Abstract
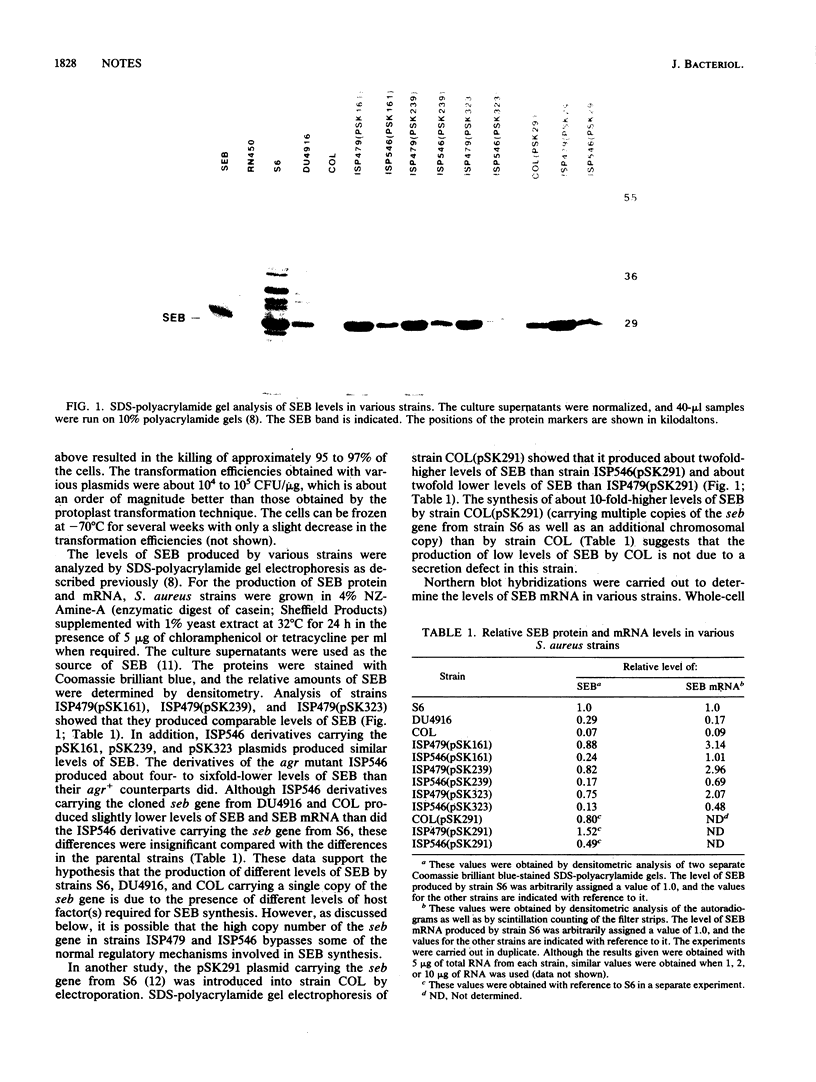
The levels of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) produced by various naturally occurring toxinogenic strains of Staphylococcus aureus are highly variable. The SEB gene (seb) from a high-producer strain, S6, has previously been cloned and characterized. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the upstream region of the seb gene from DU4916 and COL (medium- and low-level toxin-producer strains, respectively) showed that their sequence was identical to that of the seb gene from strain S6. Strains carrying the cloned seb gene from DU4916 and COL produced similar levels of SEB protein and mRNA to those produced by strains carrying the cloned seb gene from strain S6. An RNA encoded by the delta-lysin gene (hld) has been shown to regulate the genes for a number of extracellular proteins, including SEB. Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed that variable levels of hld RNA were present in various SEB-producer strains, with the order being S6 greater than DU4916 greater than COL. Our results suggest that differences in host factor(s), including the hld RNA, are responsible for the production of different amounts of SEB by many naturally occurring strains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Pattee P. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of alpha-toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):36–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.36-42.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Soltis M. T., Betley M. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type E staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2954–2960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2954-2960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill M. E., Khan S. A. Regulation of the enterotoxin B gene in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6276–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Bergdoll M. S. The primary structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. 3. The cyanogen bromide peptides of reduced and aminoethylated enterotoxin B, and the complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3518–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. B., Jr, Khan S. A. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B gene is associated with a discrete genetic element. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4033–4039. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4033-4039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Khan S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood R., Khan S. A. Role of upstream sequences in the expression of the staphylococcal enterotoxin B gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4652–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morfeldt E., Janzon L., Arvidson S., Löfdahl S. Cloning of a chromosomal locus (exp) which regulates the expression of several exoprotein genes in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Mar;211(3):435–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00425697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Brodsky R. Studies on plasmid replication. I. Plasmid incompatibility and establishment in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):285–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. H., Nowlan P., Weavers E. D., Foster T. Virulence of protein A-deficient and alpha-toxin-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus isolated by allele replacement. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3103–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3103-3110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. L., Novick R. P., Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Schlievert P. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of an accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4365–4372. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4365-4372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranelli D. M., Jones C. L., Johns M. B., Mussey G. J., Khan S. A. Molecular cloning of staphylococcal enterotoxin B gene in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5850–5854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Chromosomal locus for staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):273–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.273-278.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Genetics of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):902–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.902-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]