Abstract
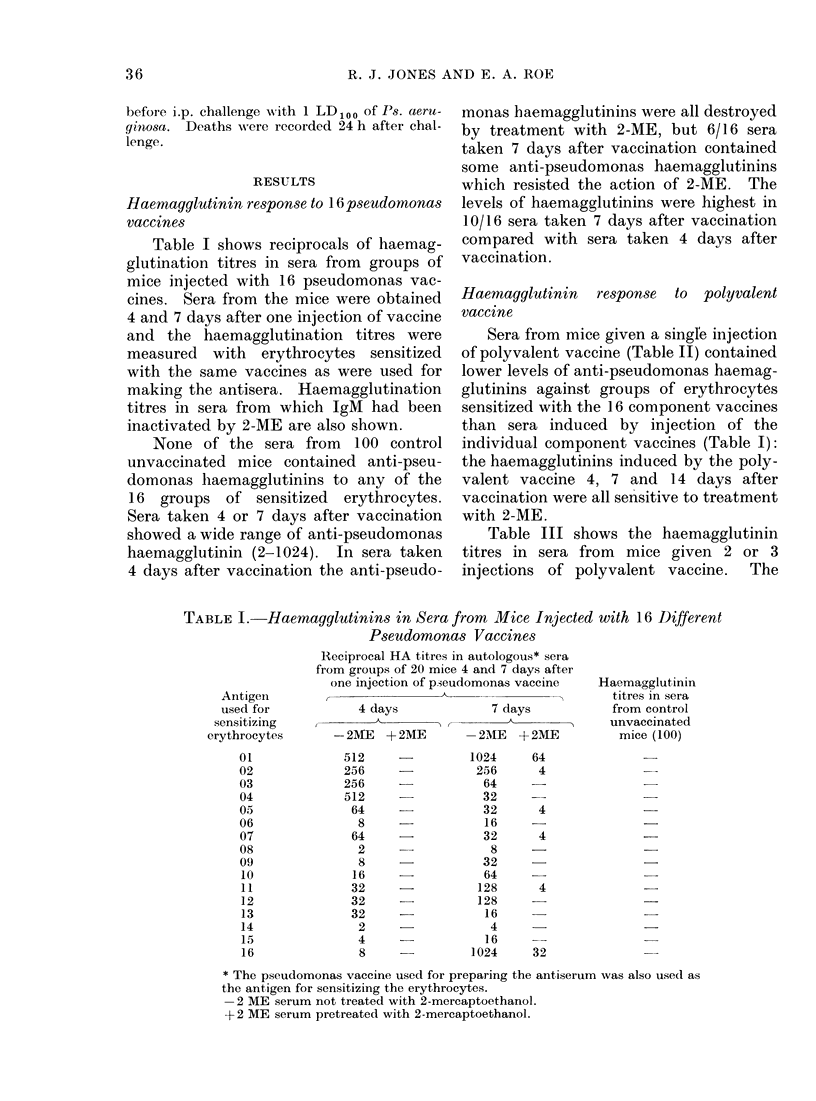
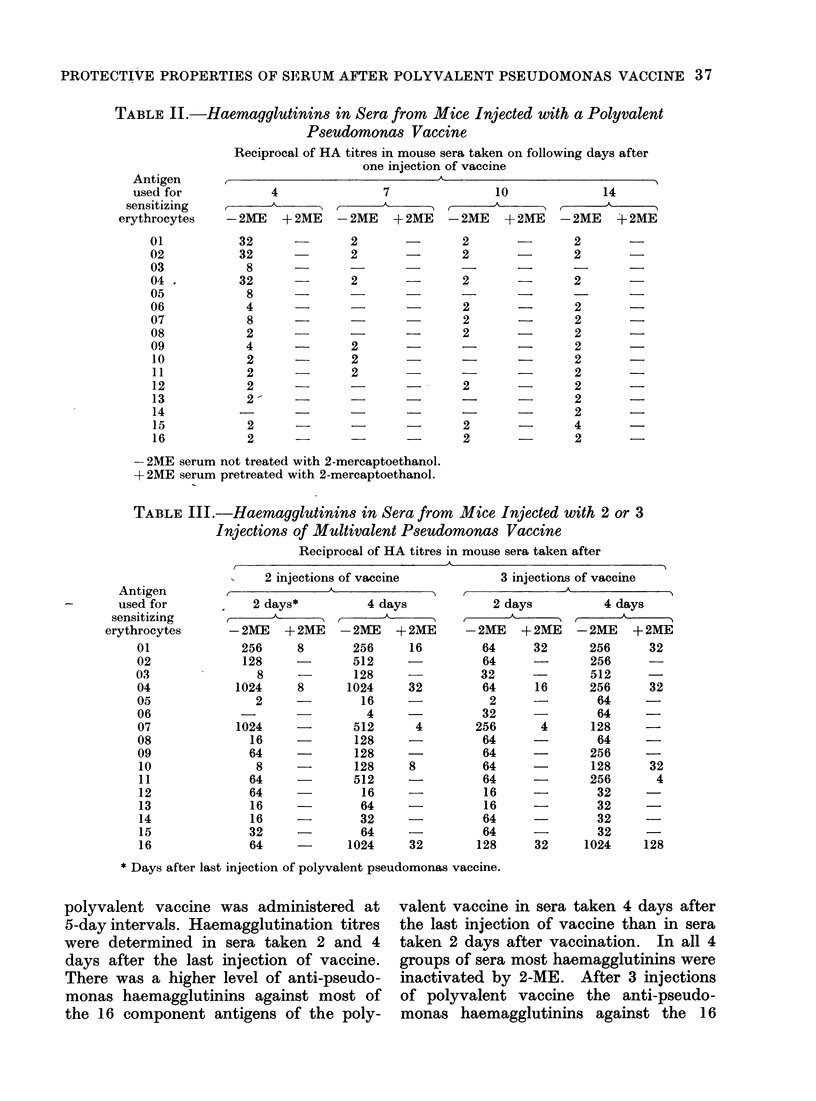
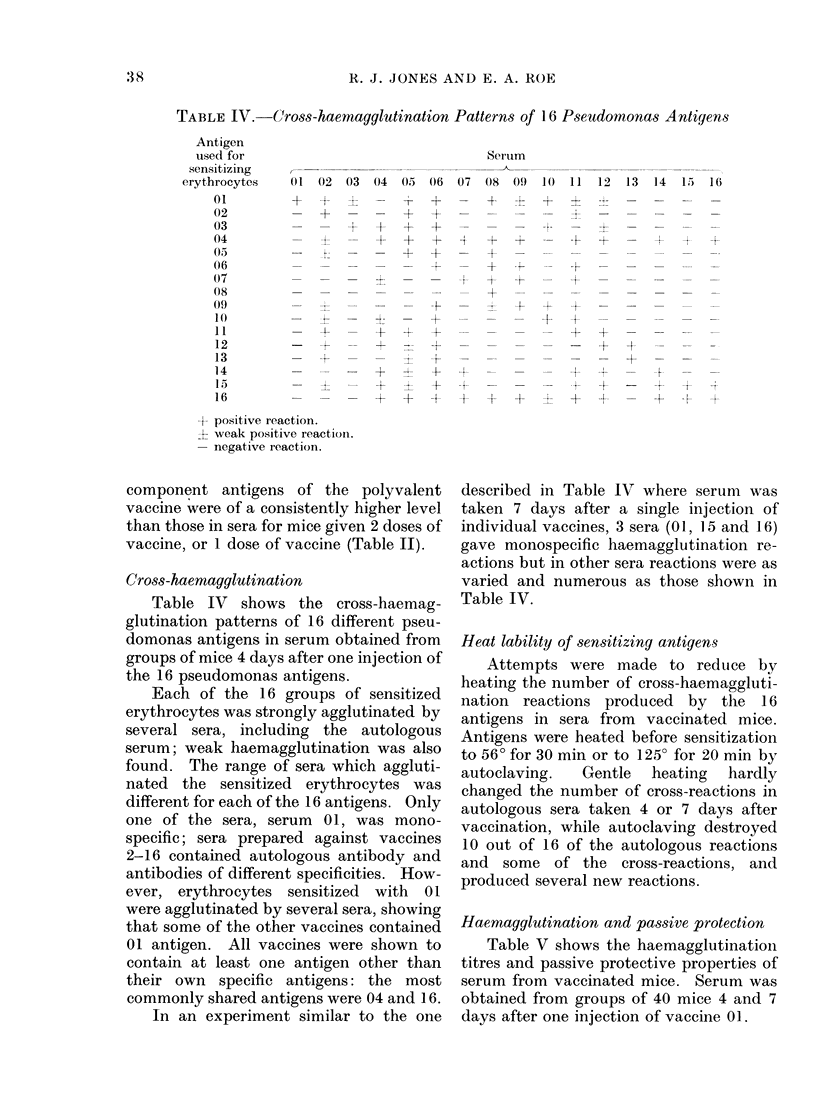
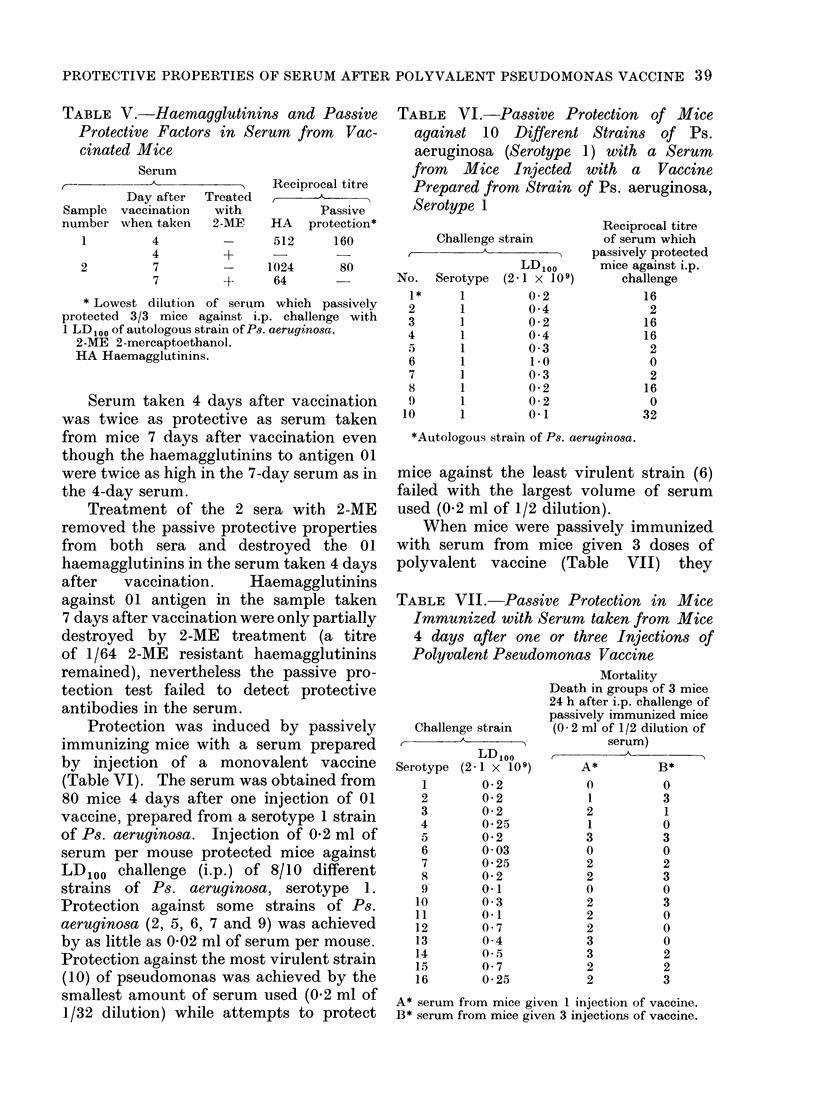
Mice given single injections of a polyvalent pseudomonas vaccine produced anti-pseudomonas haemagglutinins against the 16 component immunogens of the multivalent vaccine. Mice passively immunized with sera from vaccinated mice were protected against lethal challenge by 8/10 strains of Ps. aeruginosa of homologous serotype. Protection by the serum was inversely proportional to the virulence of the challenge strains. Anti-pseudomonas haemagglutinins were always present in sera which passively protected mice against pseudomonas infection. Low levels of anti-pseudomonas haemagglutinins were present in some sera which failed to passively immunize mice against pseudomonas infection. Anti-pseudomonas haemagglutinins and antibodies involved in passive protection were mainly in the IgM fractions of mouse serum. Control human sera contained anti-pseudomonas haemagglutinins against most serotypes of Ps. aeruginosa. Sera from patients with burns contained high levels of anti-pseudomonas haemagglutinins against some but not all serotypes of Ps. aeruginosa. Sera from both controls and patients with burns passively protected mice against pseudomonas infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Fisher M. W. Immunological determinants of pseudomonas infections of man accompanying severe burn injury. J Trauma. 