Abstract
1 The membrane properties of smooth muscle cells and neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig basilar artery were investigated by use of microelectrodes.
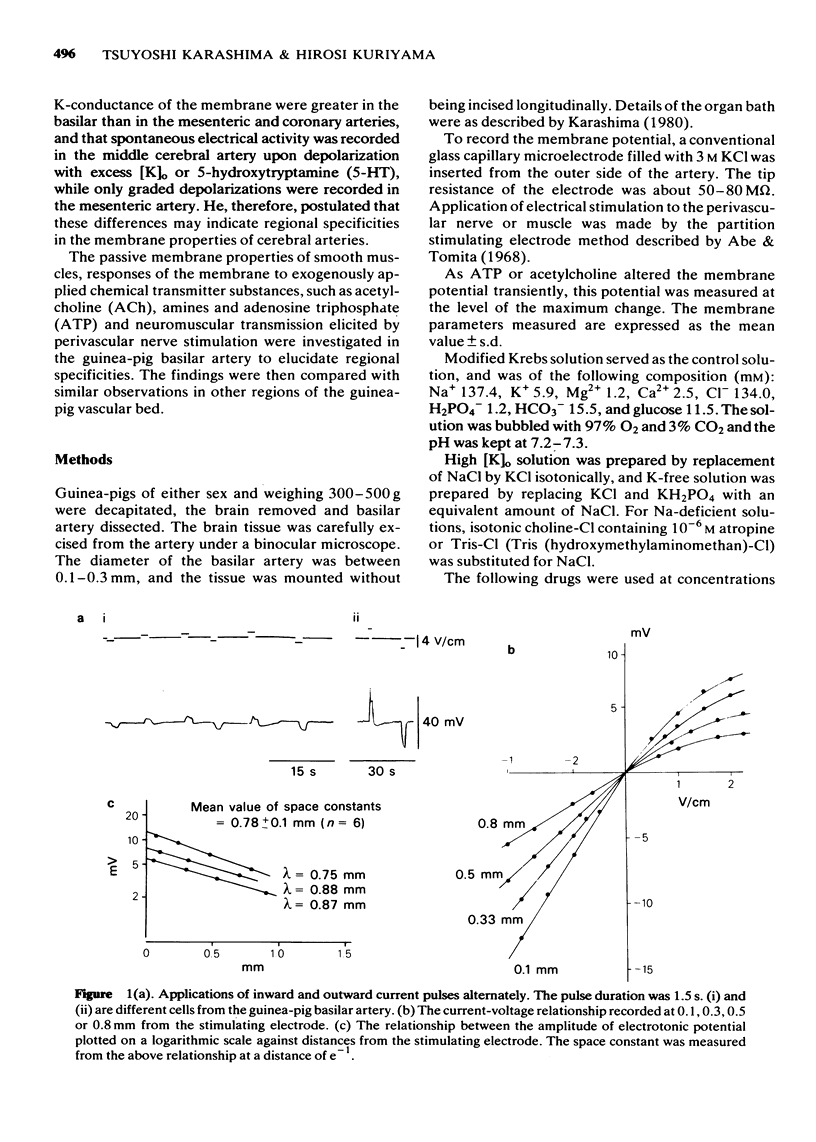
2 The membrane potential was -47.0 mV and the muscle tissue possessed cable-like properties as determined by the current-voltage relationships. The mean value of the spacè constant was 0.78 mm.
