Abstract
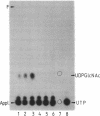
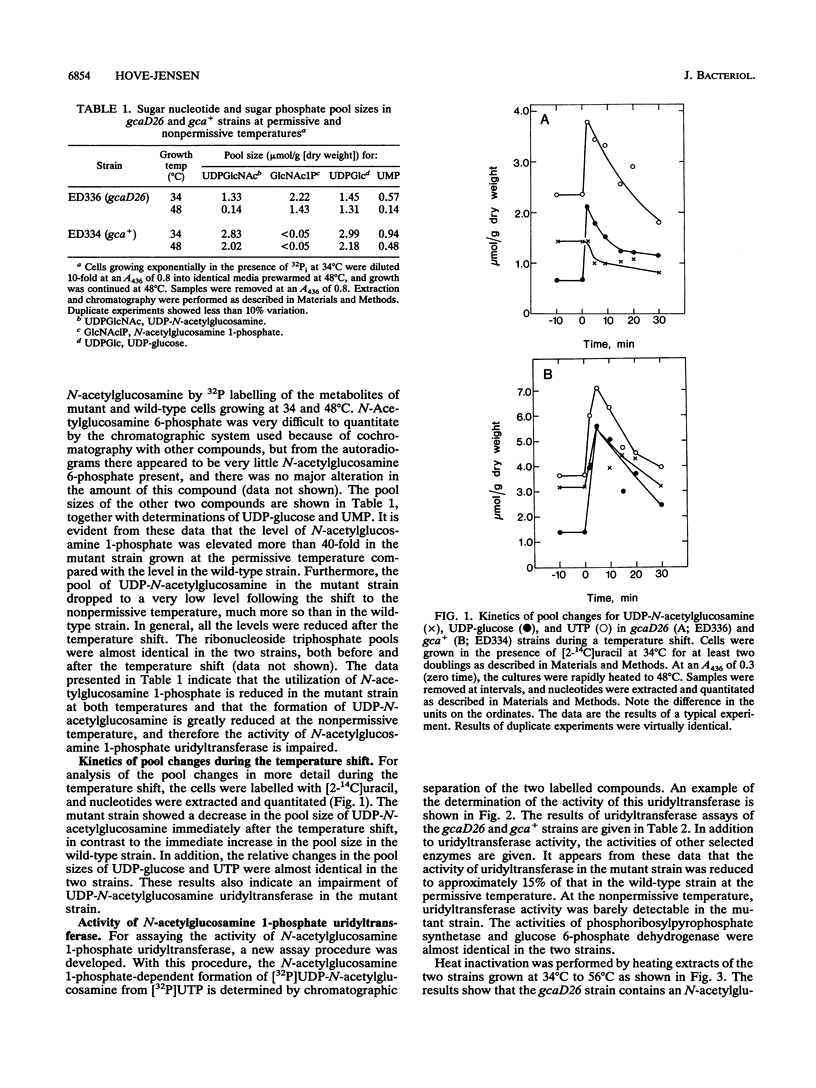
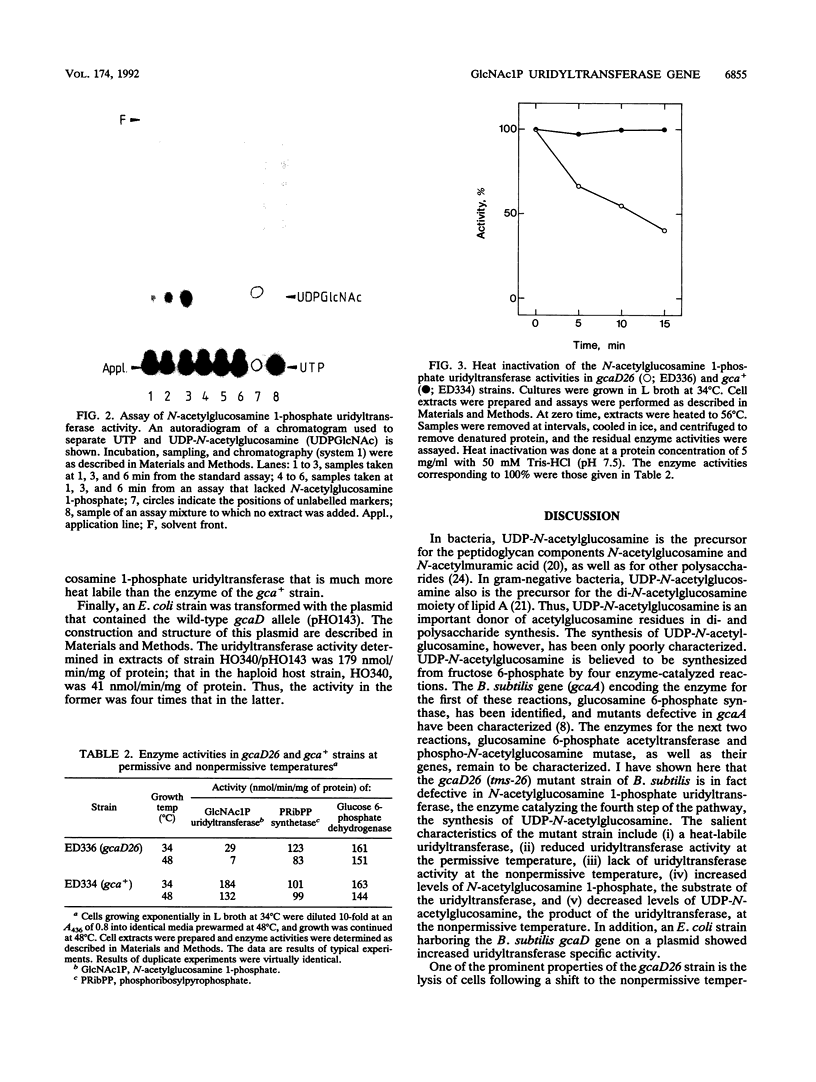
The temperature-sensitive Bacillus subtilis tms-26 mutant strain was characterized biochemically and shown to be defective in N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase activity. At the permissive temperature (34 degrees C), the mutant strain contained about 15% of the wild-type activity of this enzyme, whereas at the nonpermissive temperature (48 degrees C), the mutant enzyme was barely detectable. Furthermore, the N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase activity of the tms-26 mutant strain was much more heat labile in vitro than that of the wild-type strain. The level of N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate, the substrate of the uridyltransferase activity, was elevated more than 40-fold in the mutant strain at the permissive temperature compared with the level in the wild-type strain. During a temperature shift, the level of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine, the product of the uridyltransferase activity, decreased much more in the mutant strain than in the wild-type strain. An Escherichia coli strain harboring the wild-type version of the tms-26 allele on a plasmid contained increased N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase activity compared with that in the haploid strain. It is suggested that the gene for N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase in B. subtilis be designated gcaD.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnvig K., Hove-Jensen B., Switzer R. L. Purification and properties of phosphoribosyl-diphosphate synthetase from Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 28;192(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H., Brooks D., Young F. E. Regulation of the bacterial cell wall: analysis of a mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in biosynthesis of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.281-290.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland J. C., Marmur J. Identification of conserved genetic functions in Bacillus by use of temperature-sensitive mutants. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):302–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. E., Sonenshein A. L. Promoter-probe plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):965–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.965-967.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Uratani B., Freese E. Purine salvage pathways of Bacillus subtilis and effect of guanine on growth of GMP reductase mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):169–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.169-179.