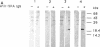Abstract
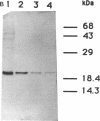
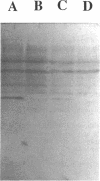
Gene grdA, which encodes selenoprotein A of the glycine reductase complex from Clostridium sticklandii, was identified and characterized. This gene encodes a protein of 158 amino acids with a calculated M(r) of 17,142. The known sequence of 15 amino acids around the selenocysteine residue and the known carboxy terminus of the protein are correctly predicted by the nucleotide sequence. An opal termination codon (TGA) corresponding to the location of the single selenocysteine residue in the polypeptide was found in frame at position 130. The C. sticklandii grdA gene was inserted behind the tac promotor of an Escherichia coli expression vector. An E. coli strain transformed with this vector produced an 18-kDa polypeptide that was not detected in extracts of nontransformed cells. Affinity-purified anti-C. sticklandii selenoprotein A immunoglobulin G reacted specifically with this polypeptide, which was indistinguishable from authentic C. sticklandii selenoprotein A by immunological analysis. Addition of the purified expressed protein to glycine reductase protein components B and C reconstituted the active glycine reductase complex. Although synthesis of enzymically active protein A depended on the presence of selenium in the growth medium, formation of immunologically reactive protein did not. Moreover, synthesis of enzymically active protein in a transformed E. coli selD mutant strain indicated that there is a nonspecific mechanism of selenocysteine incorporation. These findings imply that mRNA secondary structures of C. sticklandii grdA are not functional for UGA-directed selenocysteine insertion in the E. coli expression system.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg B. L., Baron C., Stewart V. Nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. II. Evidence that a mRNA stem-loop structure is essential for decoding opal (UGA) as selenocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22386–22391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. L., Li J., Heider J., Stewart V. Nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. I. Nucleotide sequence of the fdnGHI operon and evidence that opal (UGA) encodes selenocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22380–22385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Chen Y. Y., Mandel S. J., Kieffer J. D., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R. Recognition of UGA as a selenocysteine codon in type I deiodinase requires sequences in the 3' untranslated region. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):273–276. doi: 10.1038/353273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Stadtman T. C. Selenocysteine, a highly specific component of certain enzymes, is incorporated by a UGA-directed co-translational mechanism. Biofactors. 1988 Oct;1(3):245–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching W. M. Characterization of selenium-containing tRNAGlu from Clostridium sticklandii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jan;244(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone J. E., Del Río R. M., Davis J. N., Stadtman T. C. Chemical characterization of the selenoprotein component of clostridial glycine reductase: identification of selenocysteine as the organoselenium moiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone J. E., del Río R. M., Stadtman T. C. Clostridial glycine reductase complex. Purification and characterization of the selenoprotein component. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5337–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrichs D., Meyer M., Rieth M., Andreesen J. R. Interaction of selenoprotein PA and the thioredoxin system, components of the NADPH-dependent reduction of glycine in Eubacterium acidaminophilum and Clostridium litorale [corrected]. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5983–5991. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5983-5991.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Analysis of the reaction sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6324–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia G. E., Stadtman T. C. Selenoprotein A component of the glycine reductase complex from Clostridium purinolyticum: nucleotide sequence of the gene shows that selenocysteine is encoded by UGA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2093–2098. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2093-2098.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarback J. A., Vallee R. B. Antibody exchange immunochemistry. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12763–12766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider J., Böck A. Targeted insertion of selenocysteine into the alpha subunit of formate dehydrogenase from Methanobacterium formicicum. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):659–663. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.659-663.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G. F., Ames B. N. Isolation and characterization of a selenium metabolism mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):736–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.736-743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Forchhammer K., Zinoni F., Sawers G., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Escherichia coli genes whose products are involved in selenium metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.540-546.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi Z., Saneyoshi M., Harada F., Hara H., Nishimura S. Presumed anticodon structure of glutamic acid tRNA from E. coli: a possible location of a 2-thiouridine derivative in the first position of the anticodon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 24;40(4):866–872. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90983-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN T. C., ELLIOTT P., TIEMANN L. Studies on the enzymic reduction of amino acids. III. Phosphate esterification coupled with glycine reduction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):961–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent glycine reductase: differences in physicochemical properties and biological activities of selenoprotein A components isolated from Clostridium sticklandii and Clostridium purinolyticum. Biofactors. 1988 Dec;1(4):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Stadtman T. C. Selenoprotein A of the clostridial glycine reductase complex: purification and amino acid sequence of the selenocysteine-containing peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):368–371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C., Davis J. N., Zehelein E., Böck A. Biochemical and genetic analysis of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli mutants defective in specific incorporation of selenium into formate dehydrogenase and tRNAs. Biofactors. 1989 Mar;2(1):35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Glycine reduction to acetate and ammonia: identification of ferredoxin and another low molecular weight acidic protein as components of the reductase system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jan;113(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent clostridial glycine reductase. Purification and characterization of the two membrane-associated protein components. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. C., Stadtman T. C. Purification of protein components of the clostridial glycine reductase system and characterization of protein A as a selenoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):366–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veres Z., Tsai L., Scholz T. D., Politino M., Balaban R. S., Stadtman T. C. Synthesis of 5-methylaminomethyl-2-selenouridine in tRNAs: 31P NMR studies show the labile selenium donor synthesized by the selD gene product contains selenium bonded to phosphorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittwer A. J., Ching W. M. Selenium-containing tRNA(Glu) and tRNA(Lys) from Escherichia coli: purification, codon specificity and translational activity. Biofactors. 1989 Mar;2(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. A., Kaiser I. I. Aminoacylation of Escherichia coli cysteine tRNA by selenocysteine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Dec;171(2):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Heider J., Böck A. Features of the formate dehydrogenase mRNA necessary for decoding of the UGA codon as selenocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]