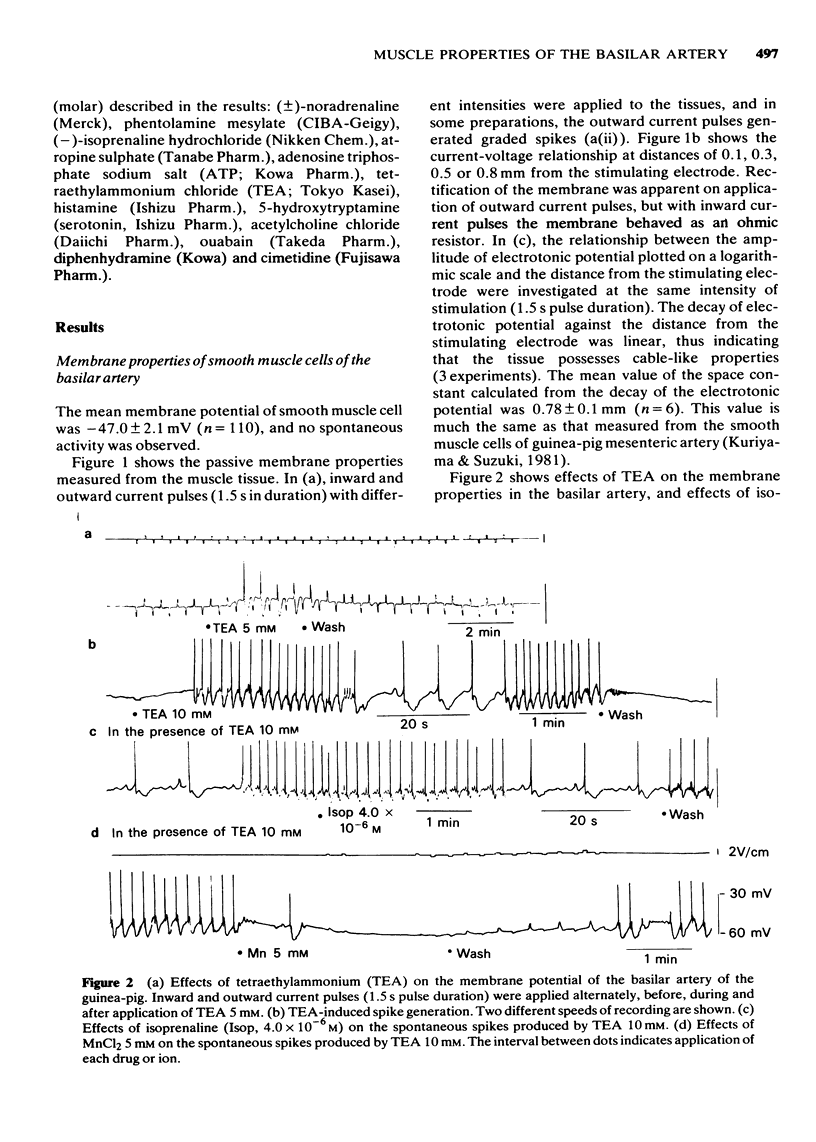
3 An outward current produced a graded response and, in some cases, spike generation. This membrane response was enhanced in the presence of tetraethylammonium (TEA, 5 mM), and an increased concentration of TEA (10 mM) generated spontaneous spikes in most of the cells. Action potentials induced by TEA were abolished in the presence of MnCl2 (5 mM) but not by isoprenaline (4 × 10-6 M).
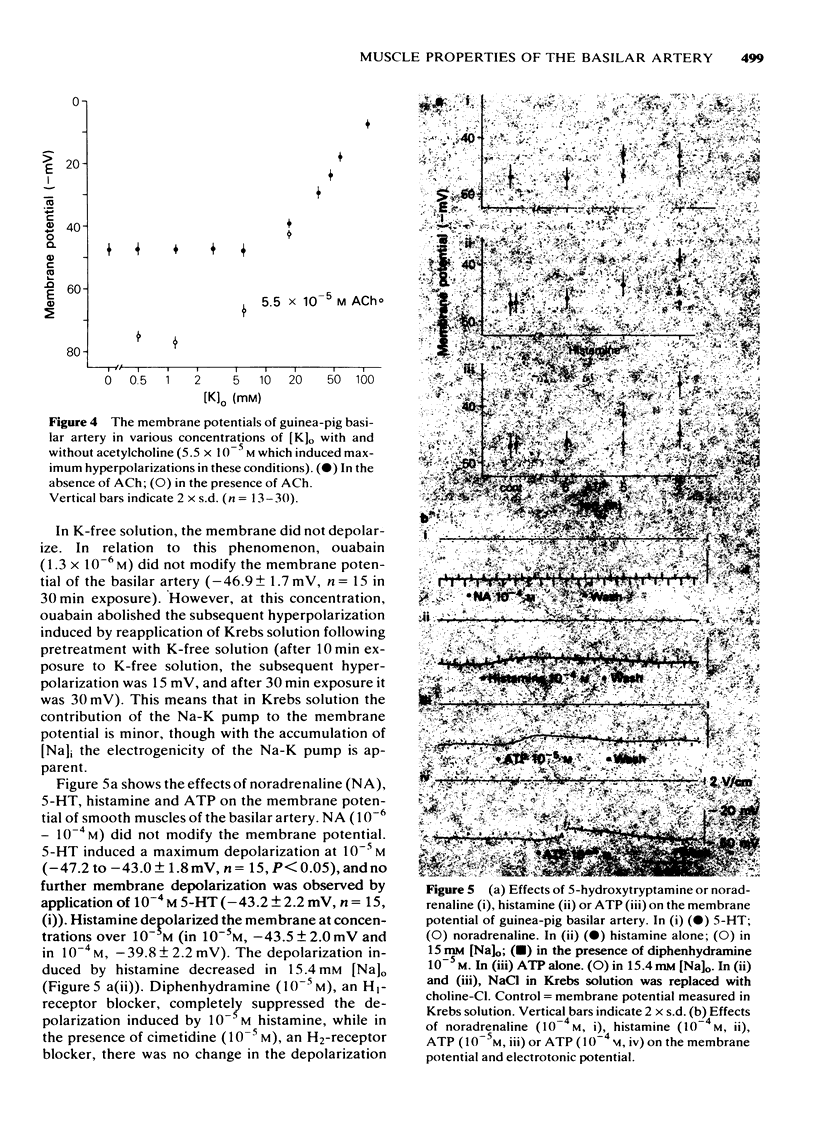
4 Acetylcholine (ACh), over 10-7 M, hyperpolarized the membrane and decreased the membrane resistance. This hyperpolarization increased in the presence of low [K]o (below 5.9 mM), but decreased in [K]o concentrations over 17.8 mM. Pretreatment with atropine (10-6 M) suppressed the ACh-induced hyperpolarization. Therefore, this action of ACh is due to an increase in the K-conductance of the membrane produced by activation of the muscarinic receptors.
5 Noradrenaline in concentrations up to 10-4 M did not modify the membrane potential and resistance, while 10-5 M, histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) depolarized the membrane. The depolarization induced by histamine or ATP was suppressed by reducing [Na]o. The histamine-induced depolarization was accompanied by an increase and the ATP-induced one by a decrease in the membrane resistance. The action of histamine was suppressed by treatment with H1- but not H2-receptor blocking agents (dephenhydramine and cimetidine, respectively).
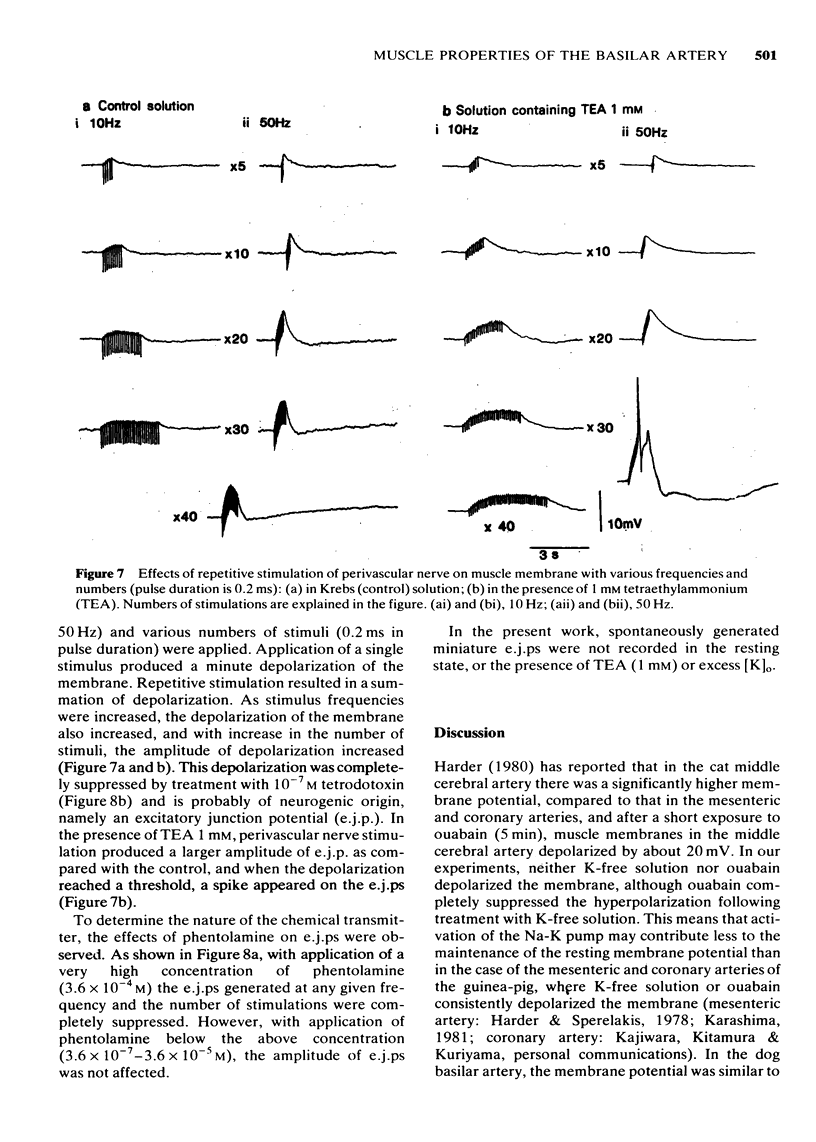
6 Perivascular nerve stimulation (0.2 ms pulse duration) evoked excitatory junction potentials (e.j.ps). An increase in the number and frequency of stimuli enhanced the e.j.p. amplitude. In the presence of 1 mM TEA, a spike was evoked on the e.j.ps. A very high concentration of phentolamine (3.6 × 10-4 M) or the usual concentration of tetrodotoxin (10-7 M) abolished the generation of e.j.ps. Spontaneously generated miniature e.j.ps were never recorded from the resting membrane.
