Abstract
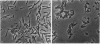
Mutation of the divIVB locus in Bacillus subtilis causes frequent misplacement of the division septum, resulting in circular minicells, short rods, and filaments of various sizes. The divIVB1 mutant allele maps to a region of the chromosome also known to encode sporulation (spo0B, spoIVF, spoIIB) and cell shape (rodB) determinants. This study reports the cloning and sequence analysis of 4.4 kb of the B. subtilis chromosome encompassing the divIVB locus. This region contains five open reading frames (ORFs) arranged in two functionally distinct gene clusters (mre and min) and transcribed colinearly with the direction of replication. Although sequence analysis reveals potential promoters preceding each gene cluster, studies with integrational plasmids suggest that all five ORFs are part of a single transcription unit. The first gene cluster contains three ORFs (mreBCD) homologous to the mre genes of Escherichia coli. We show that rodB1 is allelic to mreD and identify the rodB1 mutation. The second gene cluster contains two ORFs (minCD) homologous to minC and minD of E. coli but lacks a minE homolog. We show that divIVB1 is allelic to minD and identify two mutations in the divIVB1 allele. Insertional inactivation of either minC or minD or the presence of the divIVB region on plasmids produces a severe minicell phenotype in wild-type cells. Moreover, E. coli cells carrying the divIVB region on a low-copy-number plasmid produce minicells, suggesting that a product of this locus may retain some function across species boundaries.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Fisher W. D., Cohen A., Hardigree A. A. MINIATURE escherichia coli CELLS DEFICIENT IN DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):321–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall B., Lowe M., Lutkenhaus J. Cloning and characterization of Bacillus subtilis homologs of Escherichia coli cell division genes ftsZ and ftsA. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4855–4864. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4855-4864.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall B., Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ in Bacillus subtilis is required for vegetative septation and for asymmetric septation during sporulation. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):447–455. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi E. F., Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):161–164. doi: 10.1038/354161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corton J. C., Ward J. E., Jr, Lutkenhaus J. Analysis of cell division gene ftsZ (sulB) from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.1-7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Roels S., Losick R. Sporulation operon spoIVF and the characterization of mutations that uncouple mother-cell from forespore gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1237–1256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90931-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. R., Hoch J. A., Aronson A. I. Alteration of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase results in overproduction of the enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):981–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.981-987.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi M., Wachi M., Ishino F., Tomioka S., Ito M., Sakagami Y., Suzuki A., Matsuhashi M. Determinations of the DNA sequence of the mreB gene and of the gene products of the mre region that function in formation of the rod shape of Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4619–4624. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4619-4624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. J., Copeland J. C. Structure and replication of chromosomes in competent cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1075–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1075-1084.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Lang D., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Molecular cloning of the spo0B sporulation locus in bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):809–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.809-814.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hatfull G. F., Salmond G. P. A new cell division operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):134–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02428043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haima P., Bron S., Venema G. The effect of restriction on shotgun cloning and plasmid stability in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):335–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00329663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman A. L., Stewart G. C. The nucleotide sequence of the rodC operon of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1257–1268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karamata D., McConnell M., Rogers H. J. Mapping of rod mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.73-79.