Abstract
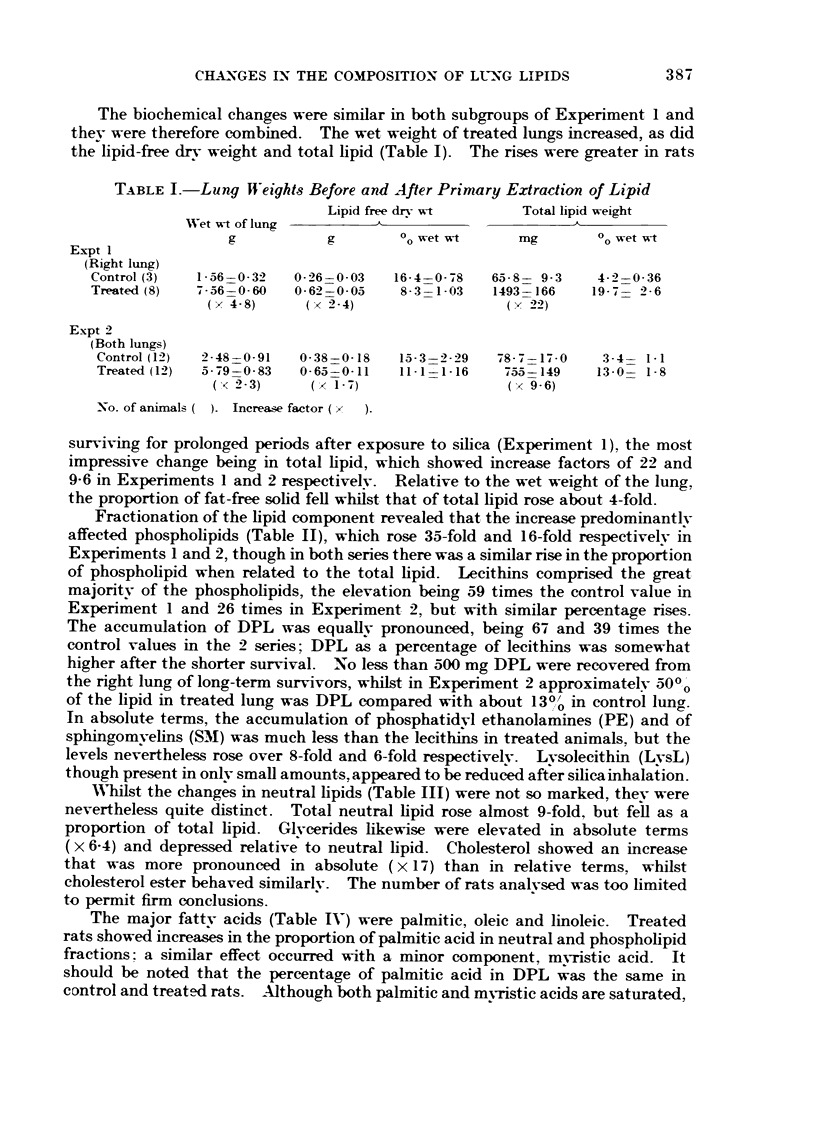
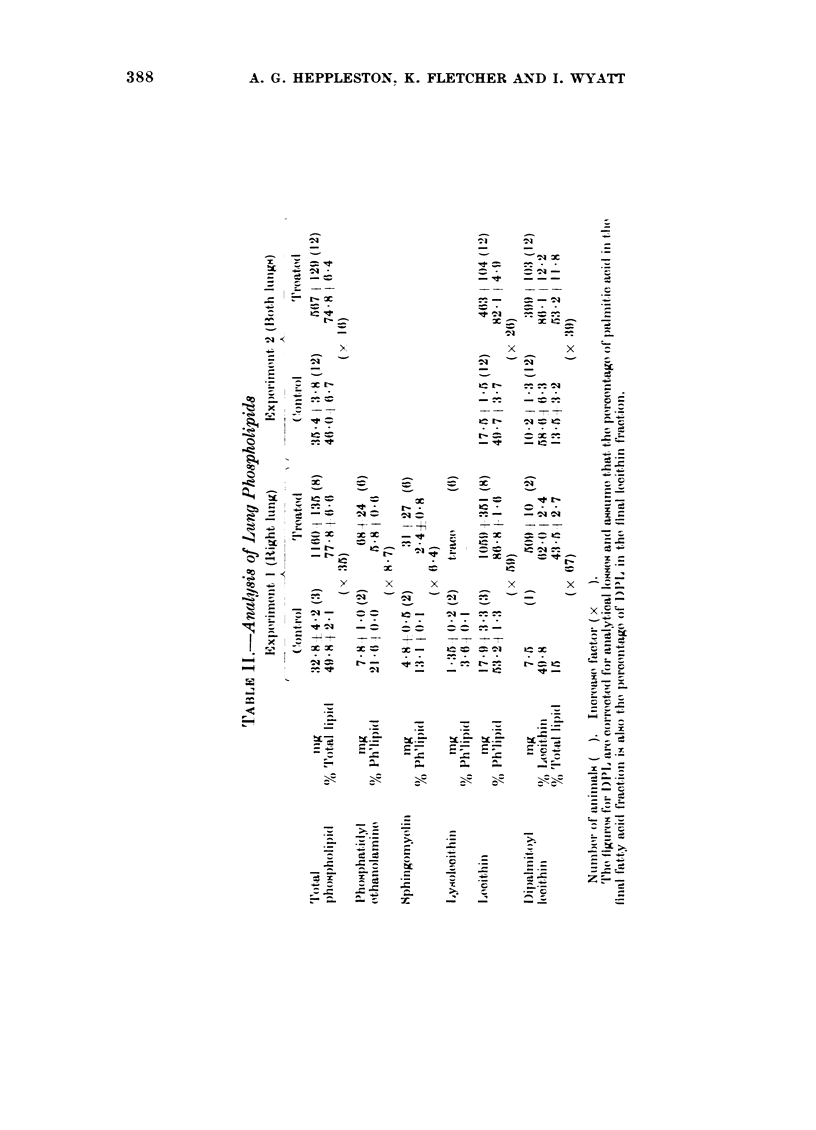
Specific pathogen-free rats, exposed to the inhalation of quartz for varying periods and surviving thereafter for several months, consistently developed alveolar lipo-proteinosis, but not typical silicosis as might have been expected. The overall lipid content of the lungs was much increased, notably the phospholipids and especially dipalmitoyl lecithin (DPL), whilst the lipid-free dry weight rose relatively little.
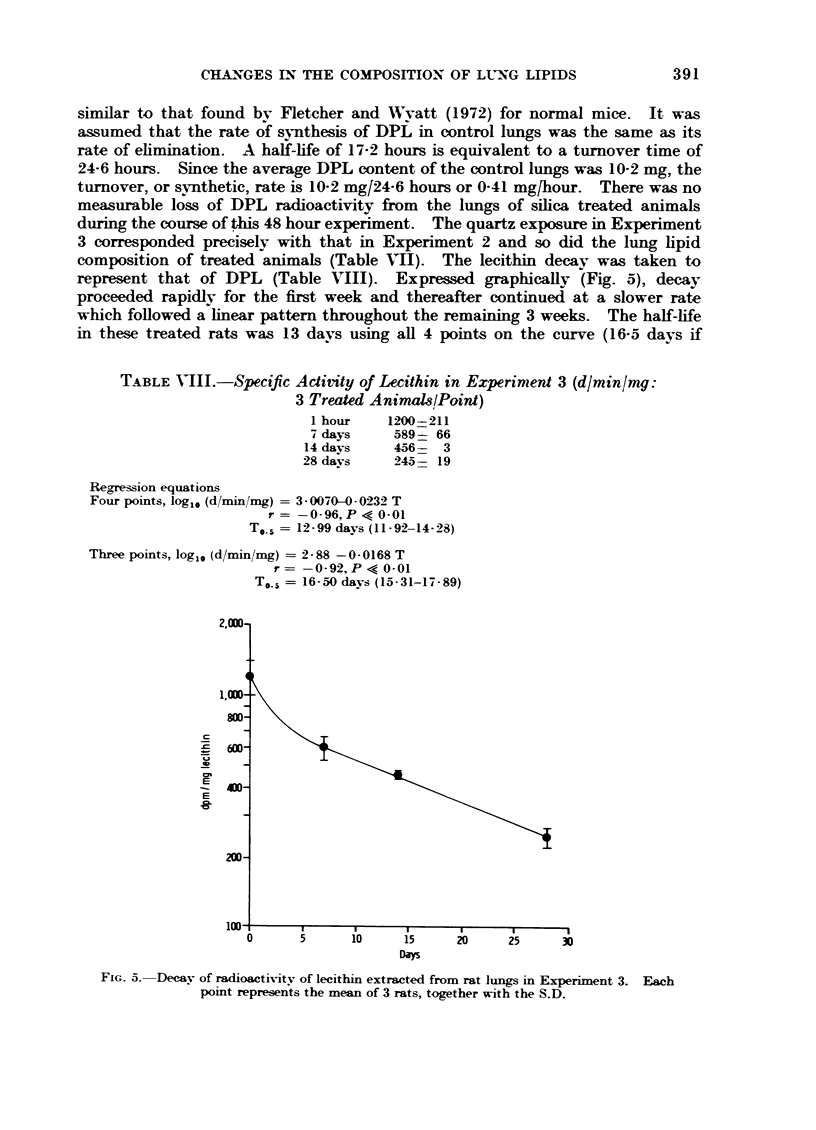
In other rats, receiving brief but intenser exposures and surviving subsequently for a limited period so that the disease would be in an active phase, the rate of incorporation of labelled palmitic acid was measured and its rate of disappearance followed for 4 weeks. As compared with controls, the rate of synthesis of DPL was tripled and its rate of loss doubled. Accumulation of DPL in the lungs may thus be explained as an imbalance between formation and removal, though both are augmented. Our evidence conflicts with the view that the basic defect in alveolar lipo-proteinosis is a diminished capacity for elimination of alveolar secretion.
