Abstract
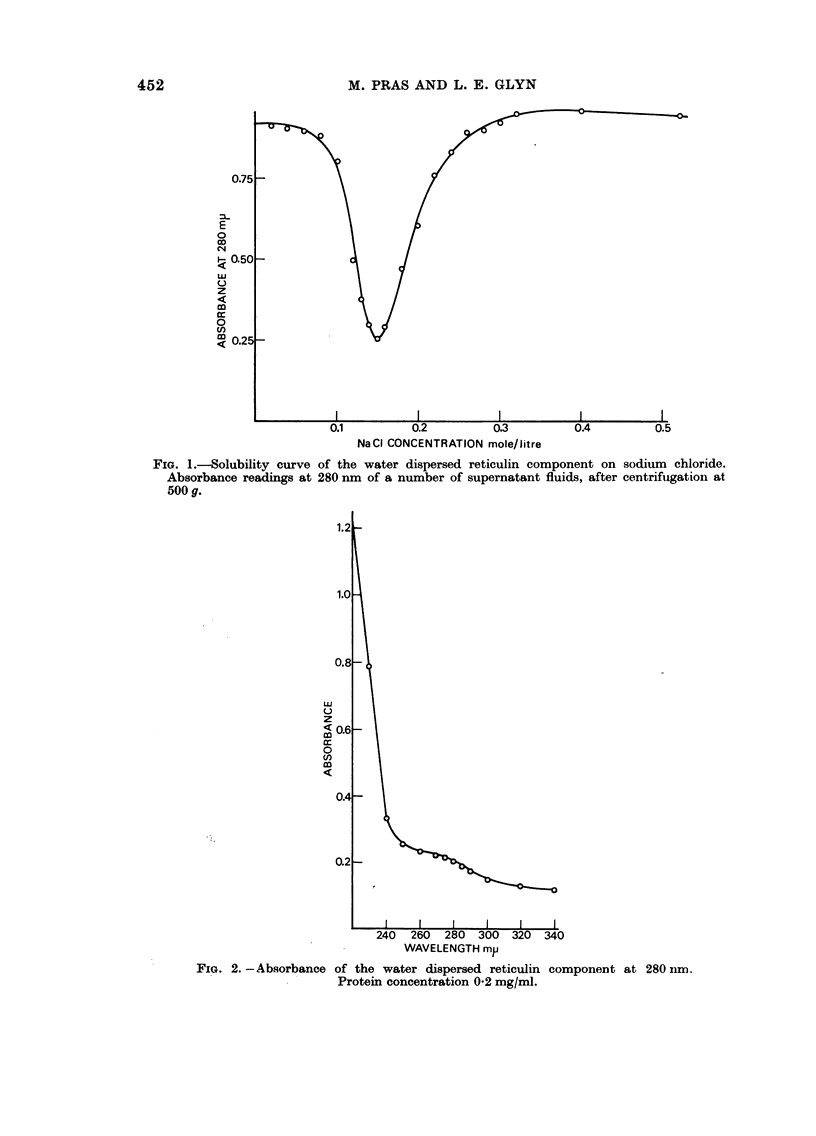
A reticulin component has been extracted from the saline insoluble residue of pig renal cortex and liver by a distilled water dispersion method. The water dispersed component, that could be precipitated by addition of NaCl up to 0·15 mol/l, was proved to be a protein distinct from collagen in that it contained no hydroxyproline and 9% glycine. The carbohydrate content was 4%, consisting mainly of galactose and mannose. The protein showed an affinity for the silver impregnation method, as used for reticulin. Antibodies to it, raised in rabbits, showed typical anti-reticulin staining by immunofluorescent techniques. It is suggested therefore that this protein, having peculiar solubility characteristics, may be a significant, non-collagenous component of reticulin.