7 The results are discussed in relation to regional specificities of smooth muscle cells of cerebral arteries in the guinea-pig.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y., Tomita T. Cable properties of smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):87–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):129–148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckles S. P. Functional activity of the noradrenergic innervation of large cerebral arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;69(2):193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07890.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., MacKenzie E. T. Amine mechanisms in the cerebral circulation. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Dec;28(4):275–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R. Comparison of electrical properties of middle cerebral and mesenteric artery in cat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):C23–C26. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.239.1.C23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder D. R., Sperelakis N. Membrane electrical properties of vascular smooth muscle from the guinea pig superior mesenteric artery. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Dec 28;378(2):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00584443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Evidence for two populations of excitatory receptors for noradrenaline on arteriolar smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):767–768. doi: 10.1038/283767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. M. Some properties of the excitatory junction potentials recorded from saphenous arteries of rabbits. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima T. Actions of nitroglycerine on smooth muscles of the guinea-pig and rat portal veins. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima T. Effects of vasopressin on smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig mesenteric vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;72(4):673–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima T., Takata Y. The effects of ATP related compounds on the electrical activity of the rat portal vein. Gen Pharmacol. 1979;10(6):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(79)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Effects of acetylcholine on the smooth muscle cell of isolated main coronary artery of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:119–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. J., Chiueh C. C., Adams M. Synaptic transmission of vasoconstrictor nerves in rabbit basilar artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan 11;61(1):55–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. J., Hume W. R., Su C., Bevan J. A. Neurogenic vasodilation of cat cerebral arteries. Circ Res. 1978 Apr;42(4):535–542. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusamvuku N. A., Sercombe R., Aubineau P., Seylaz J. Correlated electrical and mechanical responses of isolated rabbit pial arteries to some vasoactive drugs. Stroke. 1979 Nov-Dec;10(6):727–732. doi: 10.1161/01.str.10.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves M. J. Do vasomotor nerves significantly regulate cerebral blood flow? Circ Res. 1978 Oct;43(4):485–493. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.4.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard J. F., Jr, Liebmann J. E., Schlosberg A. J., Moskowitz M. A. Serotonin neurons project to small blood vessels in the brain. Science. 1979 Oct 5;206(4414):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.482930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Casteels R. Effect of histamine on the small arteries in the gracilis muscle of the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Nov;211(2):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kuriyama H. Observation of quantal release of noradrenaline from vascular smooth muscles in potassium-free solution. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(4):665–670. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y. Regional differences in electrical and mechanical properties of guinea-pig mesenteric vessels. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(5):709–728. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