The absolute plasma fatty acid content and the proportions of individual acids were unaffected in treated animals. It may therefore be concluded that the lipid accumulation derives from lung tissue rather than directly from the plasma, and type II epithelial cells appear to be a major source.
Full text
PDF


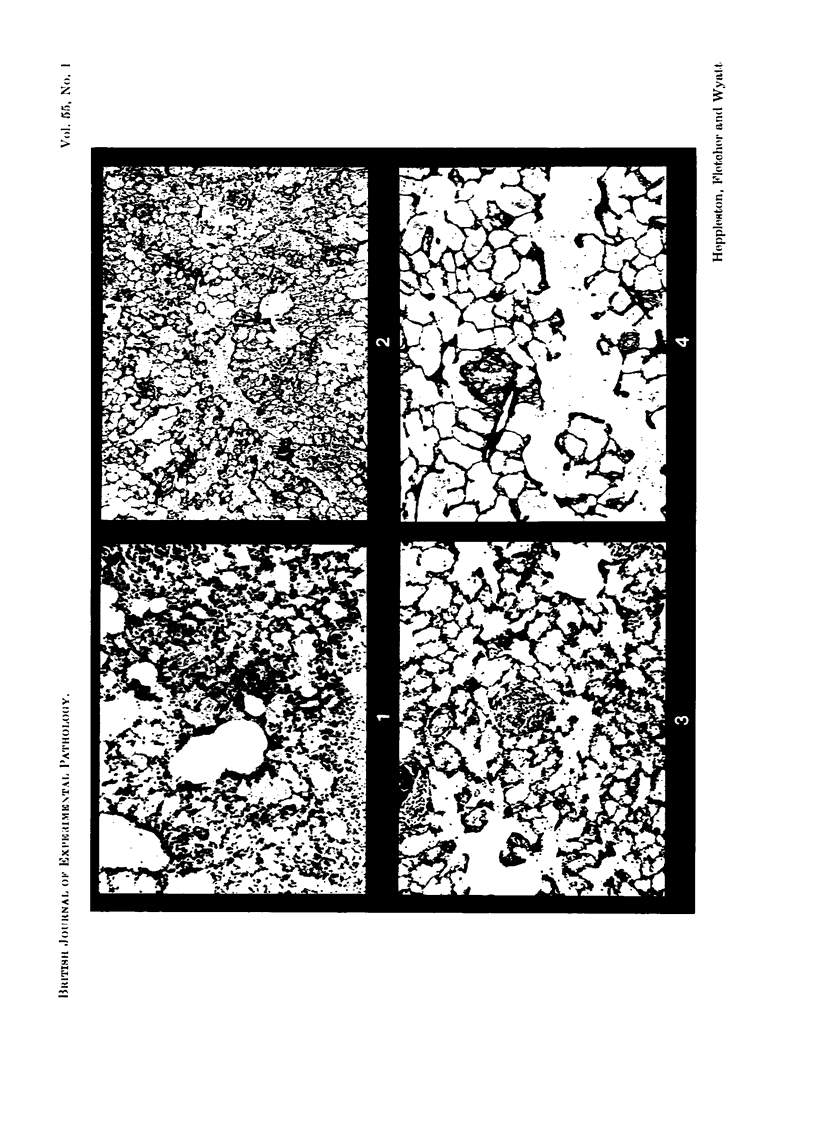






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The intracellular site of surfactant synthesis. Autoradiographic studies on murine and avian lung explants. Exp Mol Pathol. 1973 Feb;18(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(73)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. A. Comparative lipid chemistry of lungs. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Mar;127(3):387–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher K., Wyatt I. The action of paraquat on the incorporation of palmitic acid into dipalmitoyl lecithin in mouse lungs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Apr;53(2):225–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher K., Wyatt I. The composition of lung lipids after poisoning with paraquat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Dec;51(6):604–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. The disposal of dust in the lungs of silicotic rats. Am J Pathol. 