Abstract
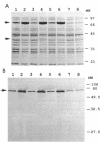
The physiological consequences of molecular chaperone overproduction in Escherichia coli are presented. Constitutive overproduction of DnaK from a multicopy plasmid containing large chromosomal fragments spanning the dnaK region resulted in plasmid instability. Co-overproduction of DnaJ with DnaK stabilized plasmid levels. To examine the effects of altered levels of DnaK and DnaJ in a more specific manner, an inducible expression system for dnaK and dnaJ was constructed and characterized. Differential rates of DnaK synthesis were determined by quantitative Western blot (immunoblot) analysis. Moderate levels of DnaK overproduction resulted in a defect in cell septation and formation of cell filaments, but co-overproduction of DnaJ overcame this effect. Further increases in the level of DnaK terminated culture growth despite increased levels of DnaJ. DnaK overproduction was found to be bacteriocidal, and this effect was also partially suppressed by DnaJ. The bacteriocidal effect was apparent only with cultures which were allowed to enter stationary phase, indicating that DnaK toxicity is growth phase dependent.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang D., Chandrasekhar G. N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli grpE gene codes for heat shock protein B25.3, essential for both lambda DNA replication at all temperatures and host growth at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):25–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.25-29.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum P., Velligan M., Lin N., Matin A. DnaK-mediated alterations in human growth hormone protein inclusion bodies. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Mar;10(3):301–304. doi: 10.1038/nbt0392-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Cellular defects caused by deletion of the Escherichia coli dnaK gene indicate roles for heat shock protein in normal metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2337-2346.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Mutations altering heat shock specific subunit of RNA polymerase suppress major cellular defects of E. coli mutants lacking the DnaK chaperone. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4027–4036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Gross C. A. Is hsp70 the cellular thermometer? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. O., James R. Identification of a gene, closely linked to dnaK, which is required for high-temperature growth of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jun;137(6):1271–1277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-6-1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Kaguni J. M., Kornberg A. Enzymatic replication of the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7370–7374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P. A new bacterial gene (groPC) which affects lambda DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Feb 28;151(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00446910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang D. S., Kaguni J. M. Interaction of dnaA46 protein with a stimulatory protein in replication from the Escherichia coli chromosomal origin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10633–10640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C., Chandrasekhar G. N., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli DnaK and GrpE heat shock proteins interact both in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1590–1596. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1590-1596.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Marszalek J., Ang D., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. Escherichia coli DnaJ and GrpE heat shock proteins jointly stimulate ATPase activity of DnaK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2874–2878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty J. S., Walker G. C. DnaK as a thermometer: threonine-199 is site of autophosphorylation and is critical for ATPase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9513–9517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Kohiyama M. Role of heat shock protein DnaK in osmotic adaptation of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4404–4410. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4404-4410.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Lebkowski J. S., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Specificity of mutations induced in transfected DNA by mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3117–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki R., Morita R., Kawamata T., Uchida H., Ohki M. A complete deletion mutant of the Escherichia coli dnaKdnaJ operon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 21;1009(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek K. H., Walker G. C. Escherichia coli dnaK null mutants are inviable at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.283-290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. Heat-shock proteins DnaK and GroEL facilitate export of LacZ hybrid proteins in E. coli. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):882–884. doi: 10.1038/344882a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. M., Eisen C., Ang D., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Isolation and characterization of dnaJ null mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4827–4835. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4827-4835.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence J., Cegielska A., Georgopoulos C. Role of Escherichia coli heat shock proteins DnaK and HtpG (C62.5) in response to nutritional deprivation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7157–7166. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7157-7166.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Hutton M. E., Neidhardt F. C. Gene-protein database of Escherichia coli K-12: edition 3. Electrophoresis. 1990 Dec;11(12):1131–1166. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150111205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Rapid purification of mammalian 70,000-dalton stress proteins: affinity of the proteins for nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1229–1237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S., Hoskins J., McKenney K. Function of DnaJ and DnaK as chaperones in origin-specific DNA binding by RepA. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):165–167. doi: 10.1038/350165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Temperature-induced synthesis of specific proteins in Escherichia coli: evidence for transcriptional control. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.843-851.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli dnaK replication protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]