Abstract
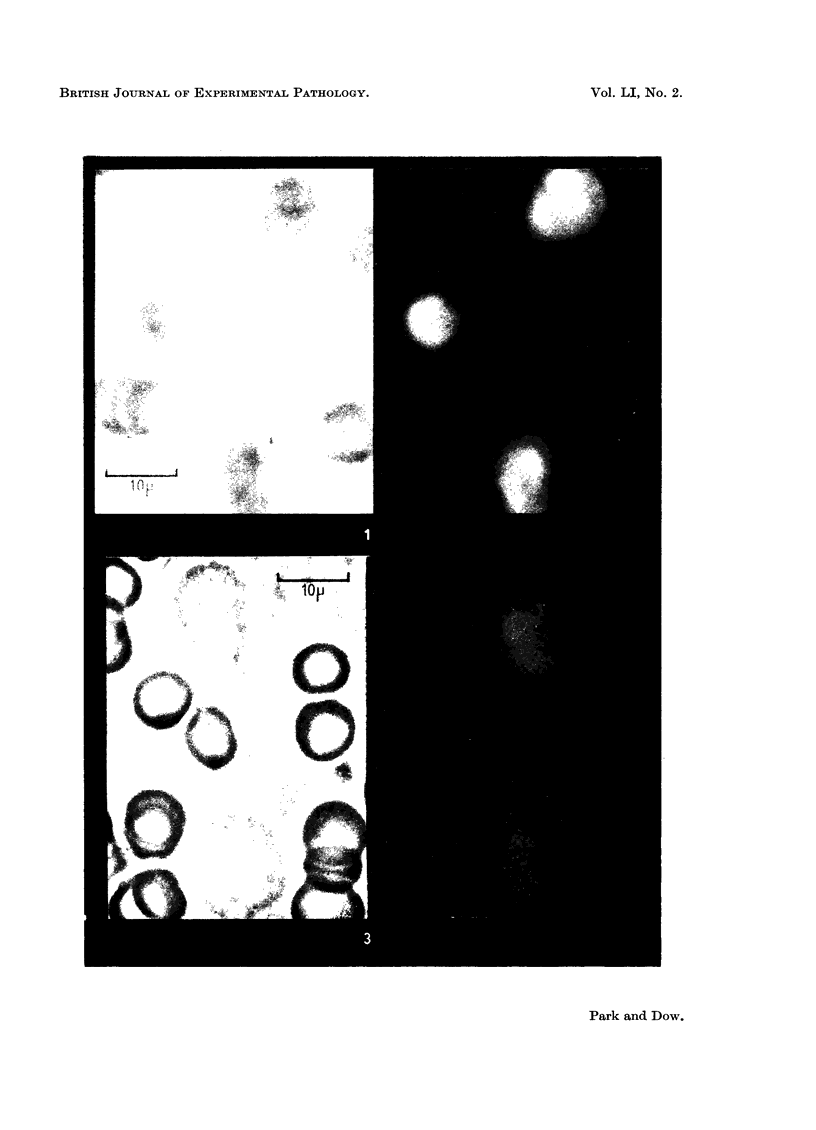
The uptake of tetracycline by human blood cells has been investigated by means of fluorescence microscopy. The intense yellow fluorescence characteristic of the drug was found only in the leucocytes; the erythrocytes appeared uniformly dark. In both lymphocytes and polymorphonuclear leucocytes the nucleus exhibited more intense fluorescence than the cytoplasm. The importance of these results is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DU BUY H. G., SHOWACRE J. L. Selective localization of tetracycline in mitochondria of living cells. Science. 1961 Jan 20;133(3447):196–197. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3447.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler J., Mach P. A study of in vitro incorporation of tetracycline antibiotics into avian and mammalian blood cells. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1965;84(4):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHN K. W. Mediation of divalent metal ions in the binding of tetracycline to macromolecules. Nature. 1961 Sep 16;191:1156–1158. doi: 10.1038/1911156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]