Abstract
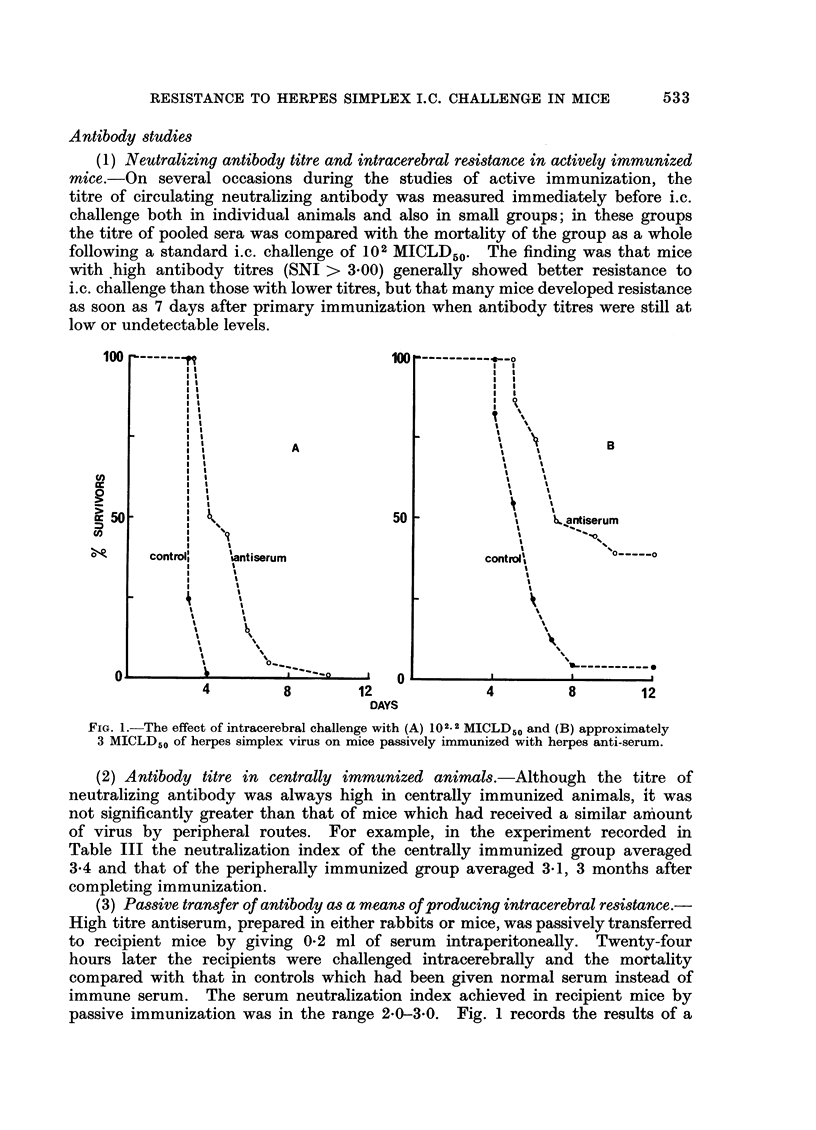
The resistance of mice to intracerebral inoculation of herpes simplex virus has been studied. Normal mice showed no natural resistance and died from acute necrotizing encephalitis. Active immunization by peripheral inoculation of virus produced some degree of protection against intracerebral inoculation. Evidence from histological studies and from passive antibody transfer experiments suggested that this intracerebral protection was mediated by cells rather than by circulating neutralizing antibody. All peripherally immunized mice developed inflammatory lesions in the brain following intracerebral challenge, but in many mice these lesions gave rise to no clinical signs of encephalitis. Following survival from intracerebral challenge all mice became solidly resistant to further intracerebral inoculation and no lesions developed in the brain following such inoculations, even when high doses of virus were given. The possibility of central immunity is discussed.