1962 May;40:493–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan W. R., Jr, Margraf J. H., Said S. I. Pulmonary lipid composition of species with and without surfactant. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):855–861. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G. Atypical reaction to inhaled silica. Nature. 1967 Jan 14;213(5072):199–199. doi: 10.1038/213199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Fletcher K., Wyatt I. Abnormalities of lung lipids following inhalation of quartz. Experientia. 1972 Aug 15;28(8):938–939. doi: 10.1007/BF01924959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Wright N. A., Stewart J. A. Experimental alveolar lipo-proteinosis following the inhalation of silica. J Pathol. 1970 Aug;101(4):293–307. doi: 10.1002/path.1711010402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Young A. E. Alveolar lipo-proteinosis: an ultrastructural comparison of the experimental and human forms. J Pathol. 1972 Jun;107(2):107–117. doi: 10.1002/path.1711070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Young A. E. Uptake of inert particulate matter by alveolar cells: an ultrastructural study. J Pathol. 1973 Nov;111(3):159–164. doi: 10.1002/path.1711110303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. O., Lamberty J., Pizzolato P., Coover J. The ultrastructure of acute silicosis. Arch Pathol. 1973 Aug;96(2):104–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaw J. L., Gupta G. S., Zaidi S. H. Lung lipids and pulmonary silicosis in rats. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1971;27(4):324–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00539363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., Györkey F., Levine B. E., Ramirez-Rivera J. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A study using enzyme histochemistry, electron microscopy, and surface tension measurement. Lab Invest. 1966 Feb;15(2):492–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez J., Schwartz B., Dowell A. R., Lee S. D. Biochemical composition of human pulmonary washings. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Mar;127(3):395–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wichert P. Bezichungen zwischen pathologischen Veränderungen und Phospholipidgehalt der menschlichen Lunge. Pneumonologie. 1971;144(3):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF02088695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]