Abstract
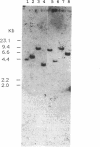
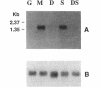
In order to isolate the structural gene involved in sucrose utilization, we screened a sucrose-induced Candida albicans cDNA library for clones expressing alpha-glucosidase activity. The C. albicans maltase structural gene (CAMAL2) was isolated. No other clones expressing alpha-glucosidase activity. were detected. A genomic CAMAL2 clone was obtained by screening a size-selected genomic library with the cDNA clone. DNA sequence analysis reveals that CAMAL2 encodes a 570-amino-acid protein which shares 50% identity with the maltase structural gene (MAL62) of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. The substrate specificity of the recombinant protein purified from Escherichia coli identifies the enzyme as a maltase. Northern (RNA) analysis reveals that transcription of CAMAL2 is induced by maltose and sucrose and repressed by glucose. These results suggest that assimilation of sucrose in C. albicans relies on an inducible maltase enzyme. The family of genes controlling sucrose utilization in C. albicans shares similarities with the MAL gene family of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and provides a model system for studying gene regulation in this pathogenic yeast.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley S. G., Creevy D. C. Effect of glucose on induction of alpha-glucosidase in Candida. Mycologia. 1966 Jul-Aug;58(4):549–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisson G., Duée E., Haser R., Payan F. Three dimensional structure of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase at 2.9 A resolution. Role of calcium in structure and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3909–3916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. S., Dubin R. A., Perkins E., Forrest D., Michels C. A., Needleman R. B. MAL63 codes for a positive regulator of maltose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1988 Sep;14(3):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00376740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. S., Dubin R. A., Perkins E., Michels C. A., Needleman R. B. Identification and characterization of the maltose permease in genetically defined Saccharomyces strain. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6148–6154. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6148-6154.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. D., Goldenthal M. J., Chow T., Buchferer B., Marmur J. Organization of the MAL loci of Saccharomyces. Physical identification and functional characterization of three genes at the MAL6 locus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00383304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowhanick T. M., Russell I., Scherer S. W., Stewart G. G., Seligy V. L. Expression and regulation of glucoamylase from the yeast Schwanniomyces castellii. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2360–2366. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2360-2366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federoff H. J., Eccleshall T. R., Marmur J. Carbon catabolite repression of maltase synthesis in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):301–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.301-307.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federoff H. J., Eccleshall T. R., Marmur J. Regulation of maltase synthesis in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1301-1308.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geber A., Higgins D. E., Waters A. P., Bennett J. E., McCutchan T. F. Small subunit ribosomal RNA of Blastomyces dermatitidis: sequence and phylogenetic analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Feb;138(2):395–399. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-2-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R., Watanabe C. K., de Boer H. A. Compilation and comparison of the sequence context around the AUG startcodons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3581–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero E., Sentandreu R. Protein secretion and compartmentalization in yeast. Microbiologia. 1988 Jun;4(2):73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. H., Marmur J. Primary structure of the maltase gene of the MAL6 locus of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1986;41(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. H., Marmur J. Upstream regulatory regions controlling the expression of the yeast maltase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2477–2483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Kwon-Chung K. J. A zinc finger protein from Candida albicans is involved in sucrose utilization. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):222–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.222-232.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella B. T., Cantwell B. A. Analysis of the expression and secretion of the Candida tsukubaensis alpha-glucosidase gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991 Jul;7(5):445–454. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella B. T., Larkin A., Bolton M., Cantwell B. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a Candida tsukubaensis alpha-glucosidase gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1991 Jul;20(1-2):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00312764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakenaite R. P., Glemzha A. A. Nekotorye svoistva dvukh form al'fa-gliukozidazy Saccharomyces cerevisiae-II. Biokhimiia. 1983 Jan;48(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Hicks J. B., Lipke P. N. Evidence that Candida stellatoidea type II is a mutant of Candida albicans that does not express sucrose-inhibitable alpha-glucosidase. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2804–2808. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2804-2808.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Riggsby W. S., Uphoff R. A., Hicks J. B., Whelan W. L., Reiss E., Magee B. B., Wickes B. L. Genetic differences between type I and type II Candida stellatoidea. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.527-532.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Wickes B. L., Merz W. G. Association of electrophoretic karyotype of Candida stellatoidea with virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1814–1819. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1814-1819.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrechts M. G., Pretorius I. S., Sollitti P., Marmur J. Primary structure and regulation of a glucoamylase-encoding gene (STA2) in Saccharomyces diastaticus. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90354-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livi G. P., Lillquist J. S., Miles L. M., Ferrara A., Sathe G. M., Simon P. L., Meyers C. A., Gorman J. A., Young P. R. Secretion of N-glycosylated interleukin-1 beta in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a leader peptide from Candida albicans. Effect of N-linked glycosylation on biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15348–15355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. C., Jacobson J. W., Giles N. H. Characterization and in vitro translation of polyadenylated messenger ribonucleic acid from Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1192-1198.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Kusunoki M., Harada W., Kakudo M. Structure and possible catalytic residues of Taka-amylase A. J Biochem. 1984 Mar;95(3):697–702. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni B. F., Needleman R. B. Identification of the upstream activating sequence of MAL and the binding sites for the MAL63 activator of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3797–3800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez M., Hernández L. M., Larriba G. A similar protein portion for two exoglucanases secreted by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 1989;151(5):391–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00416596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWAI T., HEHRE E. J. A novel amylase (Candida transglucosyl-amylase) that catalyzes glucosyl transfer from starch and dextrins. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2047–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarokin L., Carlson M. Short repeated elements in the upstream regulatory region of the SUC2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2324–2333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson B. Regional distant sequence homology between amylases, alpha-glucosidases and transglucanosylases. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80644-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma A., Kwon-Chung K. J. Rapid method to extract DNA from Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):810–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.810-812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickes B. L., Golin J. E., Kwon-Chung K. J. Chromosomal rearrangement in Candida stellatoidea results in a positive effect on phenotype. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1762–1771. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1762-1771.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]