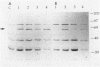
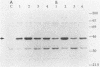
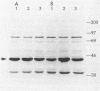
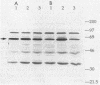
Abstract
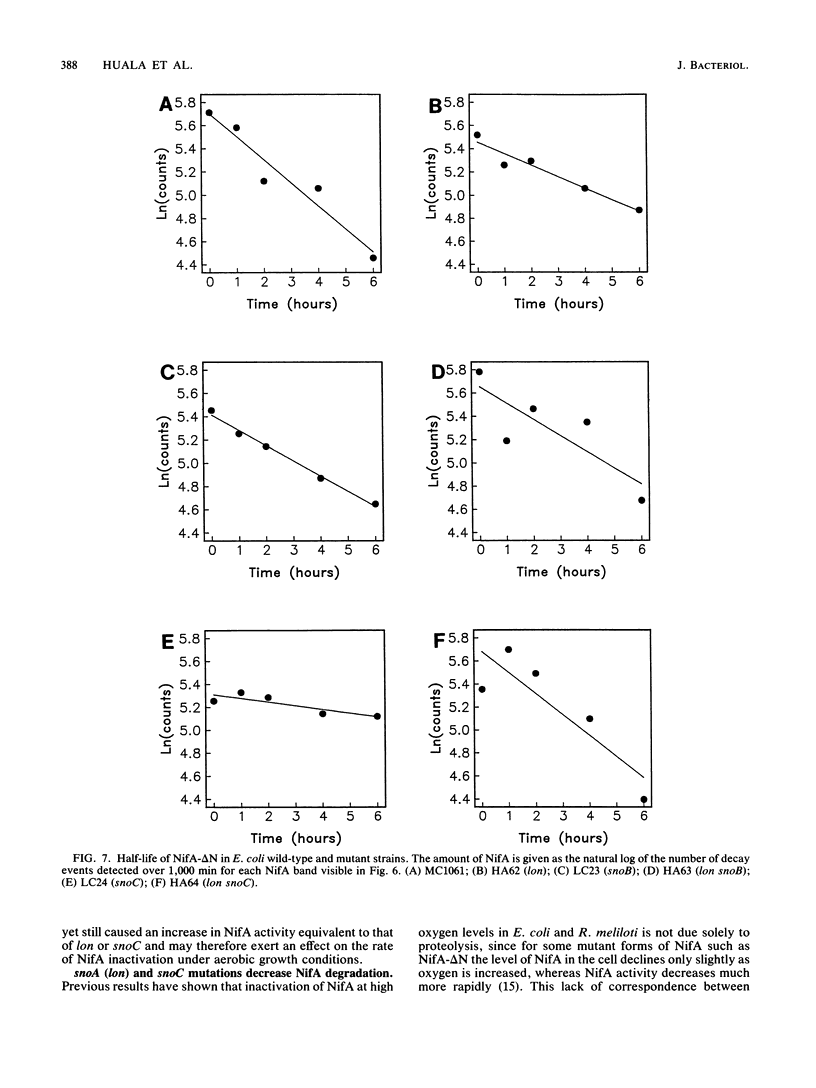
The Rhizobium meliloti NifA protein is an oxygen-sensitive transcriptional regulator of nitrogen fixation genes. Regulation of NifA activity by oxygen occurs at the transcriptional level through fixLJ and at the posttranslational level through the sensitivity of NifA to oxygen. We have previously reported that the NifA protein is sensitive to oxygen in Escherichia coli as well as in R. meliloti. To investigate whether the posttranslational regulation of NifA is dependent on host factors conserved between R. meliloti and E. coli, we carried out a Tn5 mutagenesis of E. coli and isolated mutants with increased NifA activity under aerobic conditions. Fifteen insertion mutations occurred at three unlinked loci. One locus is the previously characterized lon gene; the other two loci, which we have named snoB and snoC, define previously uncharacterized E. coli genes. The products of snoC and lon affect the rate of NifA degradation, whereas the product of snoB may affect both NifA degradation and inactivation. A snoB lon double mutant showed a higher level of NifA accumulation than did a lon mutant, suggesting that the snoB product affects the ability of NifA to be degraded by a lon-independent pathway. The effects of a snoC mutation and lon mutation were not additive, suggesting that the snoC and lon products function in the same degradative pathway.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Better M., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Deletion analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2419–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon J. L., Williams M. K., Cannon F. C. Expression and functional analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti nifA gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):7–14. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. T., Goff S. A., Webster T., Smith T., Goldberg A. L. Sequence of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. A heat-shock gene which encodes the ATP-dependent protease La. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11718–11728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Qasba P. K. Alkaline transfer of DNA to plastic membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutch C. E., Soffer R. L. Escherichia coli mutants defective in dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5998–6001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H M, Hennecke H. Direct response of Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifA-mediated nif gene regulation to cellular oxygen status. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):621–626. doi: 10.1007/BF00331174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Fritsche S., Herzog B., Hennecke H. Critical spacing between two essential cysteine residues in the interdomain linker of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium meliloti NifA is sufficient to activate transcription from the R. meliloti nifH promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3354–3365. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3354-3365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A., Silver D., Seed B. Minimal size plasmids containing an M13 origin for production of single-strand transducing particles. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):507–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsell D. A., Sauer R. T. The structural stability of a protein is an important determinant of its proteolytic susceptibility in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7590–7595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Royal N. J., Neuman de Vegvar H., Herlihy W. C., Biemann K., Schimmel P. Primary structure of a large aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1497–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.7025207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki I., Bertani G. Growth abnormalities in Hfr derivatives of Escherichia coli strain C. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):365–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker J. M., Gayda R. C., Markovitz A. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli: SOS induction and cellular location of the sulA protein, a key to lon-associated filamentation and death. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):551–561. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.551-561.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.1-24.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Jacobson F. S., Tartaglia L. A., Morgan R. W., Silveira L. A., Ames B. N. An alkyl hydroperoxide reductase induced by oxidative stress in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: genetic characterization and cloning of ahp. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2049–2055. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2049-2055.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Novel regulatory mutants of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):39–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]