Abstract
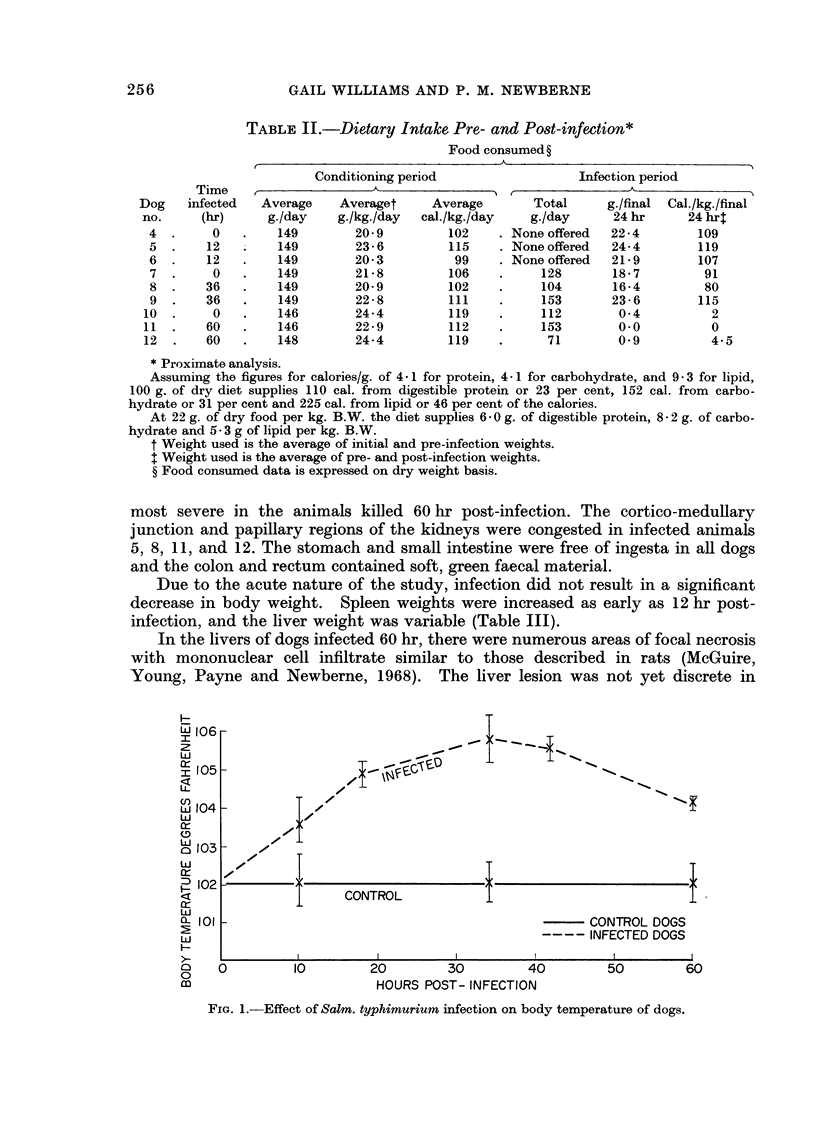
Five month old male beagles injected i.p. with a washed 18-hr culture of Salmonella typhimurium 1 × 109 organisms/kg. responded clinically with a marked depression, anorexia, and a febrile response 12 hr following infection. Animals allowed to live beyond 36 hr showed a decrease in febrile response. Although they still refused food 36 hr following infection, they appeared more alert by 60 hr post-infection. Changes at necropsy were minimal and histologic findings consistent with Salmonella infection were found in both liver and spleen. In animals infected 60 hr liver microabscesses and circumscribed foci of reticuloendothelial cell hyperplasia in the spleen indicated that the animals were responding favourably by mounting a defence against the infection.
