Abstract
DNA encoding the catabolism of the s-triazines ammelide and cyanuric acid was cloned from Pseudomonas sp. strain NRRLB-12228 and Klebsiella pneumoniae 99 with, as a probe, a 4.6-kb PstI fragment from a third strain, Pseudomonas sp. strain NRRLB-12227, which also encodes these activities. In strains NRRLB-12228 and 99 the ammelide aminohydrolase (trzC) and cyanuric acid amidohydrolase (trzD) genes are located on identical 4.6-kb PstI fragments which are part of a 12.4-kb DNA segment present in both strains. Strain NRRLB-12227 also carries this 12.4-kb DNA segment, except that a DNA segment of 0.8 to 1.85 kb encoding a third enzyme, ammeline aminohydrolase (trzB), has been inserted next to the ammelide aminohydrolase gene with the accompanying deletion of 1.1 to 2.15 kb of DNA. In addition, the s-triazine catabolic genes are flanked in strain NRRLB-12227 by apparently identical 2.2-kb segments that are not present in the other two strains and that seem to cause rearrangements in adjacent DNA.
Full text
PDF
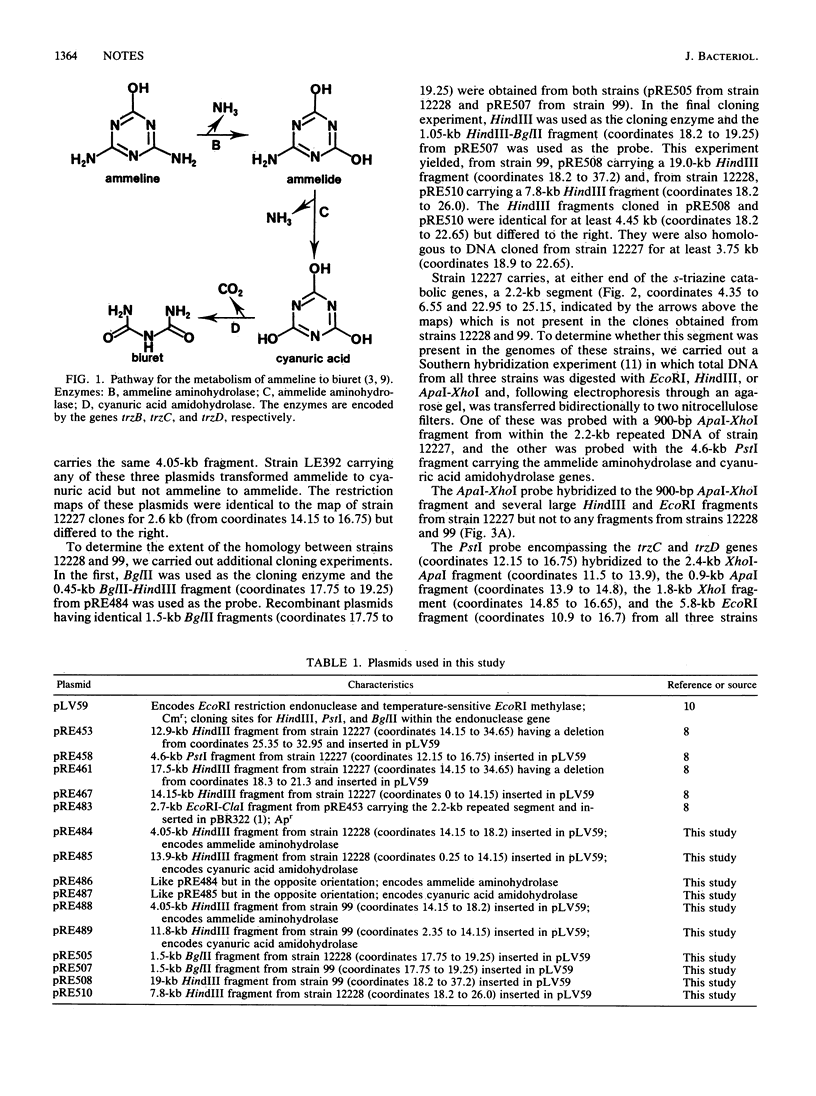

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Beilstein P., Grossenbacher H., Hütter R. Ring cleavage and degradative pathway of cyanuric acid in bacteria. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):25–30. doi: 10.1042/bj2310025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. W., Karns J. S. Cloning and analysis of s-triazine catabolic genes from Pseudomonas sp. strain NRRLB-12227. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1215–1222. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1215-1222.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jutzi K., Cook A. M., Hütter R. The degradative pathway of the s-triazine melamine. The steps to ring cleavage. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):679–684. doi: 10.1042/bj2080679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. D., Humphreys G. O. Expression of the Eco RI restriction-modification system and the construction of positive-selection cloning vectors. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]