Abstract
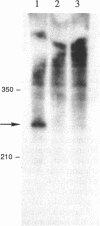
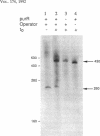
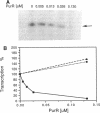
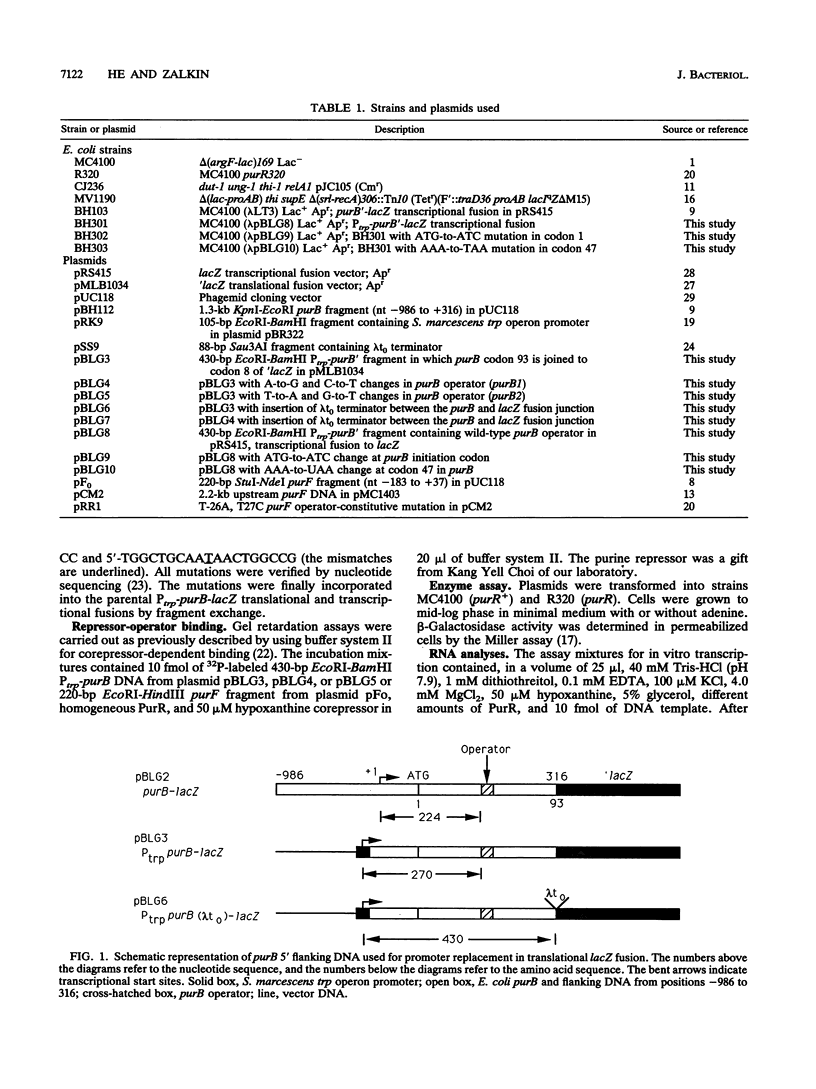
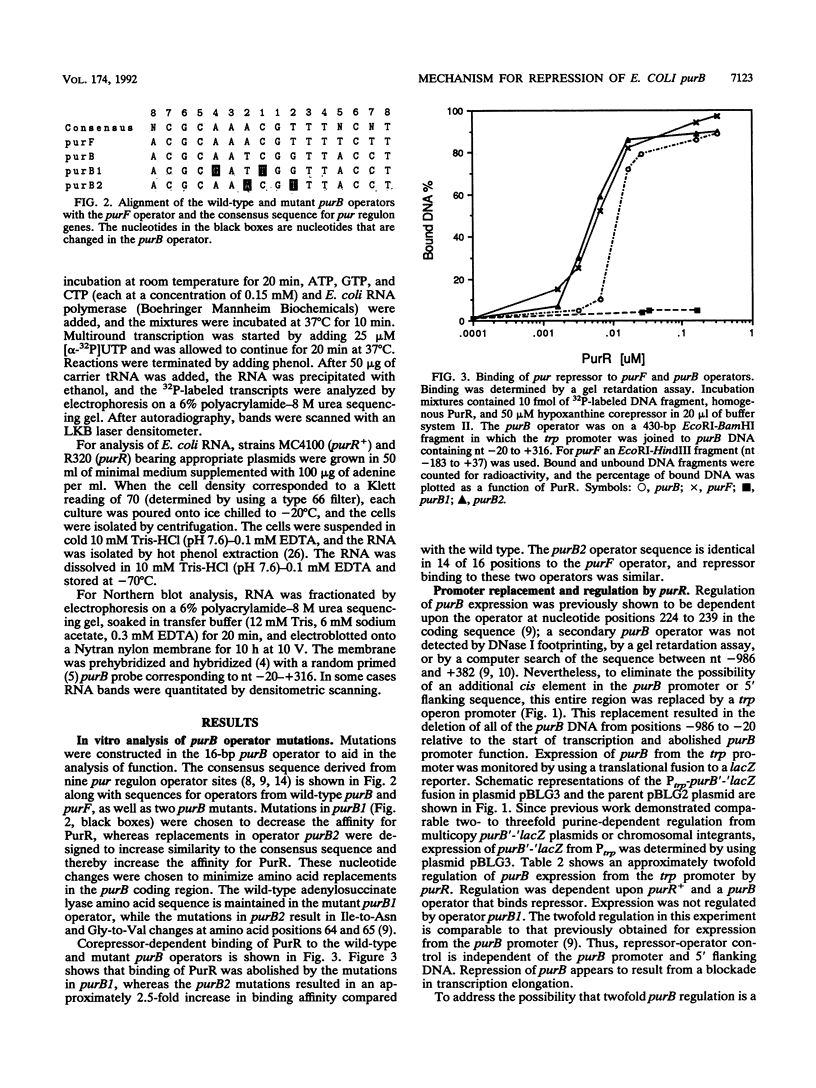
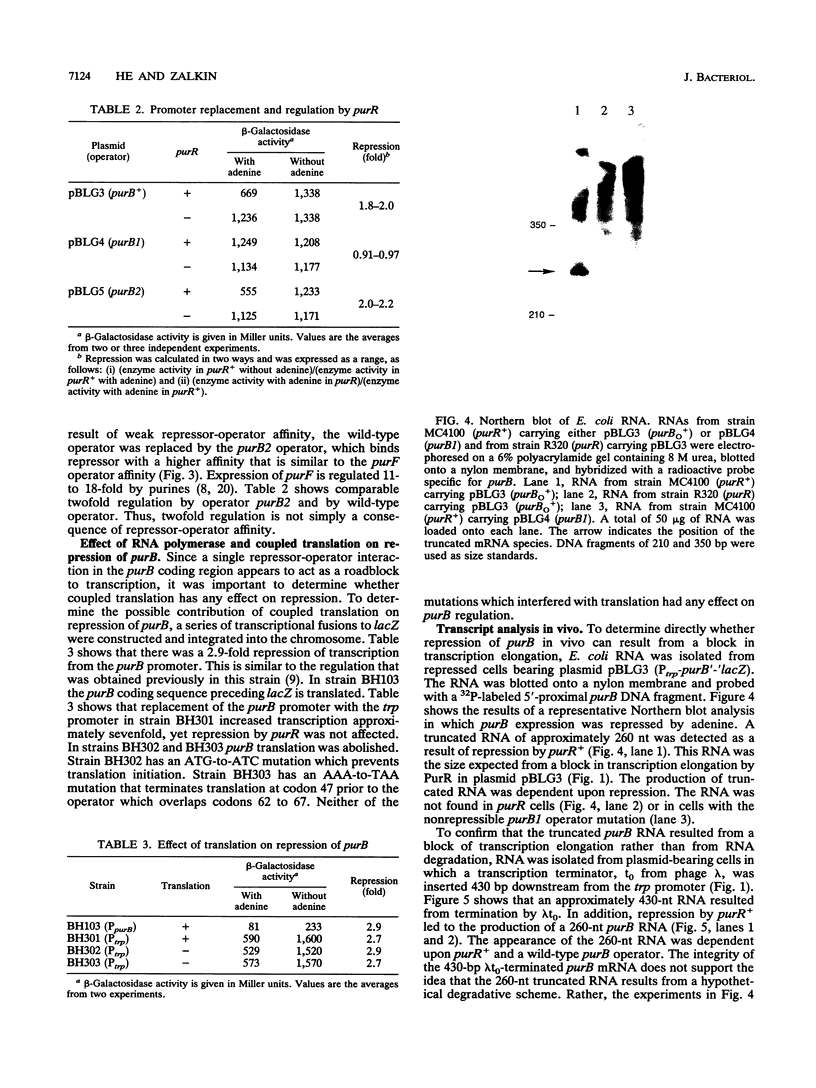
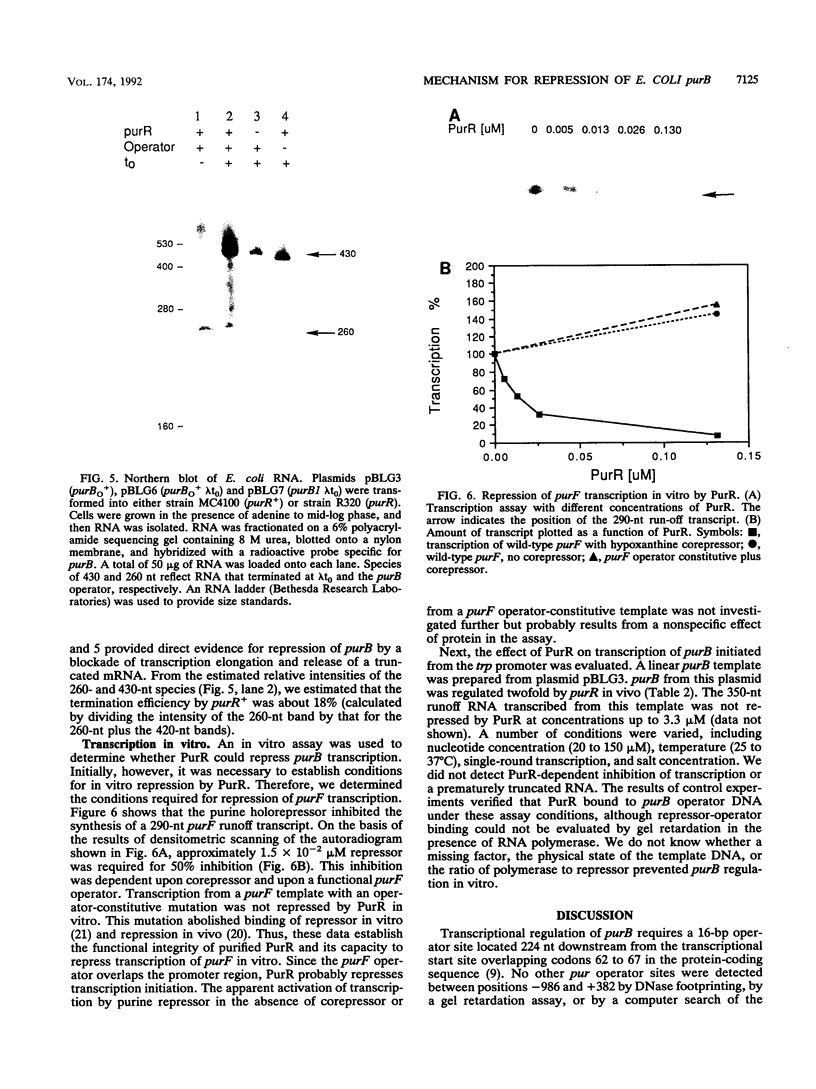
Escherichia coli purB is regulated by a repressor-operator interaction. The purB operator is 242 bp downstream from the transcription start site and overlaps condons 62 to 67 in the protein-coding sequence (B. He, J. M. Smith, and H. Zalkin, J. Bacteriol. 174:130-136, 1992). The mechanism by which the repressor-operator interaction functions to repress transcription was investigated by a combination of promoter replacement experiments and RNA analyses. By using a trp promoter replacement that deleted 5' flanking DNA to position -986, purB expression was increased sevenfold, yet normal two- to threefold regulation was maintained. This indicates that repressor-operator control is independent of the purB promoter and other 5' flanking sequences. Transcriptional regulation was likewise independent of coupled translation. An approximately 260-nucleotide truncated in vivo purB mRNA was identified which was dependent upon repressor-operator interaction. Thus, binding of purine repressor to the purB operator inhibits transcription elongation by a roadblock mechanism. The roadblock was not influenced by a sevenfold increase in promoter strength or by an operator mutation resulting in a 2.5-fold increase in repressor-operator affinity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides J., Magasanik B., Gralla J. D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):371–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.371-394.