Abstract
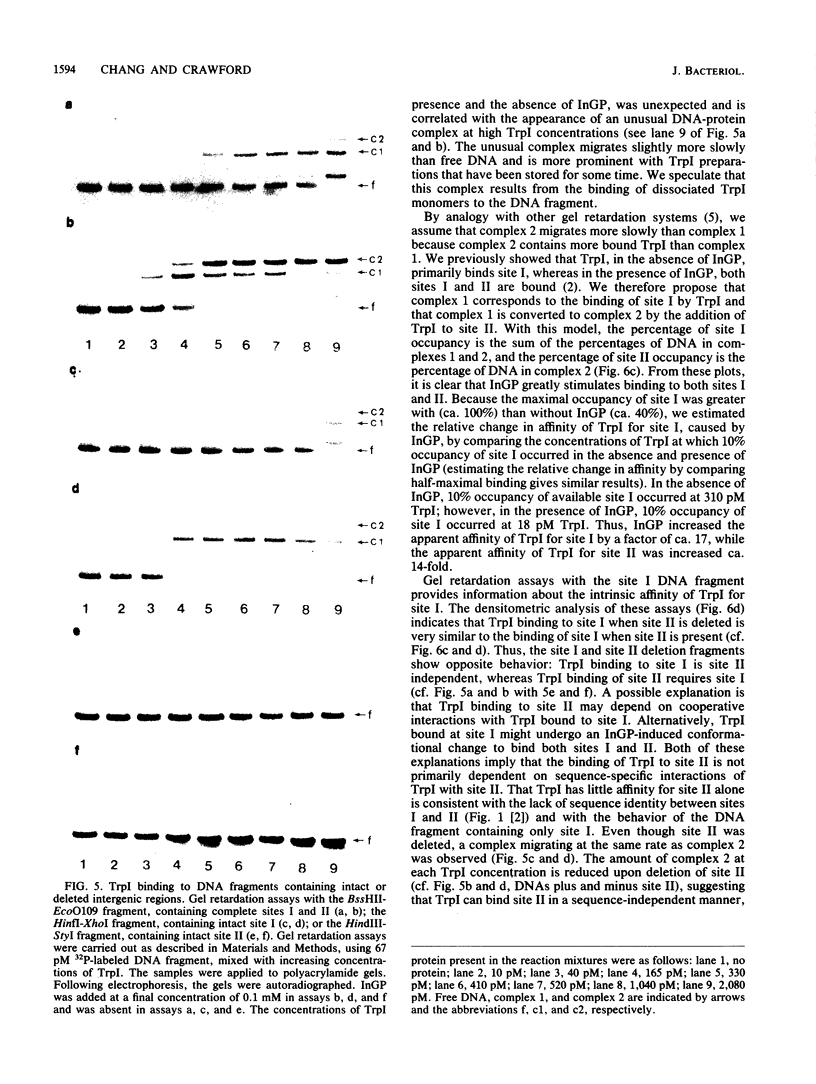
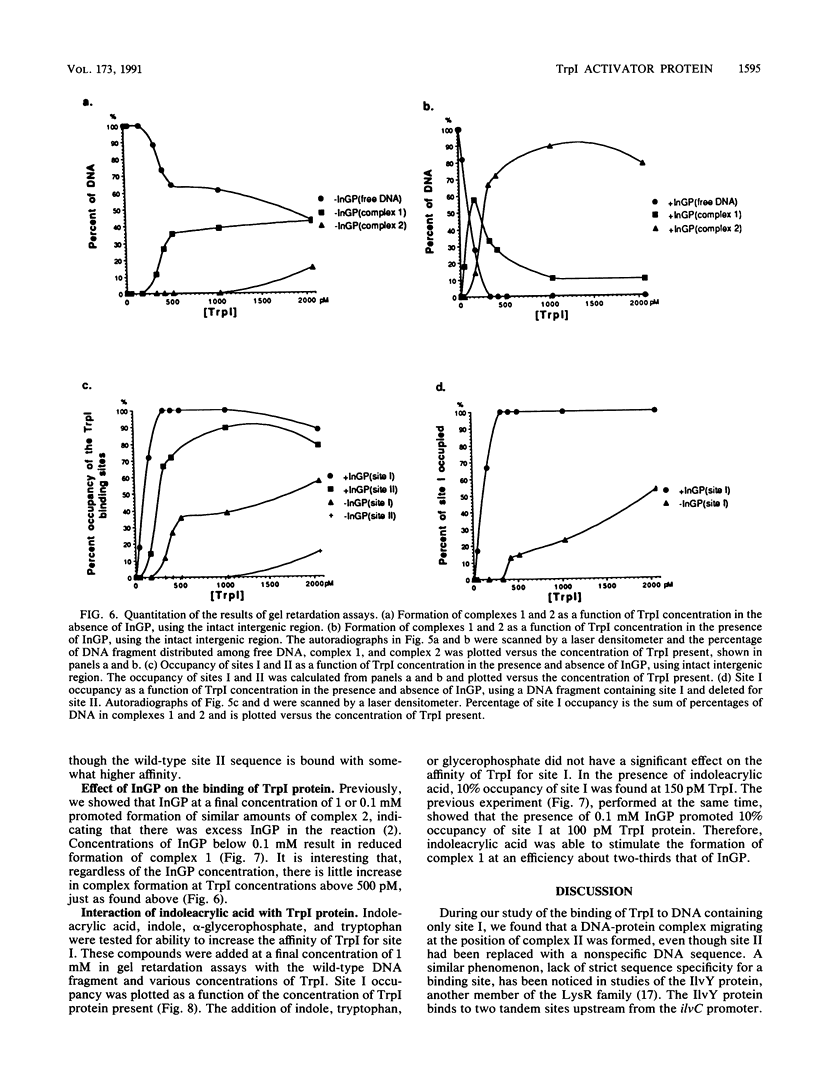
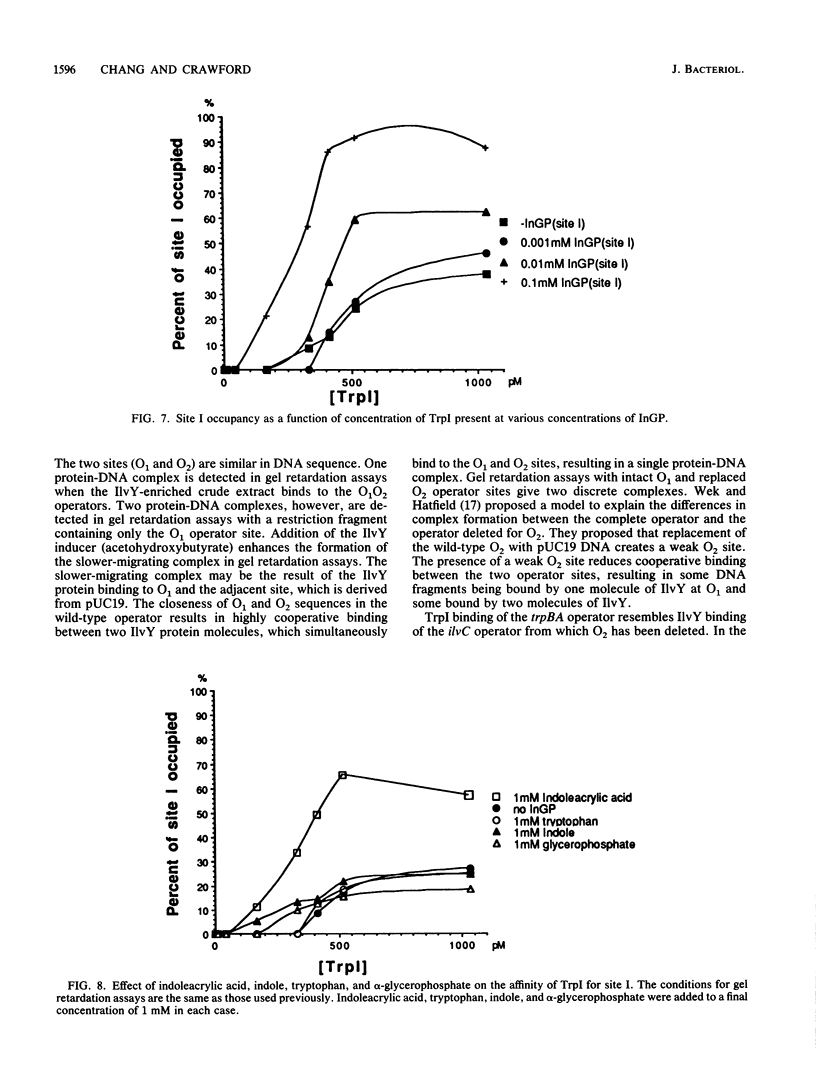
Expression of the trpBA gene pair of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is regulated by the endogenous level of indoleglycerol phosphate (InGP) and the trpI gene product. The TrpI protein binds to the -77 to -32 region of the trpBA promoter. This region is divisible into two sites: site I, which is protected by TrpI in the presence and absence of InGP; and site II, which is protected by TrpI only in the presence of InGP. Recently, the trpI gene was subcloned into an expression vector and the protein was overproduced in Escherichia coli. The TrpI protein was purified to 80 to 95% purity. The molecular weight of native TrpI protein is estimated to be 129,000 by gel exclusion chromatography, and therefore it is likely a tetramer composed of 31,000-dalton monomers. Gel retardation assays with the purified TrpI protein demonstrated that InGP increases the affinity of TrpI for sites I and II approximately 17- and 14-fold, respectively. Binding of TrpI to site I is site II independent. However, the protein has low intrinsic affinity for site II and its binding to site II is site I dependent. Therefore, binding of TrpI to site II probably requires its interaction with a second TrpI molecule at site I.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calhoun D. H., Pierson D. L., Jensen R. A. The regulation of tryptophan biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Mar 1;121(2):117–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00277526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. The roles of indoleglycerol phosphate and the TrpI protein in the expression of trpBA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):979–988. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Hadero A., Crawford I. P. Sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa trpI activator gene and relatedness of trpI to other procaryotic regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):172–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.172-183.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Gunsalus I. C. Inducibility of tryptophan synthetase in Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):717–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manch J. N., Crawford I. P. Genetic evidence for a positive-acting regulatory factor mediating induction in the tryptophan pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manch J. N., Crawford I. P. Ordering tryptophan synthase genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by cloning in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):102–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.102-107.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matchett W. H. Inhibition of tryptophan synthetase by indoleacrylic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):146–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.146-154.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paluh J. L., Yanofsky C. High level production and rapid purification of the E. coli trp repressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7851–7860. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hatfield G. W. Transcriptional activation at adjacent operators in the divergent-overlapping ilvY and ilvC promoters of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):643–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]