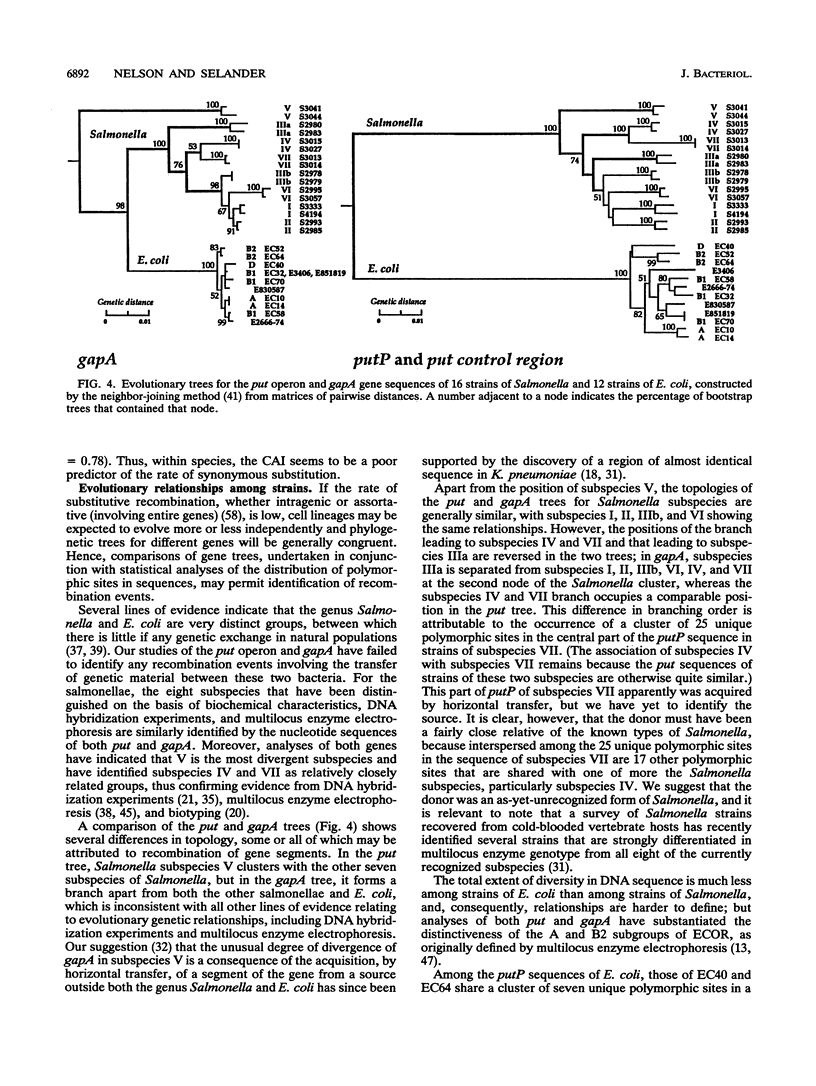
Abstract
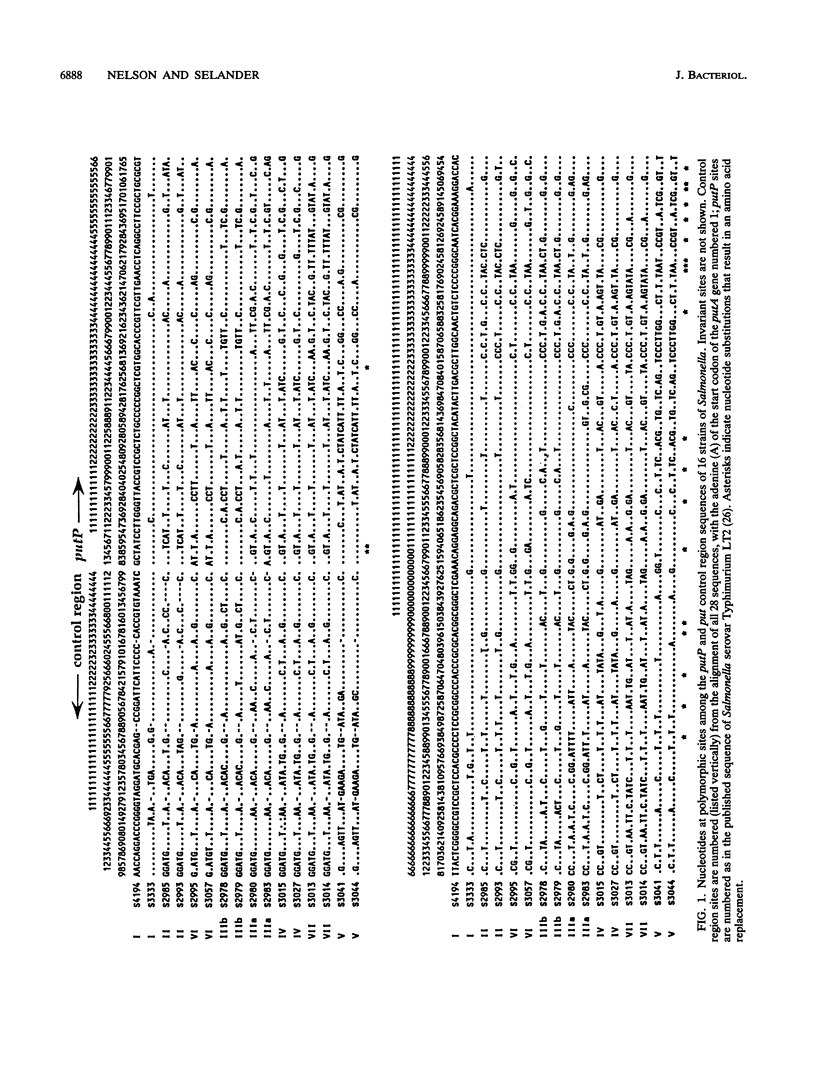
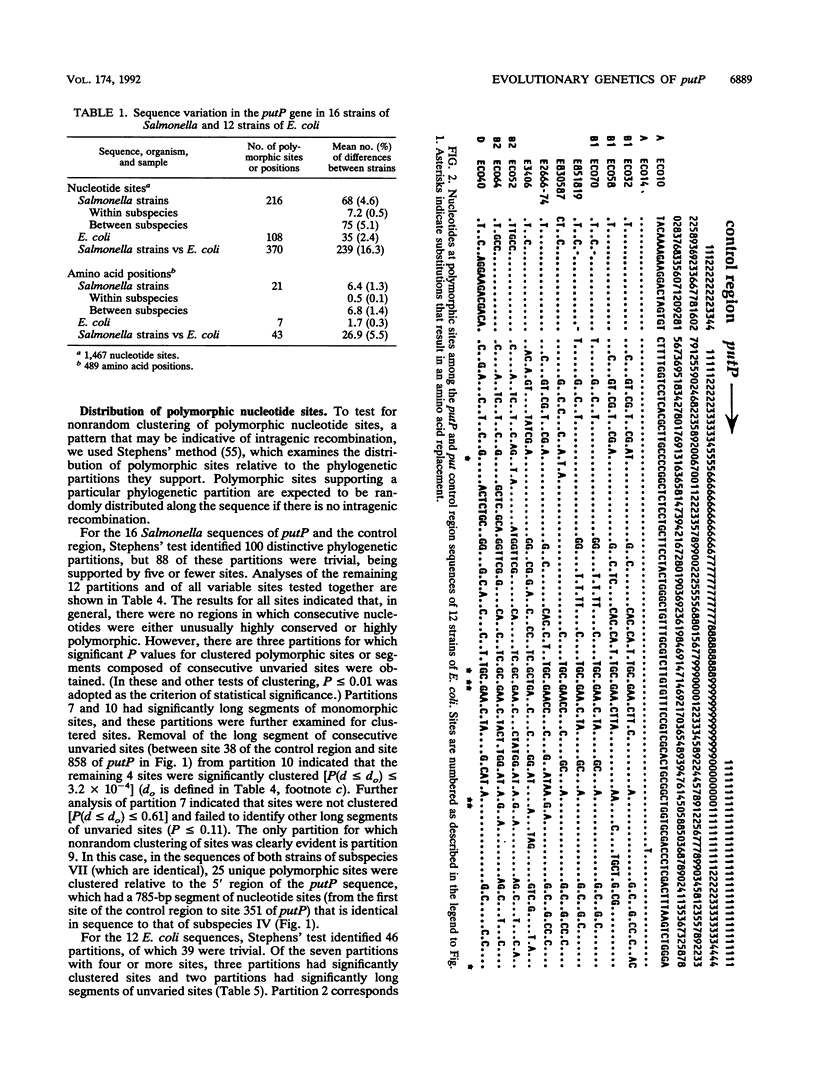
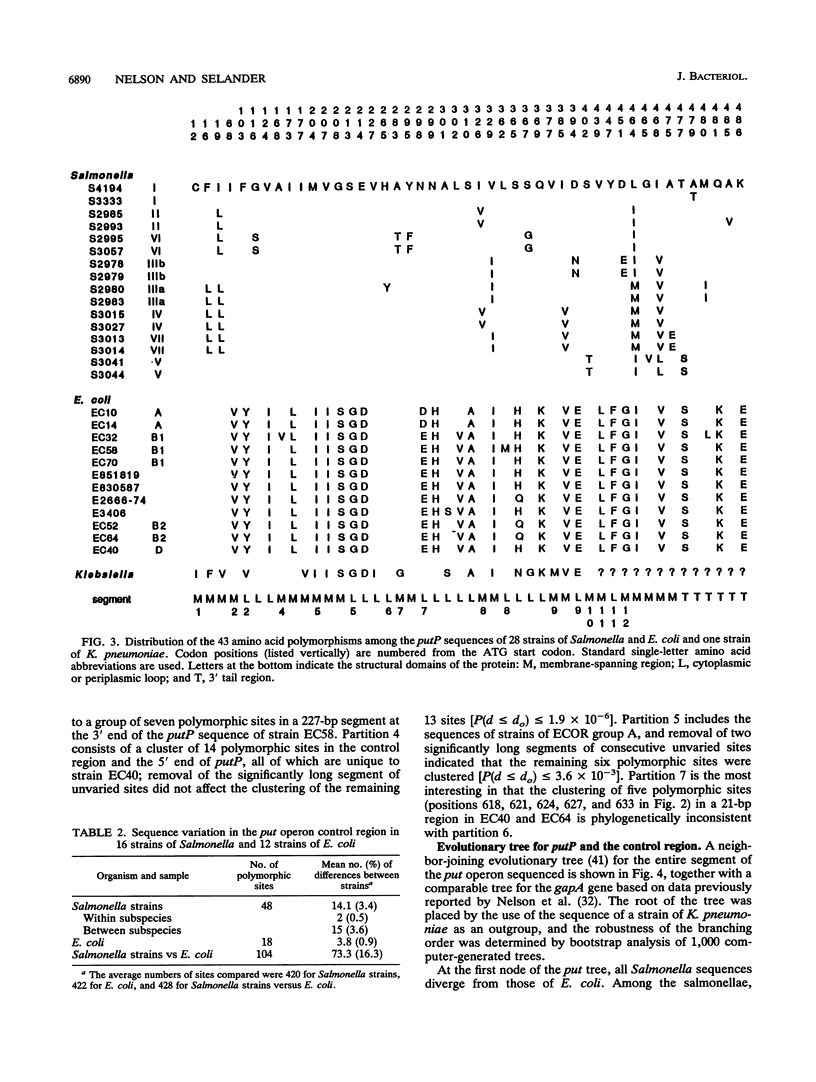
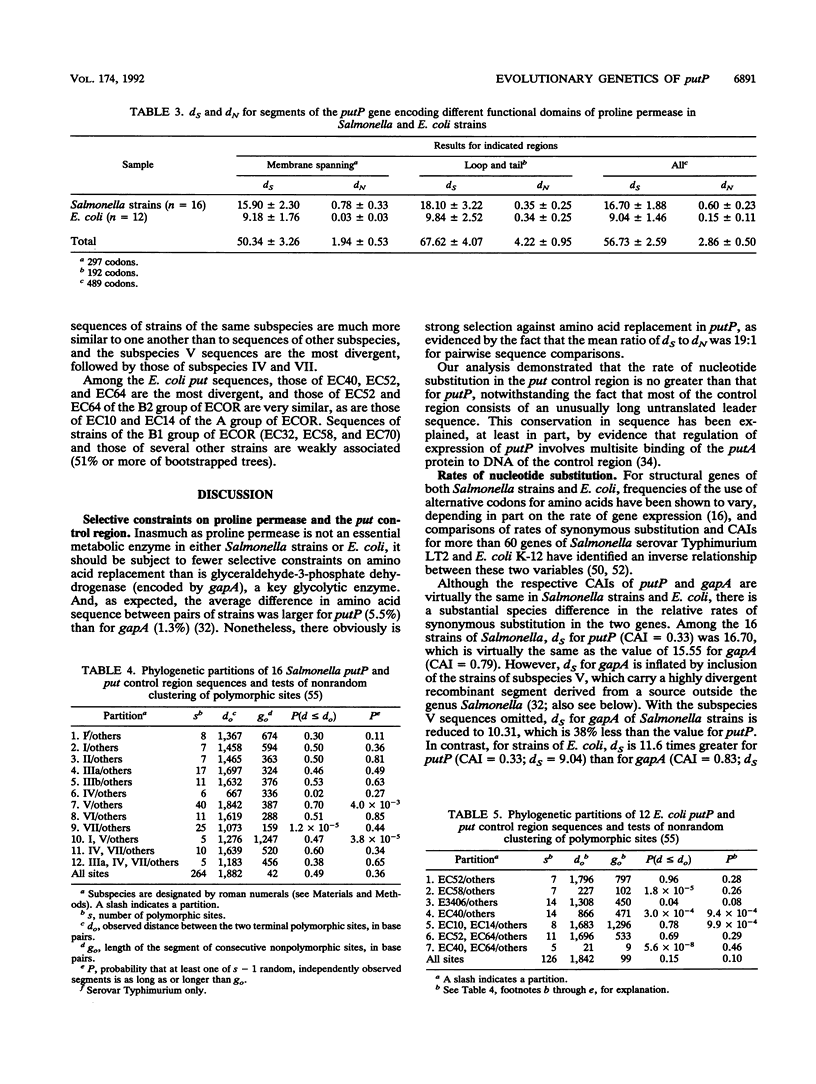
Virtually complete sequences (1,467 bp) of the proline permease gene (putP) and complete sequences (416 to 422 bp) of the control region of the proline utilization operon were determined for 16 strains of Salmonella, representing all eight subspecies, and 13 strains of Escherichia coli recovered from natural populations. Strains of Salmonella and E. coli differed, on average, at 16.3% of putP nucleotide sites and 17.5% of control region sites; the average difference between strains was much larger for Salmonella strains (4.6% of putP sites and 3.4% of control region sites) than for E. coli (2.4 and 0.9%, respectively). There was no difference in the distribution of polymorphic amino acid positions between the membrane-spanning and loop regions of the permease molecule, and rates of synonymous nucleotide substitution were virtually the same for the two domains. Statistical analysis yielded evidence of three probable cases of intragenic recombination, including the acquisition of a large segment of putP by strains of Salmonella subspecies VII from an unidentified source, the exchange of a 21-bp segment between two strains of E. coli, and the acquisition by one strain of E. coli of a cluster of 14 unique polymorphic control region sites from an unknown donor. An evolutionary tree for the putP and control region sequences was generally concordant with a tree for the gapA gene and a tree based on multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, thus providing evidence that for neither gene nor for enzyme genes in general has recombination occurred at rates sufficiently high or over regions sufficiently large to completely obscure phylogenetic relationships dependent on mutational divergence. It is suggested that the recombination rate varies among genes in relation to functional type, being highest for genes encoding cell surface and other proteins for which there is an adaptive advantage in structural diversity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcak G. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Comparative nucleotide sequence analysis of growth-rate-regulated gnd alleles from natural isolates of Escherichia coli and from Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):372–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.372-379.