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labie C., Bouché F., Bouché J. P. Minicell-forming mutants of Escherichia coli: suppression of both DicB- and MinD-dependent division inhibition by inactivation of the minC gene product. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5852–5855. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5852-5855.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner C. G., Inouye M. Low copy number plasmids for regulated low-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli with blue/white insert screening capability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4631–4631. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin P. A., Margolis P. S., Setlow P., Losick R., Sun D. Identification of Bacillus subtilis genes for septum placement and shape determination. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6717–6728. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6717-6728.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. Regulation of cell division in E. coli. Trends Genet. 1990 Jan;6(1):22–25. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder E., Woldringh C. L., Tétart F., Bouché J. P. New minC mutations suggest different interactions of the same region of division inhibitor MinC with proteins specific for minD and dicB coinhibition pathways. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):35–39. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.35-39.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. N., Mendelson N. H., Coyne S. I., Hallock L. L., Cole R. M. Minicells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):860–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.860-873.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosey E. L., Oskouian B., Stewart G. C. Lactose metabolism by Staphylococcus aureus: characterization of lacABCD, the structural genes of the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5992–5998. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5992-5998.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. A., Yasbin R. E., Young F. E. New shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli which allow rapid detection of inserted fragments. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachi M., Doi M., Okada Y., Matsuhashi M. New mre genes mreC and mreD, responsible for formation of the rod shape of Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6511–6516. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6511-6516.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachi M., Doi M., Tamaki S., Park W., Nakajima-Iijima S., Matsuhashi M. Mutant isolation and molecular cloning of mre genes, which determine cell shape, sensitivity to mecillinam, and amount of penicillin-binding proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4935–4940. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4935-4940.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachi M., Matsuhashi M. Negative control of cell division by mreB, a gene that functions in determining the rod shape of Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3123–3127. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3123-3127.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. M., Stewart G. C. Role and expression of the Bacillus subtilis rodC operon. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4341–4346. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4341-4346.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer P. A., Cook W. R., Rothfield L. I. Bacterial cell division. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:249–274. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
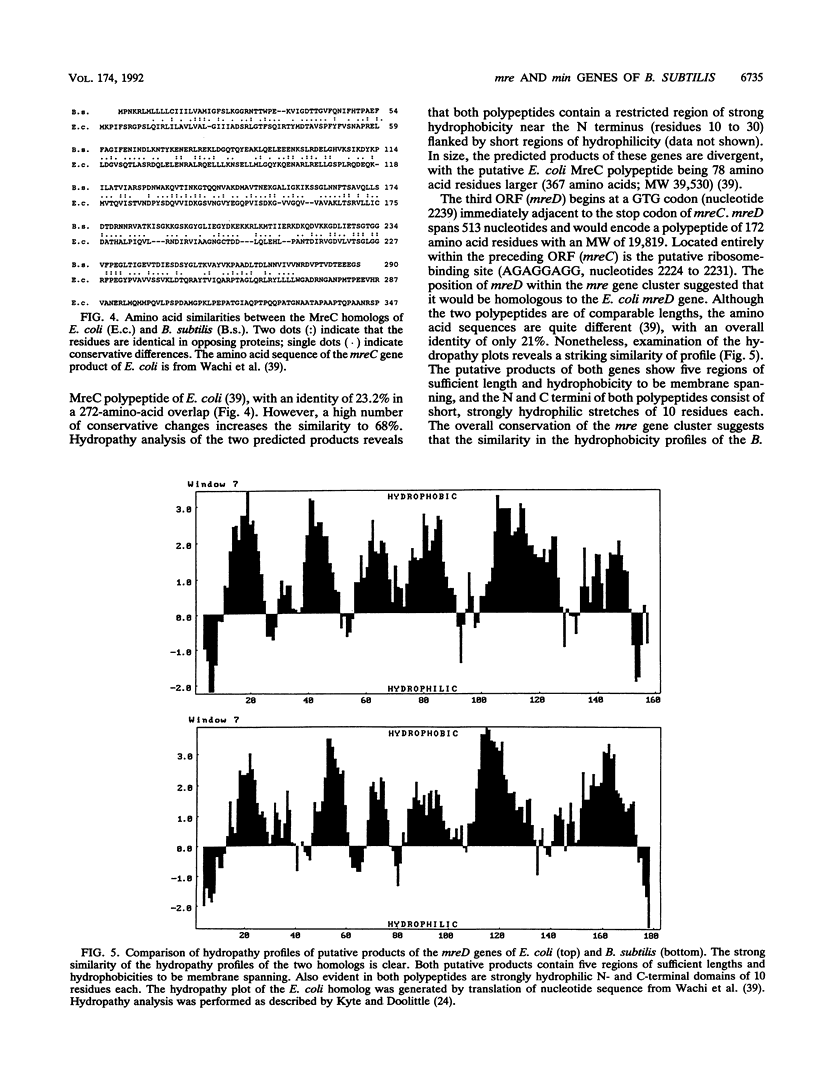
- de Boer P. A., Crossley R. E., Hand A. R., Rothfield L. I. The MinD protein is a membrane ATPase required for the correct placement of the Escherichia coli division site. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4371–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer P. A., Crossley R. E., Rothfield L. I. A division inhibitor and a topological specificity factor coded for by the minicell locus determine proper placement of the division septum in E. coli. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):641–649. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer P. A., Crossley R. E., Rothfield L. I. Central role for the Escherichia coli minC gene product in two different cell division-inhibition systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1129–1133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer P. A., Crossley R. E., Rothfield L. I. Isolation and properties of minB, a complex genetic locus involved in correct placement of the division site in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2106–2112. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2106-2112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]