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. B., Cole R. M., Klofat W., Freese E. Growth, sporulation, and enzyme defects of glucosamine mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1046–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1046-1062.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Banner C. D., Ollington J. F., Losick R., Hoch J. A., O'Connor M. B., Sonenshein A. L. Mapping a cloned gene under sporulation control by inserttion of a drug resistance marker into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.90-98.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Houlberg U., Nygaard P. Thin-layer chromatographic methods to isolate 32P-labeled 5-phosphoribosyl-alpha-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP): determination of cellular PRPP pools and assay of PRPP synthetase activity. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):254–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson D., Hove-Jensen B., Arnvig K. Primary structure of the tms and prs genes of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):565–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00332425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson D., Hove-Jensen B. Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase of Bacillus subtilis. Cloning, characterization and chromosomal mapping of the prs gene. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E. Ion-exchange thin-layer chromatography. XIV. Separation of nucleotide sugars and nucleoside monophosphates on PEI-cellulose. Anal Biochem. 1965 Dec;13(3):575–579. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E. Ion-exchange thin-layer chromatography. XV. Preparation, properties and applications of paper-like PEI-cellulose sheets. J Chromatogr. 1966 Apr;22(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)97076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):465–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.465-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Gay N. J., Saraste M., Eberle A. N. DNA sequence around the Escherichia coli unc operon. Completion of the sequence of a 17 kilobase segment containing asnA, oriC, unc, glmS and phoS. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):799–815. doi: 10.1042/bj2240799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple F. W., Sonenshein A. L. Mechanism of initiation of transcription by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase at several promoters. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 20;223(2):399–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90660-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]