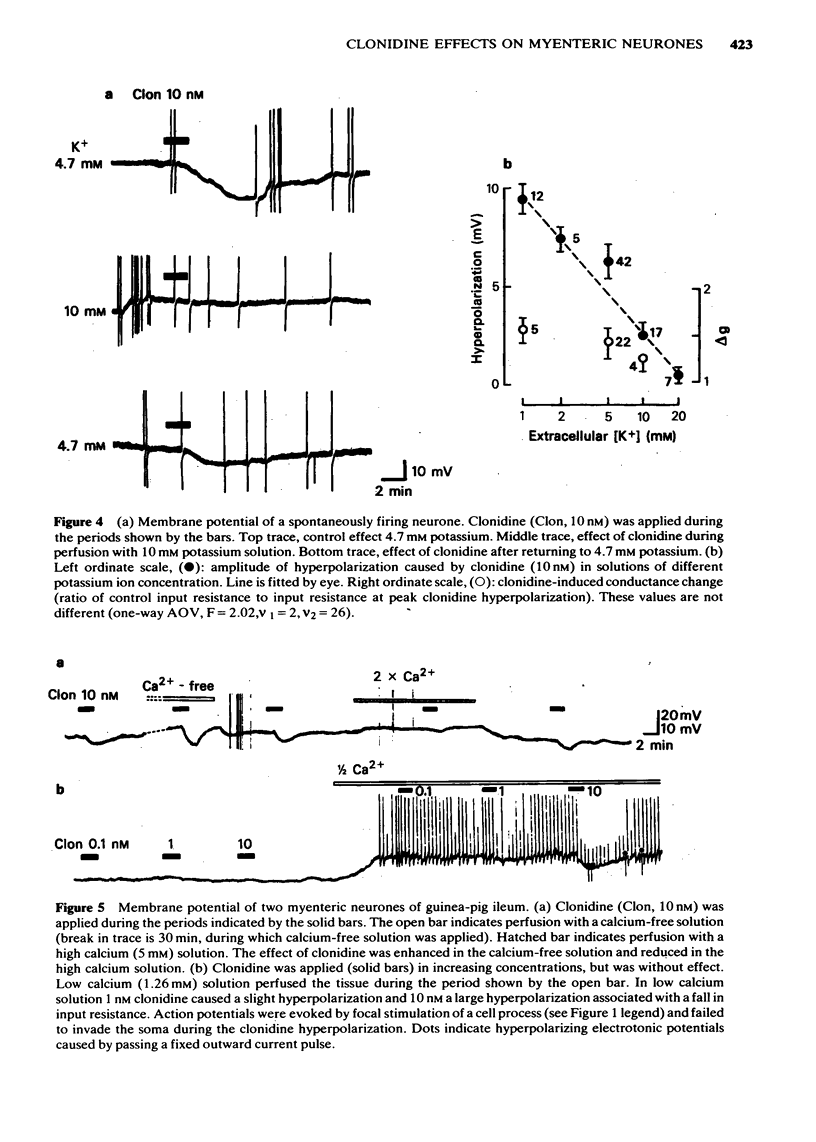
3 The amplitude of the clonidine hyperpolarization, but not the conductance increase, was greater in cells with lower resting potentials and smaller in more polarized neurones. In a given cell, membrane hyperpolarization decreased and membrane depolarization increased the clonidine effect.
4 Low potassium solutions enhanced and high potassium solutions reduced the hyperpolarizing action of clonidine but did not significantly change the conductance increase caused by clonidine.
5 The concentration-effect curve for clonidine was displaced to the left when the extracellular calcium concentration was reduced. Conversely, clonidine was almost ineffective in elevated calcium concentrations. This was true for both the hyperpolarization and the conductance increase.
6 It is suggested that clonidine activates a potassium conductance by causing an elevation in the free intracellular calcium concentration.
