Abstract
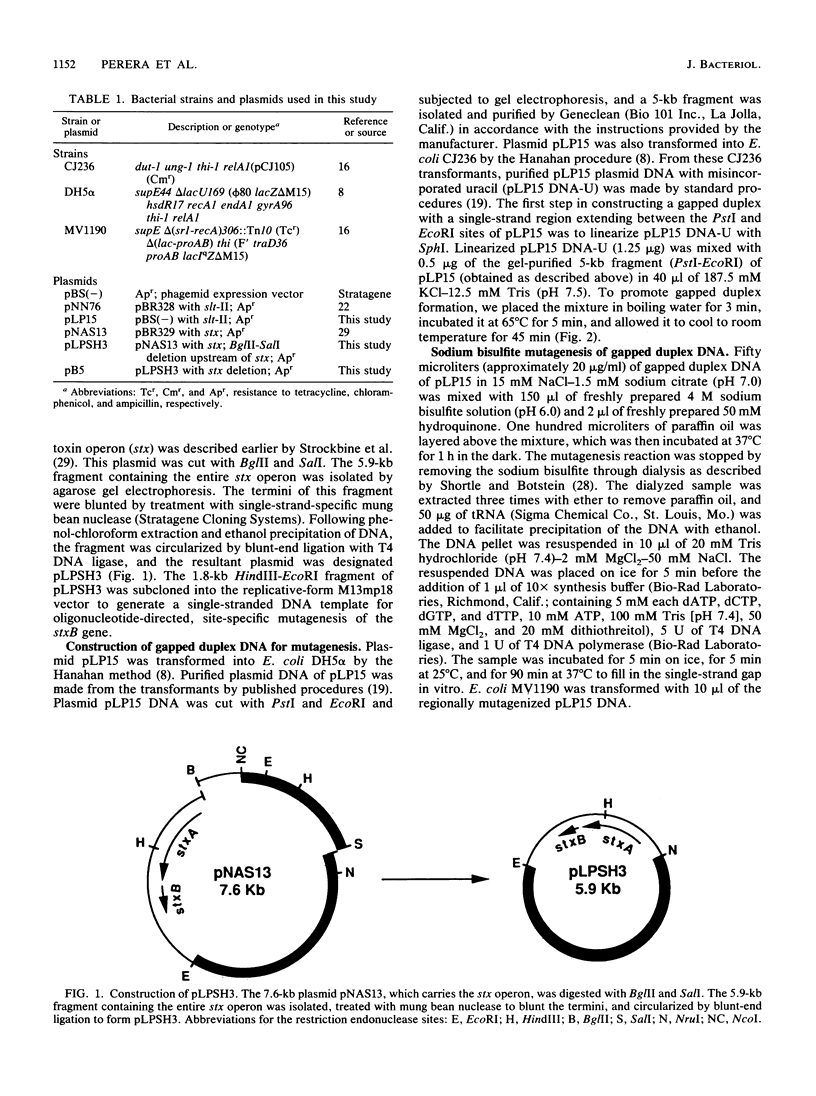
Shiga toxin of Shigella dysenteriae type I and Shiga-like toxins I and II (SLT-I and SLT-II, respectively) of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli are functionally similar protein cytotoxins. These toxin molecules have a bipartite molecular structure which consists of an enzymatically active A subunit that inhibits protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells and an oligomeric B subunit that binds to globotriaosylceramide glycolipid receptors on eukaryotic cells. Regionally directed chemical mutagenesis of the B subunit of SLT-II was used to identify amino acids in the B subunit that are critical for SLT-II holotoxin cytotoxic activity. Three noncytotoxic mutants were isolated, and their mutations were mapped. The substitutions of arginine with cysteine at codon 32, alanine with threonine at codon 42, and glycine with aspartic acid at codon 59 in the 70-amino-acid mature SLT-II B polypeptide resulted in the complete abolition of cytotoxicity. The analogous arginine, alanine, and glycine residues were conserved at codons 33, 43, and 60 in the 69-amino-acid mature B polypeptide of Shiga toxin. Comparable mutations induced in the B-subunit gene of Shiga toxin by oligonucleotide-directed, site-specific mutagenesis resulted in drastically decreased cytotoxicity (10(3)- to 10(6)-fold) as compared with that of wild-type Shiga toxin. The mutant SLT-II and Shiga toxin B subunits were characterized for stability, receptor binding, immunoreactivity, and ability to be assembled into holotoxin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson D. W., Keusch G. T., Lightowlers M., Donohue-Rolfe A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxin II using P1 glycoprotein from hydatid cysts. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):134–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie J. U., Sauer R. T. Identification of C-terminal extensions that protect proteins from intracellular proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7596–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M., Keusch G. T. Isolation and characterization of functional Shiga toxin subunits and renatured holotoxin. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1231–1236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes F. P., Barrett T. J., Green J. H., Aloisio C. H., Spika J. S., Strockbine N. A., Wachsmuth I. K. Affinity purification and characterization of Shiga-like toxin II and production of toxin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1926–1933. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1926-1933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Gentry M. K., Brown J. E. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Shiga toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):430–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.430-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harari I., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G., Arnon R. Synthetic peptides of Shiga toxin B subunit induce antibodies which neutralize its biological activity. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1618–1624. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1618-1624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. M., Perera P. Y., Vogel S. N. Examination of macrophage cell surface antigen regulation by rIFN-gamma and IFN-alpha/beta utilizing digital imaging by a novel laser detection system. Anchored cell analysis station (ACAS) 470. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Sep 29;123(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Clausen H., Nudelman E., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. P., Wadolkowski E. A., Weinstein D. L., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Functional analysis of the Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxin type II variant binding subunits by using site-directed mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):653–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.653-658.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M., Donohue-Rolfe A. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea: evidence for an N-linked glycoprotein shigella toxin receptor and receptor modulation by beta-galactosidase. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):238–248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. R. Tinkering with enzymes: what are we learning? Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1252–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.3296192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Brown J. E., Strömberg N., Westling-Ryd M., Schultz J. E., Karlsson K. A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Richardson S., Petric M., Brunton J. L., De Grandis S., Karmali M. Glycolipid binding of purified and recombinant Escherichia coli produced verotoxin in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8834–8839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobassaleh M., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M., Grand R. J., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea: evidence for a developmentally regulated glycolipid receptor for shigella toxin involved in the fluid secretory response of rabbit small intestine. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1023–1031. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Strockbine N. A., Neill R. J. Cloning of genes for production of Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin type II. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2675–2680. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2675-2680.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Marques L. R., O'Brien A. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Shiga-like toxin II of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and use of the monoclonal antibodies in a colony enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2127-2131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Ward S., O'Brien A. D., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Comparison of the glycolipid receptor specificities of Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variants. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):611–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.611-618.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Wharton R. P., Seltzer S., Kacinski B. M., Clarke N. D., Rupp W. D. Identification of the uvrA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Botstein D. Directed mutagenesis with sodium bisulfite. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:457–468. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Jackson M. P., Sung L. M., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of the genes for Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1116–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1116-1122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surewicz W. K., Surewicz K., Mantsch H. H., Auclair F. Interaction of Shigella toxin with globotriaosyl ceramide receptor-containing membranes: a fluorescence study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):126–132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Perera L. P., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. In vivo formation of hybrid toxins comprising Shiga toxin and the Shiga-like toxins and role of the B subunit in localization and cytotoxic activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3743–3750. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3743-3750.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Samuel J. E., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4223–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4223-4230.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]