Abstract
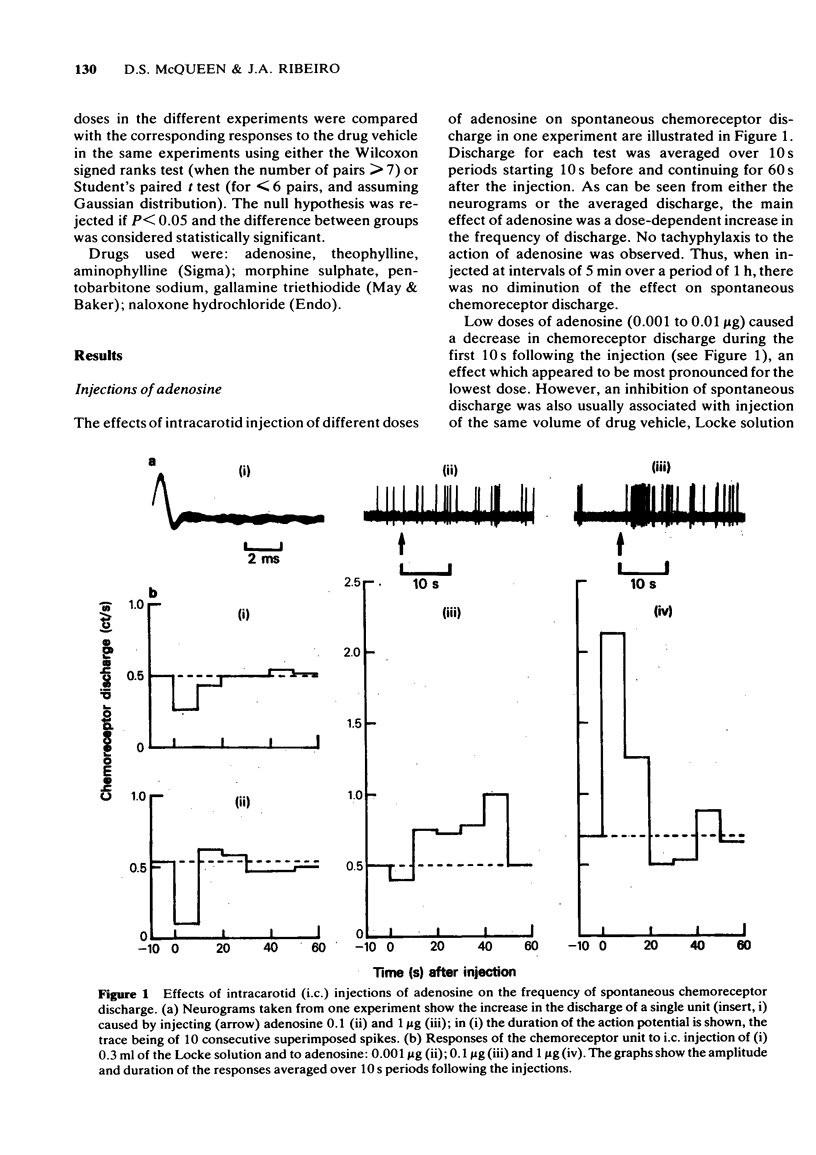
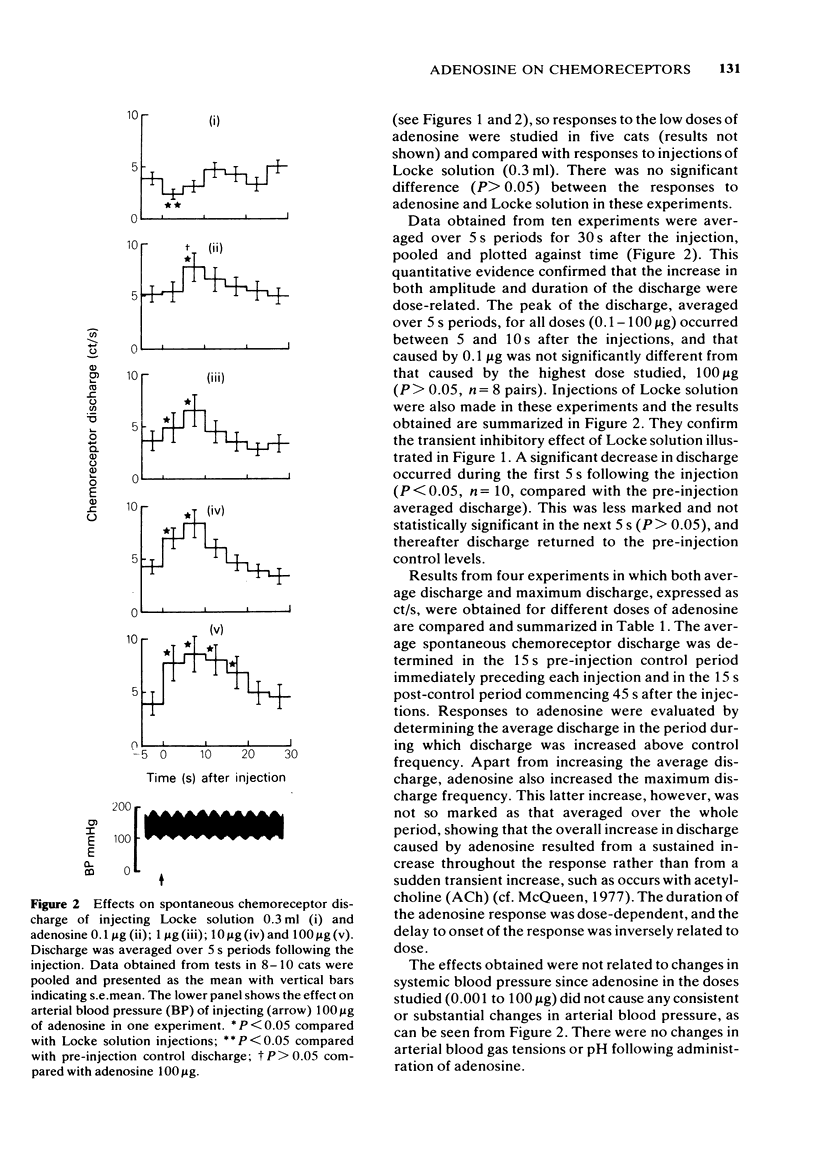
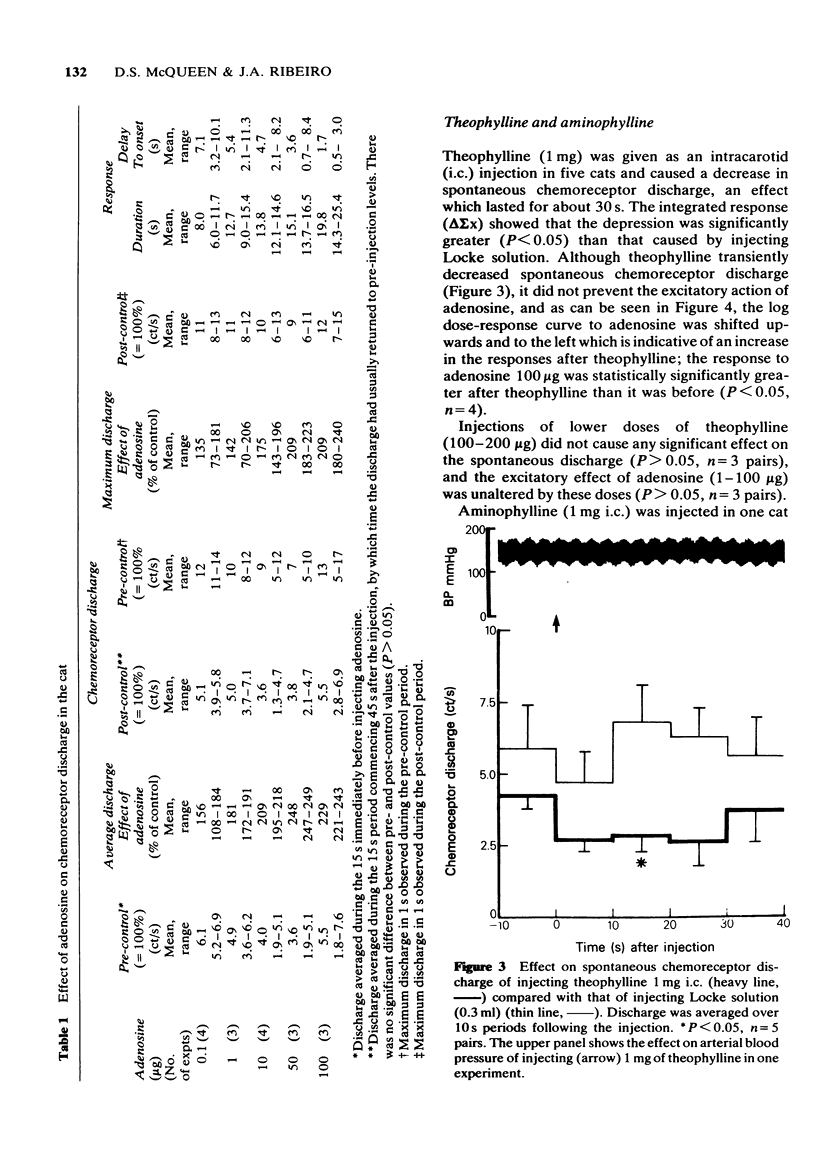
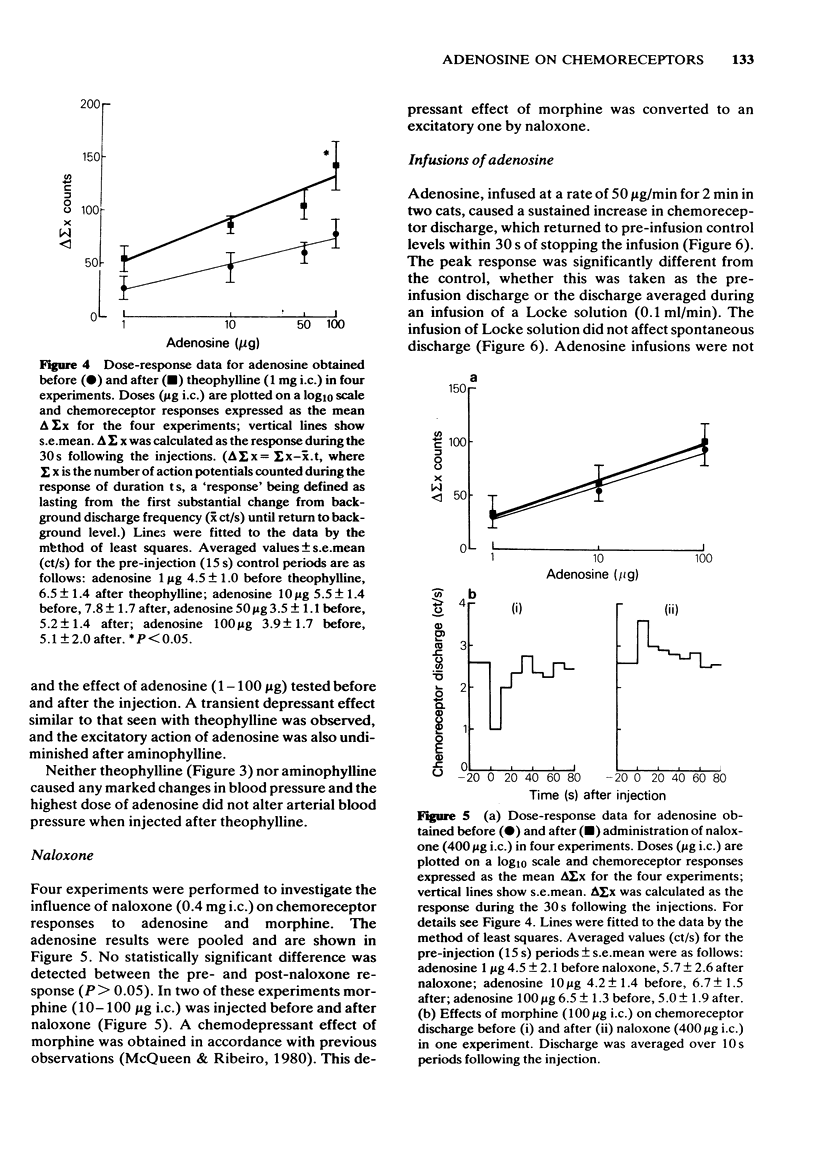
1 The effects of intracarotid (i.c.) injections or infusions of adenosine on chemoreceptor activity recorded from the peripheral end of a sectioned carotid sinus nerve have been studied in cats anaesthetized with pentobarbitone. 2 Adenosine injections (0.1-100 micrograms) caused a rapid and marked increase of spontaneous chemoreceptor discharge, the intensity, duration and onset of which was dose-dependent. Infusion of adenosine, 50 microgram/min, also evoked an increase in discharge which persisted for the duration of the infusion. 3 Both theophylline (1 mg i.c.) and aminophylline (1 mg i.c.) caused short-lasting decreases in spontaneous discharge but did not prevent the excitatory effect of adenosine. Theophylline increased the excitatory action of adenosine. 4 Naloxone (400 micrograms i.c.) antagonized the depressant effect of morphine on chemoreceptor discharge but not the excitatory action of adenosine. 5 It is concluded that exogenous adenosine can excite the cat carotid chemoreceptors, an effect which is not prevented by theophylline in the doses studied. The physiological significance of the findings is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleehen T., Keele C. A. Observations on the algogenic actions of adenosine compounds on the human blister base preparation. Pain. 1977 Aug;3(4):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(77)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiocchio S. R., Biscardi A. M., Tramezzani J. H. Catecholamines in the carotid body of the cat. Nature. 1966 Nov 19;212(5064):834–835. doi: 10.1038/212834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L. P., Taylor K. M., Gregson R. P., Quinn R. J. Stimulation of guinea-pig brain adenylate cyclase by adneosine analogues with potent pharmacological activity in vivo. Life Sci. 1980 Mar 31;26(13):1079–1088. