Abstract
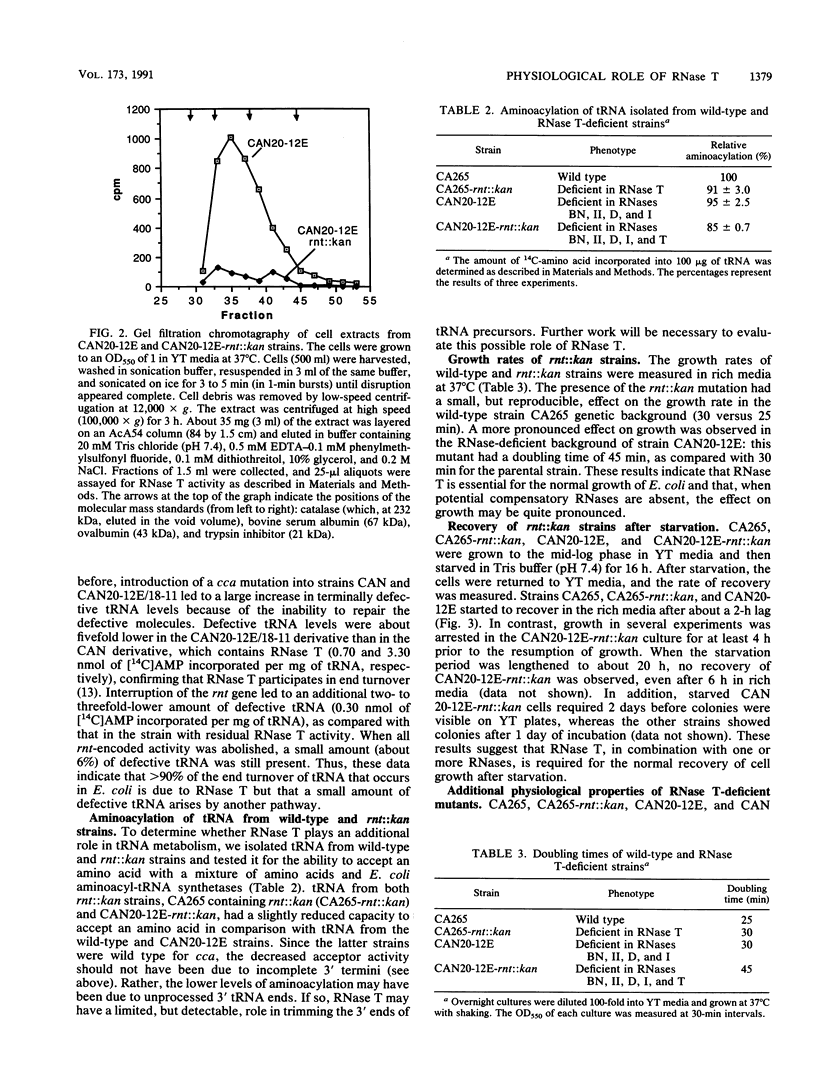
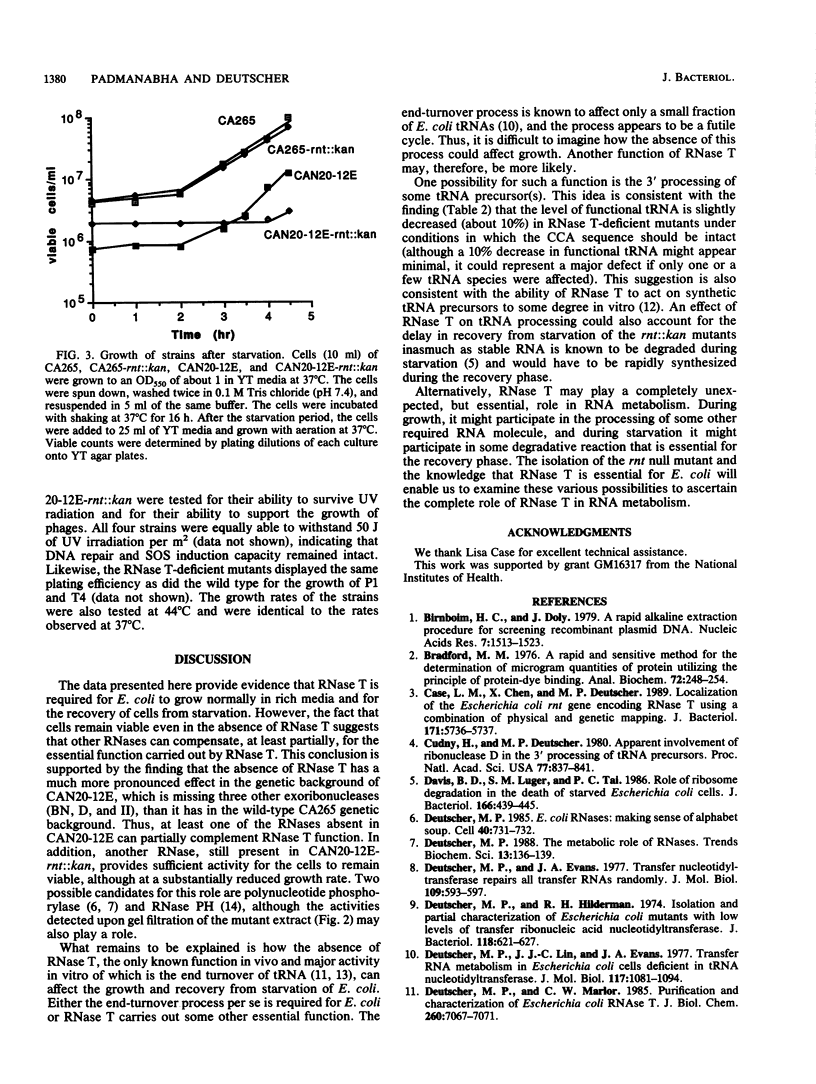
To determine the essentiality and role of RNase T in RNA metabolism, we constructed an Escherichia coli chromosomal rnt::kan mutation by using gene replacement with a disrupted, plasmid-borne copy of the rnt gene. Cell extracts of a strain with mutations in RNases BN, D, II, and I and an interuppted rnt gene were devoid of RNase T activity, although they retained a low level (less than 10%) of exonucleolytic activity on tRNA-C-C-[14C]A due to two other unidentified RNases. A mutant lacking tRNA nucleotidyltransferase in addition to the aforementioned RNases accumulated only about 5% as much defective tRNA as did RNase T-positive cells, indicating that this RNase is responsible for essentially all tRNA end turnover in E. coli. tRNA from rnt::kan strains displayed a slightly reduced capacity to be aminoacylated, raising the possibility that RNase T may also participate in tRNA processing. Strains devoid of RNase T displayed slower growth rates than did the wild type, and this phenotype was accentuated by the absence of the other exoribonucleases. A strain lacking RNase T and other RNases displayed a normal response to UV irradiation and to the growth of bacteriophages but was severely affected in its ability to recover from a starvation regimen. The data demonstrate that the absence of RNase T affects the normal functioning of E. coli, but it can be compensated for to some degree by the presence of other RNases. Possible roles of RNase T in RNA metabolism are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case L. M., Chen X. N., Deutscher M. P. Localization of the Escherichia coli rnt gene encoding RNase T by using a combination of physical and genetic mapping. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5736–5737. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5736-5737.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudny H., Deutscher M. P. Apparent involvement of ribonuclease D in the 3' processing of tRNA precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Luger S. M., Tai P. C. Role of ribosome degradation in the death of starved Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.439-445.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. E. coli RNases: making sense of alphabet soup. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):731–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Evans J. A. Transfer RNA nucleotidyltransferase repairs all transfer RNAs randomly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 5;109(4):593–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Hilderman R. H. Isolation and partial characterization of Escherichia coli mutants with low levels of transfer ribonucleic acid nucleotidyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):621–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.621-627.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Lin J. J., Evans J. A. Transfer RNA metabolism in Escherichia coli cells deficient in tRNA nucleotidyltransferase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 25;117(4):1081–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Marlor C. W. Purification and characterization of Escherichia coli RNase T. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7067–7071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Marlor C. W., Zaniewski R. RNase T is responsible for the end-turnover of tRNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6427–6430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Marlor C. W., Zaniewski R. Ribonuclease T: new exoribonuclease possibly involved in end-turnover of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4290–4293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Marshall G. T., Cudny H. RNase PH: an Escherichia coli phosphate-dependent nuclease distinct from polynucleotide phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4710–4714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. The metabolic role of RNases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Apr;13(4):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. M., Aldea M., Washburn B. K., Babitzke P., Kushner S. R. New method for generating deletions and gene replacements in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4617–4622. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4617-4622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Deutscher M. P. tRNA nucleotidyltransferase is not essential for Escherichia coli viability. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2473–2477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




