Abstract
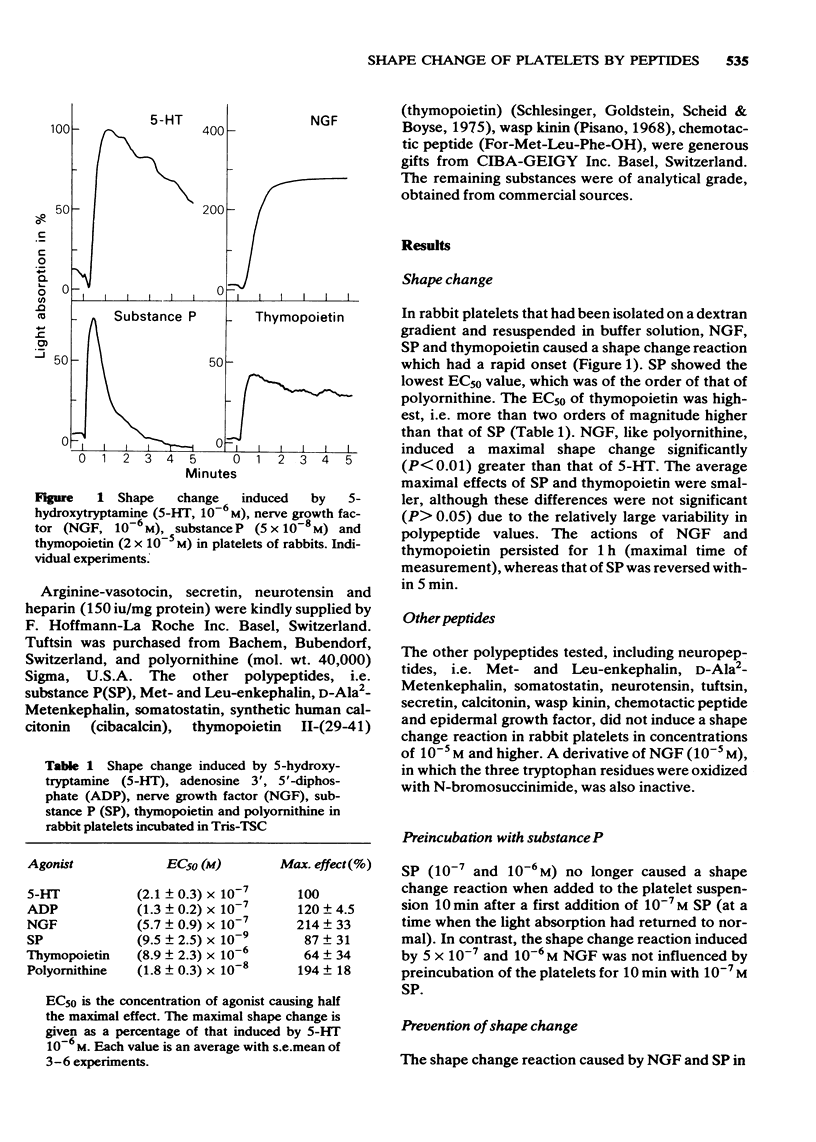
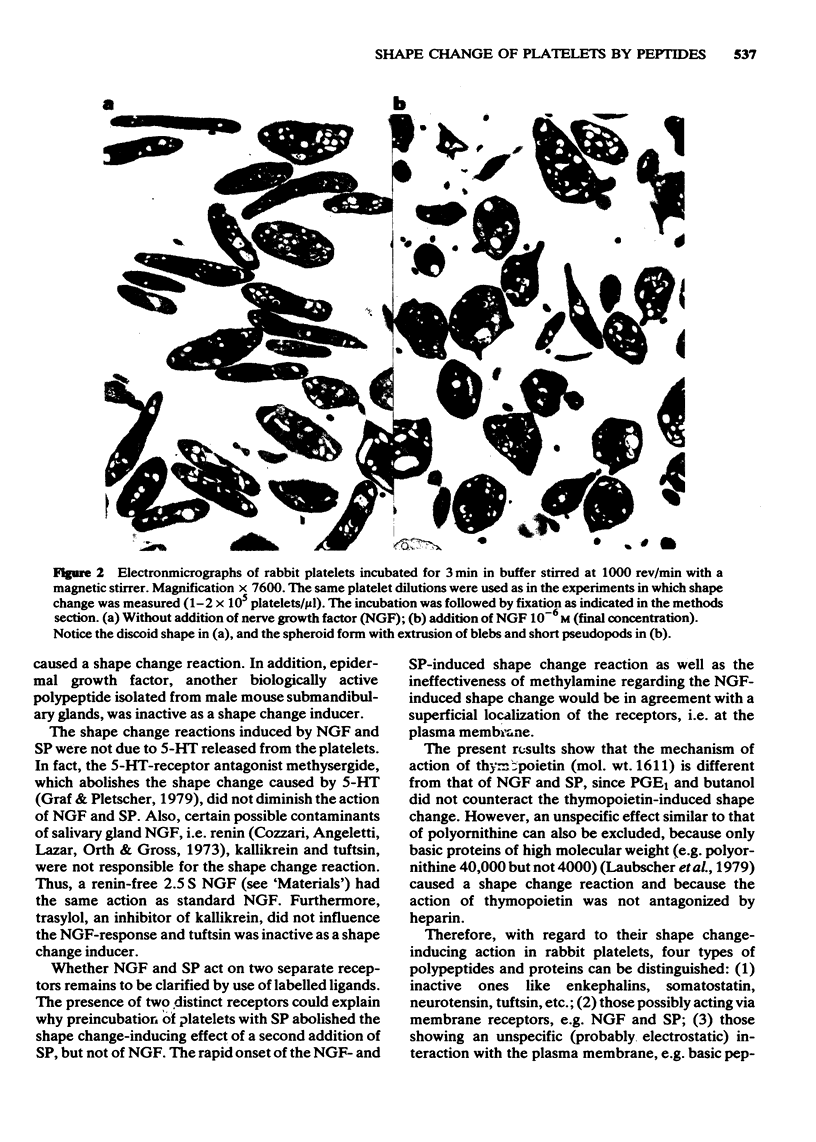
1 Nerve growth factor (NGF), substance P (SP) and thymopoietin all caused shape change reactions of rapid onset in rabbit platelets. NGF had the highest maximal effect, and SP the lowest EC50 (concentration causing half maximal shape change). The action of SP was reversible within 5 min, whereas that of NGF lasted for at least 1 h. A series of other peptides were inactive. 2 After preincubation of platelets with SP, a second application of SP no longer caused a shape change reaction, whereas the effect of NGF was not influenced. 3 An oxidized NGF-derivative without biological activity did not cause a shape change reaction, neither did epidermal growth factor. 4 Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) and pretreatment of the platelets with 3% butanol, which counteract the shape changes caused by 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, also antagonized those induced by NGF and SP. Neither heparin nor methysergide, an antagonist of 5-HT-receptors, influenced the shape change induced by NGF or SP. The action of NGF was also antagonized by a specific antibody to NGF. 5 Thymopoietin, like the basic polypeptide polyornithine (mol. wt. 40,000) was not antagonized by PGE1 and butanol. Heparin, which counteracted the effect of polyornithine, did not influence that of thymopoietin. 6 In conclusion, different modes of action are involved in the shape change of blood platelets induced by polypeptides and proteins. SP and NGF may act by stimulating specific membrane receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. R., Handin R. I. Solubilization and characterization of a platelet membrane ADP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3866–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born G. V., Dearnley R., Foulks J. G., Sharp D. E. Quantification of the morphological reaction of platelets to aggregating agents and of its reversal by aggregation inhibitors. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:193–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born G. V. Observations on the change in shape of blood platelets brought about by adenosine diphosphate. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):487–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzari C., Angeletti P. U., Lazar J., Orth H., Gross F. Separation of isorenin activity from nerve growth factor (NGF) activity in mouse submaxillary gland extracts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Jun 1;22(11):1321–1327. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton E. L. Tissue culture assay of nerve growth factor and of the specific antiserum. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Mar;59(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90645-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier W. A., Hogue-Angeletti R. A., Sherman R., Bradshaw R. A. Topography of mouse 2.5S nerve growth factor. Reactivity of tyrosine and tryptophan. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3281–3293. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf M., Laubscher A., Richards J. G., Pletscher A. Blood platelets isolated by polysaccharide gradients: reaction to 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Feb;93(2):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf M., Pletscher A. Shape change of blood platelets--a model for cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors? Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;65(4):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M., Fox J. E., Lynham J. A. Cyclic nucleotides in platelet function. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Oct 31;40(2):232–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubscher A., Pletscher A., Honegger C. G., Richards J. G. Shape change of blood platelets brought about by myelin basic protein and other basic polypeptides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00499878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Davies P. J., Pastan I. Amines inhibit the clustering of alpha2-macroglobulin and EGF on the fibroblast cell surface. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):661–663. doi: 10.1038/277661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H., Matranga V., Cascino D., Vittorelli L. Reconstitution of membranes and embryonic development in dissociated blastula cells of the sea urchin by reinsertion of aggregation-promoting membrane proteins extracted with butanol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):288–292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten U., Thoenen H. Effect of glucocorticoids on nerve growth factor-mediated enzyme induction in organ cultures of rat sympathetic ganglia: enchanced response and reduced time requirement to initiate enzyme induction. J Neurochem. 1977 Jul;29(1):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb03925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J. Vasoactive peptides in venoms. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):58–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger D. H., Goldstein G., Scheid M. P., Boyse E. A. Chemical synthesis of a peptide fragment of thymopoietin II that induces selective T cell differentiation. Cell. 1975 Aug;5(4):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Shooter E. M. Comparison of the arginine esteropeptidases associated with the nerve and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):165–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K., Gagnon C., Guroff G., Thoenen H. Purification of nerve growth factor antibodies by affinity chromatography. J Neurochem. 1976 Jun;26(6):1207–1211. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb07008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]