Abstract
Experiments were performed on healthy (non-infected) and Plasmodium knowlesi-infected rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) to determine the activity of the kinin-destroying enzymes (kininases) present in the circulation.
Methods for the studies and estimation of kininases in the circulating blood of control and P. knowlesi-infected animals are described. The activity of the enzymes, present in the blood in all animals investigated, was evaluated from both methods employed by incubation with synthetic bradykinin. The isolated rat uterus served as the test organ.
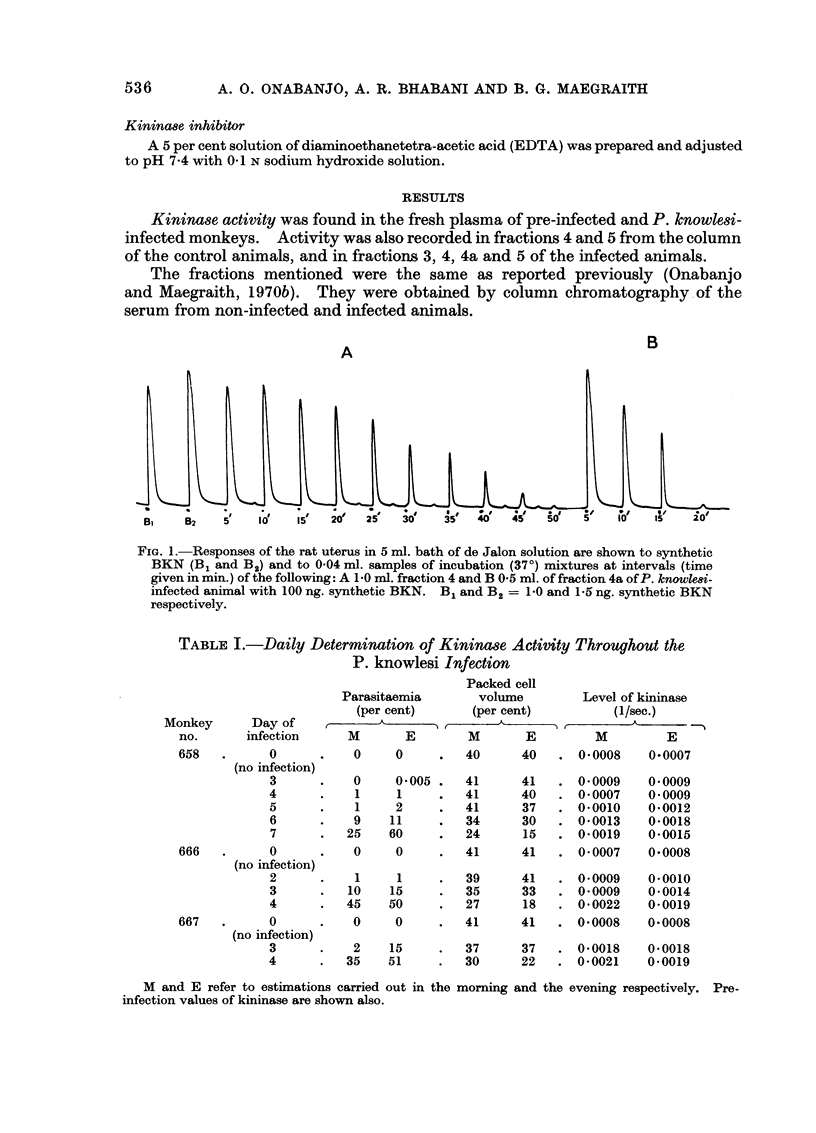
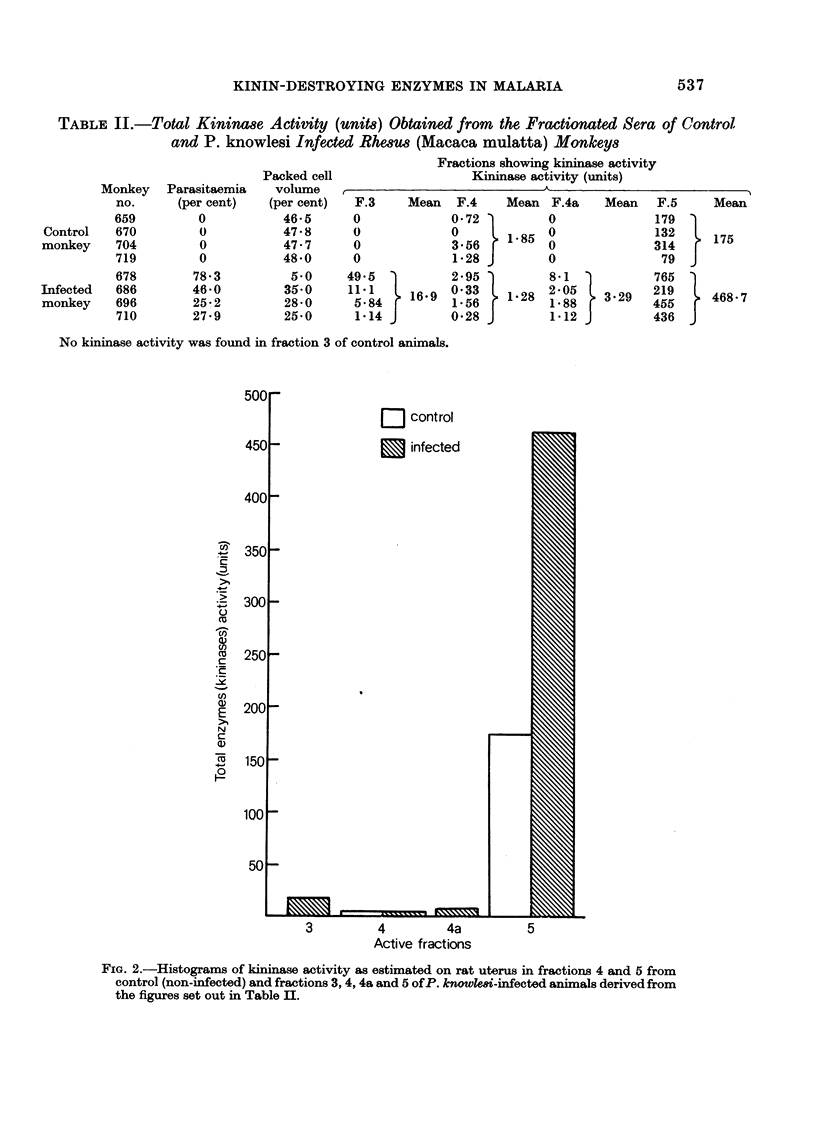
Studies were made on protein peak fractions obtained by column chromatography from sera of uninfected and infected animals. Kininases activity was present in fractions 4 and 5 of the control animals and in fractions 3, 4, 4a and 5 of the infected animals.
The total mean value of kininase activity in the separated fractions of control animals was 179 enzyme units as compared with 489 units in monkeys infected with P. knowlesi. In the plasma, the pre-infection level of kininases obtained in the 3 animals studied was 0·0007-0·0008 (expressed in reciprocals of seconds); in the late stages of the infection, the level was 0·0022, with a subsequent drop of 0·0002-0·0004 at the terminal stages.
It is concluded that increase in kininases activity in malarial infection in relation to the normal values obtained for circulating kinins suggested a rapid turn-over of the latter. In this case, the balance of kininases: kinins in P. knowlesi infection thus serve as a regulatory mechanism in minimising the damage caused on the capillary endothelium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOK L., GRANT P. T., KERMACK W. O. Proteolytic enzymes of the erythrocytic forms of roden and simian species of malarial plasmodia. Exp Parasitol. 1961 Nov;11:372–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(61)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tella A., Maegraith B. G. Studies on bradykinin and bradykininogen in malaria. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1966 Sep;60(3):304–317. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1966.11686421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