1970 Jul;10(7):565–574. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197007000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. W., Fisher M. W., MacMillan B. G., Altemeier W. A. Prevention of invasive pseudomonas infection in burns with a new vaccine. Arch Surg. 1969 Aug;99(2):249–256. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340140121018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: immune status in patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):628–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.628-635.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAINES S., LANDY M. Prevalence of antibody to Pseudomonas in normal human sera. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jun;69(6):628–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.6.628-633.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBNER K. F., GENGOZIAN N. DEPRESSION OF THE PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE BY DL-PENICILLAMINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Feb;118:561–565. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. J., Syeklocha D. Comparative studies on the protective potential of antisera directed against four antigenic preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Oct;18(10):1607–1611. doi: 10.1139/m72-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J. Early protection by vaccines in burns. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Feb;52(1):100–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Hall M., Ricketts C. R. Passive protective properties of serum fractions from mice inoculated with an anti-pseudomonas vaccine. Immunology. 1972 Dec;23(6):889–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEFALIDES N. A., ARANA J. A., BAZAN A., VELARDE N., ROSENTHAL S. M. EVALUATION OF ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS AND GAMMA-GLOBULIN, PLASMA, ALBUMIN AND SALINE-SOLUTION THERAPY IN SEVERE BURNS. BACTERIOLOGIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC STUDIES. Ann Surg. 1964 Apr;159:496–506. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196404000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Yu B. H., Armstrong D. Agar-Gel Precipitating Antibody in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):495–503. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.495-503.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