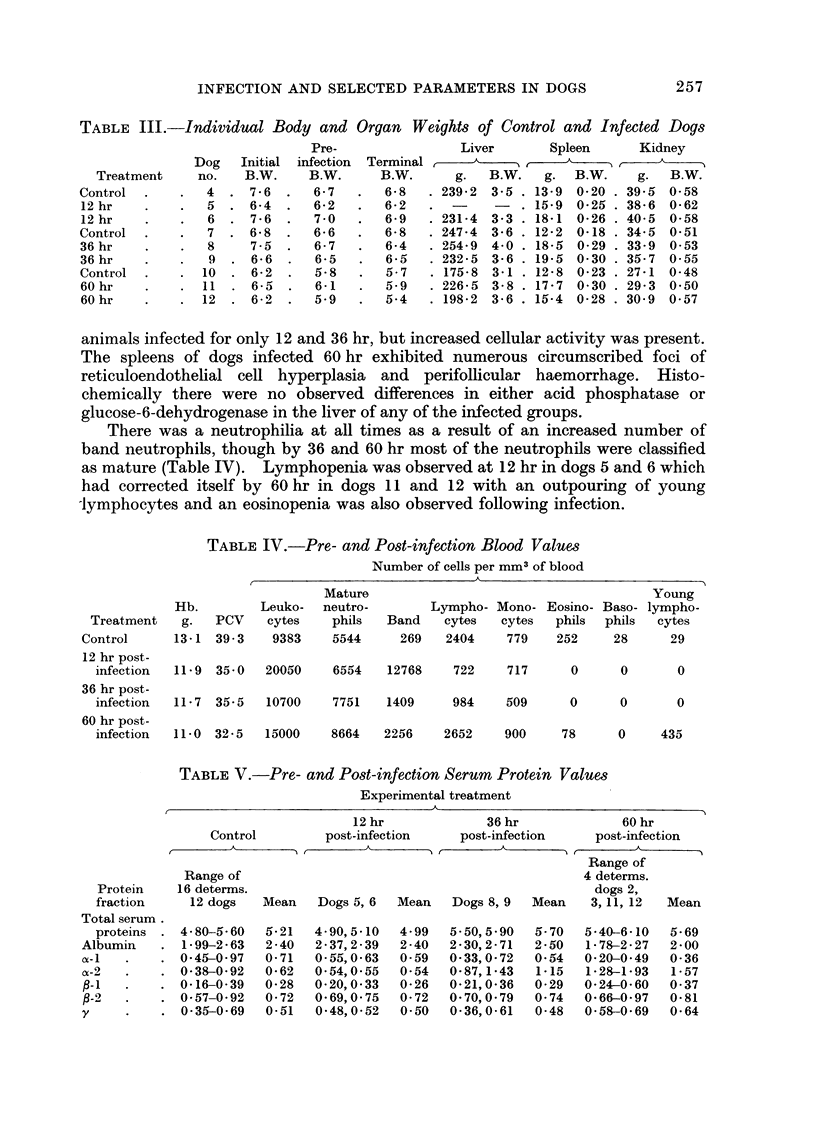
As a result of infection there was an outpouring of band neutrophils resulting in an increase in the absolute numbers of circulating white blood cells. Associated with the neutrophilia was an early lymphopenia and eosinopenia.
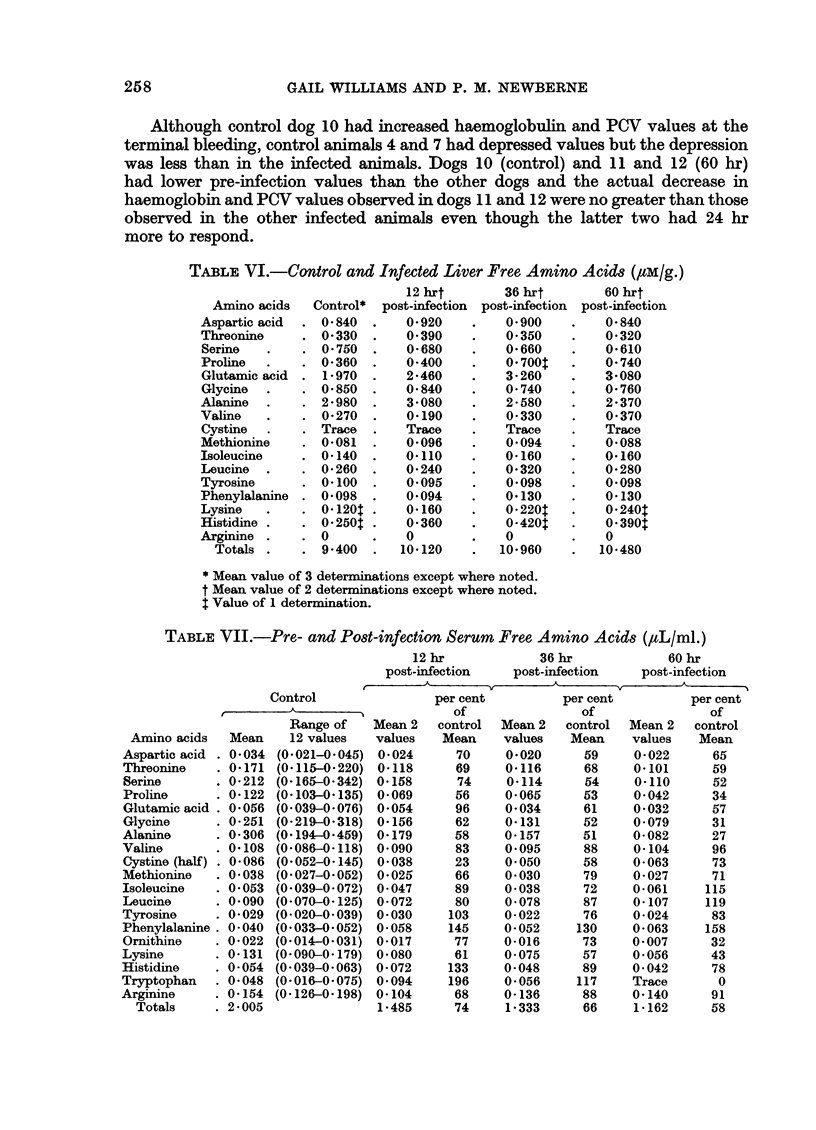
The total free amino acids were depressed in serum and increased in the liver at all time periods observed, but the degree of change as well as the specific amino acids affected varied; however, alterations in concentration of amino acids in serum of animals infected with Salmonella were similar to those observed in dogs infected with the virus of canine distemper. In both viral and bacterial infected dogs serum phenylalanine was increased and tyrosine remained the same or decreased, resulting in a significant alteration in the phenylalanine/tyrosine (P/T) ratio.
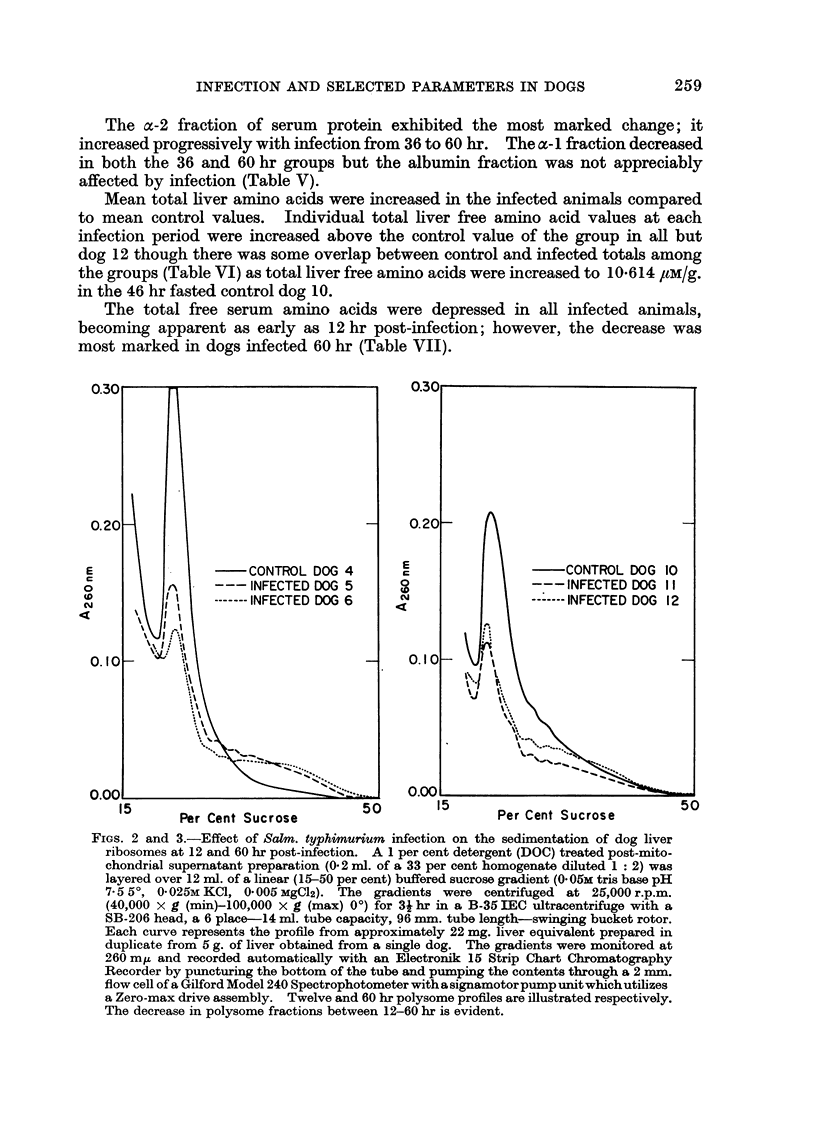
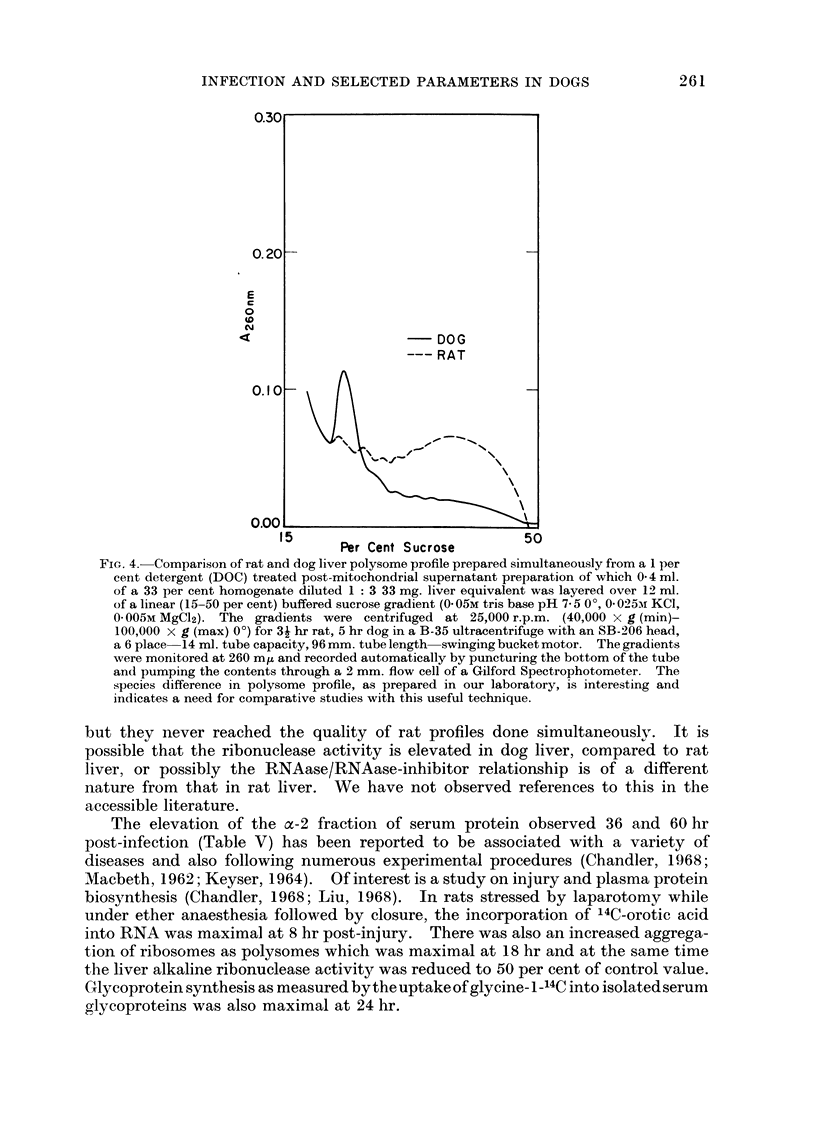
As with distemper infected dogs, an increase of the alpha-2 fraction of serum proteins was detected at 36 hr following infection. There was a decrease in the monosome peak and a corresponding increase in the polysome fraction