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J., Burnstock G., Vanhoutte P. M. Modulation of the evoked release of noradrenaline in canine saphenous vein via presynaptic receptors for adenosine but not ATP. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 May 15;55(4):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J., McQueen D. S. Inhibitory action of dopamine on cat carotid chemoreceptors. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:425–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. S., Rogus E. M., Dehghani A. Catecholamines and 3',5' cyclic AMP in carotid body chemoreception in the cat. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;78:245–258. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9035-4_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Hirst G. D. The effect of adenosine on the release of the transmitter from the phrenic nerve of the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):629–645. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson L., Hedqvist P., Fredholm B. B., Lundgren G. Inhibition of acetylcholine release in guinea pig ileum by adenosine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Dec;104(4):469–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Fredholm B. B. Effects of adenosine on adrenergic neurotransmission; prejunctional inhibition and postjunctional enhancement. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;293(3):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00507344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollins C., Stone T. W. Adenosine inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid release from slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 May;69(1):107–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Fahrenkrug J., Nilsson G., Terenius L. Peptides in the cat carotid body (glomus caroticum): VIP-, enkephalin-, and substance P-like immunoreactivity. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Nov;107(3):279–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S. A quantitative study of the effects of cholinergic drugs on carotid chemoreceptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):515–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S., Ribeiro J. A. Inhibitory actions of methionine-enkephalin and morphine on the cat carotid chemoreceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(1):297–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10939.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis M. L., Michaelis E. K., Myers S. L. Adenosine modulation of synaptosomal dopamine release. Life Sci. 1979 May 28;24(22):2083–2092. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne M. P., Butlar P. J. New theory for receptor mechanism of carotid body chemoreceptors. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):701–703. doi: 10.1038/254701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A. Purinergic modulation of transmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1979 Sep 21;80(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Walker J. The effects of adenosine triphosphate and adenosine diphosphate on transmission at the rat and frog neuromuscular junctions. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;54(2):213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb06931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio R., Berne R. M., Bockman E. L., CURNISH R. R. Relationship between adenosine concentration and oxygen supply in rat brain. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1896–1902. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Jhamandas K. H. Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenine nucleotides and morphine: antagonism by theophylline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggins G. R., Gruol D. L., Padjen A. L., Formans D. S. Purine and pyrimidine mononucleotides depolarise neurones of explanted amphibian sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):263–265. doi: 10.1038/270263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Is adenosine the mediator of opiate action on neuronal firing rate? Nature. 1979 Sep 20;281(5728):227–228. doi: 10.1038/281227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaeghe R. H., Vanhoutte P. M., Shepherd J. T. Inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmission in canine blood vessels by adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Circ Res. 1977 Feb;40(2):208–215. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Knoll J. The inhibitory effect of adenosine and related nucleotides on the release of acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1976;1(5):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Wakade T. D. Inhibition of noradrenaline release by adenosine. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:35–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Pearse A. G., McGregor G. P., Bryant M. G., Bloom S. R., Emson P. C., Bisgard G. E., Will J. A. Enkephalin-, VIP- and substance P-like immunoreactivity in the carotid body. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):269–271. doi: 10.1038/284269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn H. R., Rubio R., Berne R. M. Brain adenosine production in the rat during 60 seconds of ischemia. Circ Res. 1979 Oct;45(4):486–492. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.4.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata P. Effects of dopamine on carotid chemo- and baroreceptors in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):235–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata P., Hess A., Bliss E. L., Eyzaguirre C. Chemical, electron microscopic and physiological observations on the role of catecholamines in the carotid body. Brain Res. 1969 Jul;14(2):473–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