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltran P., Musser J. M., Helmuth R., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Frerichs W. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Ferris K., McWhorter A. C., Wells J. G., Cravioto A. Toward a population genetic analysis of Salmonella: genetic diversity and relationships among strains of serotypes S. choleraesuis, S. derby, S. dublin, S. enteritidis, S. heidelberg, S. infantis, S. newport, and S. typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7753–7757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisercić M., Feutrier J. Y., Reeves P. R. Nucleotide sequences of the gnd genes from nine natural isolates of Escherichia coli: evidence of intragenic recombination as a contributing factor in the evolution of the polymorphic gnd locus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3894–3900. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3894-3900.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. M., Maloy S. Regulation of proline utilization in enteric bacteria: cloning and characterization of the Klebsiella put control region. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):783–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.783-790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Anderson K. L., Alberro M. R. A naturally occurring horizontal gene transfer from a eukaryote to a prokaryote. J Mol Evol. 1990 Nov;31(5):383–388. doi: 10.1007/BF02106053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowson C. G., Hutchison A., Woodford N., Johnson A. P., George R. C., Spratt B. G. Penicillin-resistant viridans streptococci have obtained altered penicillin-binding protein genes from penicillin-resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5858–5862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBose R. F., Dykhuizen D. E., Hartl D. L. Genetic exchange among natural isolates of bacteria: recombination within the phoA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7036–7040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykhuizen D. E., Green L. Recombination in Escherichia coli and the definition of biological species. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7257–7268. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7257-7268.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn D. R., Myers R. S., Kent C. R., Maloy S. R. Regulation of proline utilization in Salmonella typhimurium: molecular characterization of the put operon, and DNA sequence of the put control region. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):125–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00333408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzer P. J., Inouye S., Inouye M., Whittam T. S. Phylogenetic distribution of branched RNA-linked multicopy single-stranded DNA among natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6175–6181. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6175-6181.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R. G., Ochman H. Production of single-stranded DNA templates by exonuclease digestion following the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5865–5865. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. R. Estimating the recombination parameter of a finite population model without selection. Genet Res. 1987 Dec;50(3):245–250. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300023776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R. Capsulation in distantly related strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b: genetic drift and gene transfer at the capsulation locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1374–1379. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1374-1379.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. G., Ochman H., Hartl D. L. Molecular and evolutionary relationships among enteric bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Aug;137(8):1911–1921. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-8-1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Popoff M. Y., Laurent B., Hermant D. Individualisation d'une septième sous-espèce de Salmonella: S. choleraesuis subsp. indica subsp. nov. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Cloning and structure of group C1 O antigen (rfb gene cluster) from Salmonella enterica serovar montevideo. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Feb;138(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomholt H., Poulsen K., Caugant D. A., Kilian M. Molecular polymorphism and epidemiology of Neisseria meningitidis immunoglobulin A1 proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazodier P., Davies J. Gene transfer between distantly related bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:147–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R., Bridges M. M. Molecular evolution of the Escherichia coli chromosome. III. Clonal frames. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):505–517. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K., Maloy S. DNA sequence of the putP gene from Salmonella typhimurium and predicted structure of proline permease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3057–3057. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao T., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Nucleotide sequence of putC, the regulatory region for the put regulon of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):364–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00325707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao T., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Nucleotide sequence of putP, the proline carrier gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):70–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00330424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):418–426. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Jin L. Variances of the average numbers of nucleotide substitutions within and between populations. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 May;6(3):290–300. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Whittam T. S., Selander R. K. Nucleotide polymorphism and evolution in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (gapA) in natural populations of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6667–6671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Selander R. K. Standard reference strains of Escherichia coli from natural populations. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):690–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.690-693.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrovsky de Spicer P., O'Brien K., Maloy S. Regulation of proline utilization in Salmonella typhimurium: a membrane-associated dehydrogenase binds DNA in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):211–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.211-219.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Reinholdt J., Kilian M. A comparative genetic study of serologically distinct Haemophilus influenzae type 1 immunoglobulin A1 proteases. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2913–2921. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2913-2921.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Evins G. M., Heiba A. A., Plikaytis B. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. A., Dykhuizen D. E., Hartl D. L. Confidence interval for the number of selectively neutral amino acid polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6225–6228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. Statistical tests for detecting gene conversion. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Sep;6(5):526–538. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Smith N. H., Li J., Beltran P., Ferris K. E., Kopecko D. J., Rubin F. A. Molecular evolutionary genetics of the cattle-adapted serovar Salmonella dublin. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3587–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3587-3592.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M. Determinants of DNA sequence divergence between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: codon usage, map position, and concerted evolution. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jul;33(1):23–33. doi: 10.1007/BF02100192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The rate of synonymous substitution in enterobacterial genes is inversely related to codon usage bias. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):222–230. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. H., Beltran P., Selander R. K. Recombination of Salmonella phase 1 flagellin genes generates new serovars. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2209–2216. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2209-2216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Bowler L. D., Zhang Q. Y., Zhou J., Smith J. M. Role of interspecies transfer of chromosomal genes in the evolution of penicillin resistance in pathogenic and commensal Neisseria species. J Mol Evol. 1992 Feb;34(2):115–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00182388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. C. Statistical methods of DNA sequence analysis: detection of intragenic recombination or gene conversion. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):539–556. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus A., Leslie J. F., Milkman R. Molecular evolution of the Escherichia coli chromosome. I. Analysis of structure and natural variation in a previously uncharacterized region between trp and tonB. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):345–358. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Molecular analysis of a Salmonella enterica group E1 rfb gene cluster: O antigen and the genetic basis of the major polymorphism. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):429–443. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