7 Clonidine reversibly depressed the amplitude of the nicotinic fast excitatory postsynaptic potential and the noncholinergic slow excitatory postsynaptic potential.
8 All the effects of clonidine were shared by adrenaline and the actions of both were reversed or prevented by phentolamine (100 nM—1 μM).
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andréjak M., Pommier Y., Mouillé P., Schmitt H. Effects of some alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;314(1):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00498434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Burnstock G., Holman M. E. Transmission from perivascular inhibitory nerves to the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):527–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Caulfield M. P. Hyperpolarizing 'alpha 2'-adrenoceptors in rat sympathetic ganglia. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;65(3):435–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Calcium requirement for the alpha-action of catecholamines on guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Jun 15;197(1128):271–284. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Increase of membrane conductance by adrenaline in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):89–102. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. The simultaneous demonstration of adrenergic fibres and enteric ganglion cells. Histochem J. 1973 Jul;5(4):343–349. doi: 10.1007/BF01004802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Volle R. L. The actions of the catecholamines on transmission in the superior cervical ganglion of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Oct;154(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterization of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors regulating cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;64(2):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. The effect of different calcium concentrations on the inhibitory effect of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;63(3):417–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egashira K. Hyperpolarization by noradrenaline in guinea pig liver cells: effects of ouabain and external Ca2+. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(3):473–485. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkleman B. On the nature of inhibition in the intestine. J Physiol. 1930 Sep 18;70(2):145–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. Presynaptic inhibition at mammalian peripheral synapse? Nature. 1974 Aug 2;250(465):430–431. doi: 10.1038/250430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Silinsky E. M. Some effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and noradrenaline on neurones in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):817–832. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., McAfee D. A. Alpha-drenergic inhibition of calcium-dependent potentials in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:191–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. Histochemical studies of the autonomic innervation of the gut. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Sep;149(3):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Slow synaptic potentials in neurones of the myenteric plexus. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:505–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu K., Nakamura M. The electrogenesis of adrenaline-hyperpolarization of sympathetic ganglion cells in bullfrogs. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(1):63–77. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A. Adrenaline and transmission in the sympathetic ganglion of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Sep 10;26(2-3):252–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Kobayashi H. Adrenergic mediation of slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Jul;37(4):805–814. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.4.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Regoli D., Quirion R., Lemaire S., St-Pierre S., Rioux F. Studies on the inhibitory action of somatostatin in the electrically stimulated rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 May 15;55(4):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E., Fischbach G. D. Enkephalin inhibits release of substance P from sensory neurons in culture and decreases action potential duration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):526–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Presynaptic action of noradrenaline in the myenteric plexus. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):29P–30P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Henderson G., Katayama Y., Johnson S. M. Electrophysiological evidence for presynaptic inhibition of acetylcholine release by 5-hydroxytryptamine in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1980;5(3):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. The calcium-dependent slow after-hyperpolarization in myenteric plexus neurones with tetrodotoxin-resistant action potentials. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):709–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle strip. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):10–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouot B. M., U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Multiple alpha 2-noradrenergic receptor sites in rat brain: selective regulation of high-affinity [3H]clonidine binding by guanine nucleotides and divalent cations. J Neurochem. 1980 Feb;34(2):374–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAUMANN W. Zusammenhänge zwischen der Wirkung der Analgetica und Sympathicomimetica auf den Meerschweinchen-Dunndarm. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1958;233(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Starke K. Binding of 3H-clonidine to an alpha-adrenoceptor in membranes of guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;309(3):207–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00504752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner U., Starke K., Schümann H. J. Actions of clonidine and 2-(2-methyl-6-ethyl-cyclohexylamino)-2-oxazoline on postganglionic autonomic nerves. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Feb;195(2):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Differentiation between pre- and postjunctional alpha-receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit aorta. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):225–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Adrenergic inhibition of serotonin release from neurons in guinea pig Auerback's plexus. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):594–603. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