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. lac Repressor blocks transcribing RNA polymerase and terminates transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4134–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbole D. J., Zalkin H. Detection of pur operon-attenuated mRNA and accumulated degradation intermediates in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10894–10902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner Y., Gralla J. D. Dual mechanism of repression at a distance in the lac operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8968–8972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber R., Adhya S. Interaction of spatially separated protein-DNA complexes for control of gene expression: operator conversions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9683–9687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He B., Shiau A., Choi K. Y., Zalkin H., Smith J. M. Genes of the Escherichia coli pur regulon are negatively controlled by a repressor-operator interaction. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4555–4562. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4555-4562.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He B., Smith J. M., Zalkin H. Escherichia coli purB gene: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation by purR. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):130–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.130-136.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzer M., Bujard H. Promoters largely determine the efficiency of repressor action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8973–8977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makaroff C. A., Zalkin H. Regulation of Escherichia coli purF. Analysis of the control region of a pur regulon gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10378–10387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng L. M., Kilstrup M., Nygaard P. Autoregulation of PurR repressor synthesis and involvement of purR in the regulation of purB, purC, purL, purMN and guaBA expression in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):373–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng L. M., Nygaard P. Identification of hypoxanthine and guanine as the co-repressors for the purine regulon genes of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2187–2192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paluh J. L., Zalkin H., Betsch D., Weith H. L. Study of anthranilate synthase function by replacement of cysteine 84 using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1889–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfes R. J., Zalkin H. Escherichia coli gene purR encoding a repressor protein for purine nucleotide synthesis. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and interaction with the purF operator. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19653–19661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfes R. J., Zalkin H. Purification of the Escherichia coli purine regulon repressor and identification of corepressors. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5637–5642. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5637-5642.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfes R. J., Zalkin H. Regulation of Escherichia coli purF. Mutations that define the promoter, operator, and purine repressor gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19649–19652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek S., Grosse F. A cloning cartridge of lambda t(o) terminator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3185–3185. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellitti M. A., Pavco P. A., Steege D. A. lac repressor blocks in vivo transcription of lac control region DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Kuroda M. I., Yanofsky C., Henner D. J. Novel form of transcription attenuation regulates expression the Bacillus subtilis tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):461–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.461-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Yager T. D. The elongation-termination decision in transcription. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):809–812. doi: 10.1126/science.1536005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]