of the liver post-mitochondrial supernatant preparation associated with infection. The significance of this change in the liver polysome profile following infection is not yet understood.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Relation of ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor to the isolation of polysomes from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1283–1288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler A. M., Neuhaus O. W. Injury and plasma protein biosynthesis. I. Hepatic nucleic acid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):186–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Polysome profiles obtained from mammalian tissues by an improved procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 30;138(3):616–618. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90562-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYSER J. W. CLINICAL USES OF SEROMUCOID ESTIMATION. Postgrad Med J. 1964 Apr;40:184–189. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.40.462.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Neuhaus O. W. Injury and plasma protein biosynthesis. II. Hepatic microsomal activity and polysomal organization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90503-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitruka B. M., Alexander M., Carmichael L. E. Gas chromatography for detection of viral infections. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):309–311. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. Role of amino acid supply in regulating ribosome function. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1231–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberne P. M. Overnutrition on resistance of dogs to distemper virus. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1701–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberne P. M., Young V. R., Gravlee J. F. Effects of caloric intake and infection on some aspects of protein metabolism in dogs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Apr;50(2):172–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. R., Chen S. C., Newberne P. M. Effect of infection on skeletal muscle ribosomes in rats fed adequate or low protein. J Nutr. 1968 Mar;94(3):361–368. doi: 10.1093/jn/94.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