Full text
PDF



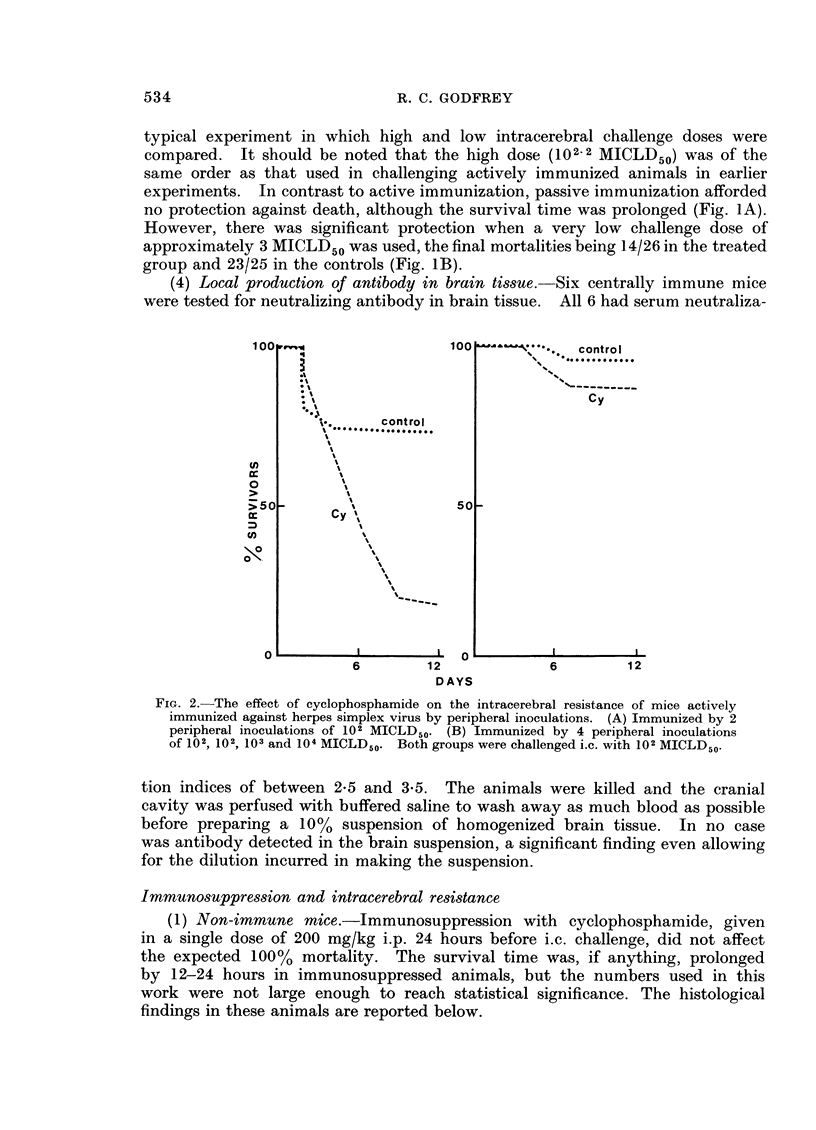





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPLEYARD G., WESTWOOD J. C. THE GROWTH OF RABBITPOX VIRUS IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:391–401. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADISH C. J., FARLEY J. O., FERRIER H. E. Studies on the nature of the nature of the neutralization reaction and the competition for neutralizing antibody between components of the virus system of foot-and-mouth disease. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:378–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEEVER F. S., DAIKOS G. Studies of the protective effect of gamma globulin against herpes simplex infections in mice. J Immunol. 1950 Jul;65(1):135–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. The plaque assay of animal viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1961;8:319–378. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Mechanism of immunologically specific killing of tumour cells by macrophages. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):168–170. doi: 10.1038/236168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRISCH A. W., DAVIES G. H. INHIBITION OF HEMAGGLUTININ SYNTHESIS BY CYTOXAN. Cancer Res. 1965 Jun;25:745–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Zisman B., Allison A. C. Macrophages and age-dependent resistance to Herpes simplex virus in mice. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1160–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T. THE PATHOGENESIS OF HERPES VIRUS ENCEPHALITIS. II. A CELLULAR BASIS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANCE WITH AGE. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:359–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T. Inflammatory response to viral infection. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1971;49:305–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N., Cole G. A. Fatal Japanese encephalitis virus infection in immunosuppresed spider monkeys. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):161–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Tissue injury in lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection: virus-induced immunologically specific release of a cytotoxic factor from immune lymphoid cells. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. W., Doherty P. C., Dawson A. M. Louping-ill encephalomyelitis in the sheep. 3. Immunoglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Oct;81(4):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER C. E. Further studies on the effect of neutralizing antibody upon the course of herpes simplex infections in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1960 Apr;84:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik I., Carter G. B., Grant D. P. The persistence of louping ill virus in immunosuppressed guinea-pigs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Aug;52(4):395–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik I., Keppie J., Grant D. P. A method of testing the efficacy of louping-ill vaccines in sheep. Vet Rec. 1970 May 30;86(22):659–660. doi: 10.1136/vr.86.22.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik I., Peacock S., Grant D. P., Batter-Hatton D. The pathogenesis of western equine encephalitis virus (W.E.E.) in adult hamsters with special reference to the long and short term effects on the C.N.S. of the attenuated clone 15 variant. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):59–77. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik I., Smith C. E., Grant D. P., Peacock S. The effect of immunosuppression on viral encephalitis, with special reference to cyclophosphamide. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Aug;51(4):434–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]