Full text
PDF



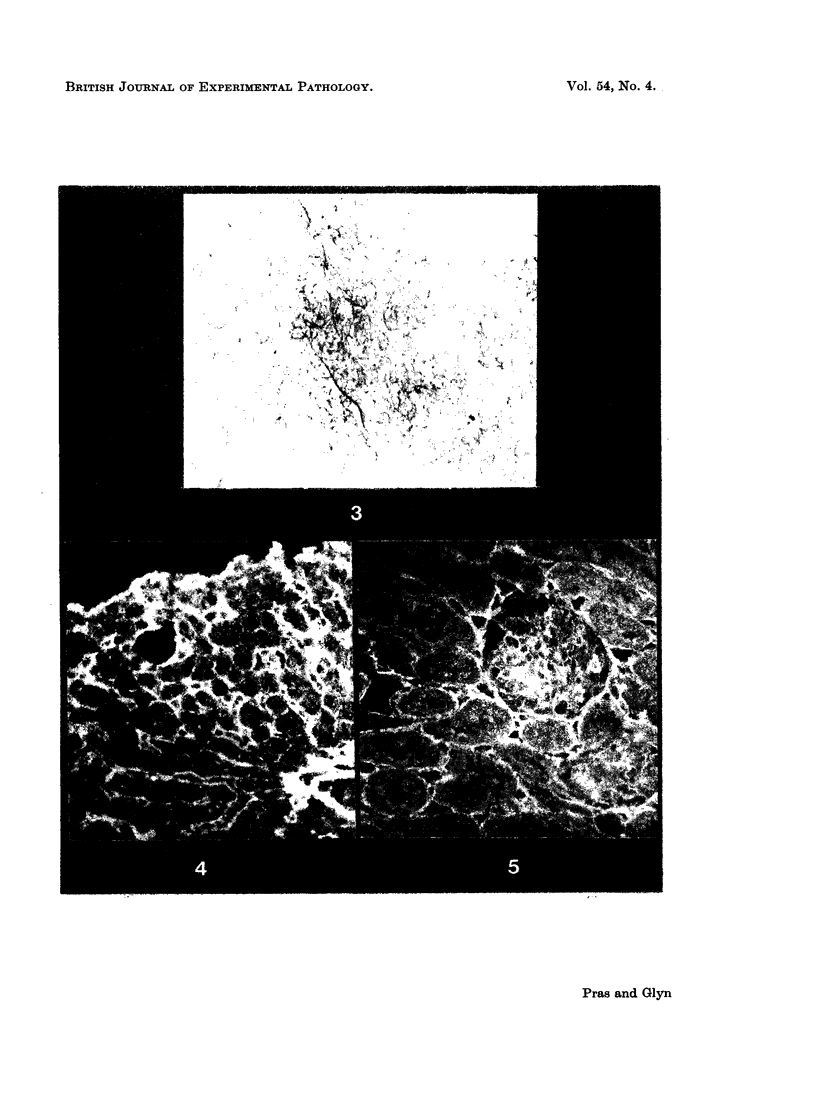


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FRANCOIS C., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 4. The determination of mannose in hen's-egg albumin by radioisotope dilution. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:335–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0830335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLEGG R. E., EIDINGER D., LEBLOND C. P. Presence of carbohydrates distinct from acid mucopolysaccharides in connective tissue. Science. 1954 Nov 19;120(3125):839–840. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3125.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLEGG R. E., EIDINGER D., LEBLOND C. P. Some carbohydrate components of reticular fibers. Science. 1953 Nov 20;118(3073):614–616. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3073.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallory F. B., Parker F. Reticulum. Am J Pathol. 1927 Sep;3(5):515–526.21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J., Frei J. V., Cohen J. J., Rose B., Richter M. Basement membrane specific antisera produced to solubilized tissue fractions. Immunology. 1966 Aug;11(2):155–162. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCHTLER H. ON THE ORIGINAL DEFINITION OF THE TERM "RETICULIN". J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Jul;12:552–552. doi: 10.1177/12.7.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCHTLER H. ON THE ORIGINAL DEFINITION OF THE TERM "RETICULIN". J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Jul;12:552–552. doi: 10.1177/12.7.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulitzeanu D., Slavin M., Karaman H., Goldman W. Antigenic components of rat connective tissue. II. Fluorescent antibody studies with antisera to connective tissue antigens. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Apr;48(2):159–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody studies with agents of varicella and herpes zoster propagated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):789–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDRUM G. M., KENT P. W., EASTOE J. E. The constitution of human renal reticulin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Feb;36(1):49–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEMM E. W., WILLIS A. J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):508–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0570508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]