Abstract
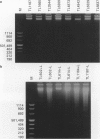
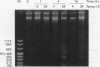
One of the main obstacles encountered when trying to culture human seminoma (SE) cells in vitro is massive degeneration of the tumour cells. We investigated whether dissociation of tumour tissue, to obtain single-cell suspensions for in vitro culture, results in the onset of apoptosis. Using morphological analysis and in situ end labelling, less than 4% of apoptotic tumour cells were detected in intact tissue from 11 out of 14 SEs. In these 11 tumours, apoptosis-specific DNA ladders, indicative of internucleosomal double-strand DNA cleavage, were not detected on electrophoresis gels. In contrast, three SEs with over 12% of apoptotic tumour cells in the intact tissue and all analysed (pure) SE cell suspensions, obtained after mechanical dissociation of intact tumour tissue, showed DNA ladders. Flow cytometric analysis of end labelled SE suspensions showed DNA breaks in up to 85% of the tumour cells. As indicated by cell morphology and DNA degradation, SE cells appear to rapidly enter the apoptotic pathway upon mechanical disruption of their microenvironment. No expression of p53 and of the apoptosis-inhibitor bcl-2 was detectable in intact SE tissue or cell suspensions. Our data suggest that abrogation of apoptosis might be crucial to succeed in culturing human SE cells in vitro.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. W., Damjanov I., Simon D., Banting G. S., Carlin C., Dracopoli N. C., Føgh J. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2. Differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki S., Shimada Y., Kaji K., Hayashi H. Apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells by fibroblast growth factor deprivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1194–1200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91155-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Wright J. J., McBride O. W., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardon S., Vignon F., Montcourrier P., Rochefort H. Steroid receptor-mediated cytotoxicity of an antiestrogen and an antiprogestin in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 1;47(5):1441–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Hart I. K., Coles H. S., Burne J. F., Voyvodic J. T., Richardson W. D., Raff M. C. Cell death and control of cell survival in the oligodendrocyte lineage. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90531-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttke T. M., Sandstrom P. A. Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1994 Jan;15(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Sklar J. Nucleotide sequence of a t(14;18) chromosomal breakpoint in follicular lymphoma and demonstration of a breakpoint-cluster region near a transcriptionally active locus on chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7439–7443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Perkins G. R., Rodriguez-Tarduchy G., Nieto M. A., López-Rivas A. Growth factors as survival factors: regulation of apoptosis. Bioessays. 1994 Feb;16(2):133–138. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Bruno S., Del Bino G., Gorczyca W., Hotz M. A., Lassota P., Traganos F. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992;13(8):795–808. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehner L. P. Germ cell tumors of the mediastinum. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990 Nov;7(4):266–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizenberg O., Faber-Elman A., Gottlieb E., Oren M., Rotter V., Schwartz M. Direct involvement of p53 in programmed cell death of oligodendrocytes. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 15;14(6):1136–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosså S. D., Droz J. P., Stoter G., Kaye S. B., Vermeylen K., Sylvester R. Cisplatin, vincristine and ifosphamide combination chemotherapy of metastatic seminoma: results of EORTC trial 30874. EORTC GU Group. Br J Cancer. 1995 Mar;71(3):619–624. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin I., Deed R., Cooke J., Zsebo K., Dexter M., Wylie C. C. Effects of the steel gene product on mouse primordial germ cells in culture. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):807–809. doi: 10.1038/352807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstein A. F. Cellular components of early testicular cancer. Eur Urol. 1993;23 (Suppl 2):9–18. doi: 10.1159/000474693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstein A. F., Schütte B., Becker H., Hartmann M. Morphology of normal and malignant germ cells. Int J Androl. 1987 Feb;10(1):1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1987.tb00160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Burne J. F., King M. P., Miyashita T., Reed J. C., Raff M. C. Bcl-2 blocks apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):365–369. doi: 10.1038/361365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Zsebo K., Hogan B. L. Derivation of pluripotential embryonic stem cells from murine primordial germ cells in culture. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostofi F. K. Pathology of germ cell tumors of testis: a progress report. Cancer. 1980 Apr 15;45(7 Suppl):1735–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostofi F. K., Sesterhenn I. A., Davis C. J., Jr Immunopathology of germ cell tumors of the testis. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1987 Nov;4(4):320–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murty V. V., Houldsworth J., Baldwin S., Reuter V., Hunziker W., Besmer P., Bosl G., Chaganti R. S. Allelic deletions in the long arm of chromosome 12 identify sites of candidate tumor suppressor genes in male germ cell tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11006–11010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nooter K., Boersma A. W., Oostrum R. G., Burger H., Jochemsen A. G., Stoter G. Constitutive expression of the c-H-ras oncogene inhibits doxorubicin-induced apoptosis and promotes cell survival in a rhabdomyosarcoma cell line. Br J Cancer. 1995 Mar;71(3):556–561. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olie R. A., Looijenga L. H., Boerrigter L., Top B., Rodenhuis S., Langeveld A., Mulder M. P., Oosterhuis J. W. N- and KRAS mutations in primary testicular germ cell tumors: incidence and possible biological implications. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 Feb;12(2):110–116. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. p53: the ultimate tumor suppressor gene? FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3169–3176. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce M., De Felici M. Apoptosis in mouse primordial germ cells: a study by transmission and scanning electron microscope. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1994 May;189(5):435–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00185438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce M., Farrace M. G., Piacentini M., Dolci S., De Felici M. Stem cell factor and leukemia inhibitory factor promote primordial germ cell survival by suppressing programmed cell death (apoptosis). Development. 1993 Aug;118(4):1089–1094. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.4.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawson C. L., Loo D. T., Duimstra J. R., Hedstrom O. R., Schmidt E. E., Barnes D. W. Death of serum-free mouse embryo cells caused by epidermal growth factor deprivation. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):671–680. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Hanks S. K., Hunter T., van der Geer P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):786–791. doi: 10.1038/372786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Shutter J. R., Hockenbery D., Kanagawa O., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skakkebaek N. E., Berthelsen J. G., Giwercman A., Müller J. Carcinoma-in-situ of the testis: possible origin from gonocytes and precursor of all types of germ cell tumours except spermatocytoma. Int J Androl. 1987 Feb;10(1):19–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1987.tb00161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson C. M., Barry M. A., Eastman A. Analysis of events associated with cell cycle arrest at G2 phase and cell death induced by cisplatin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 2;82(9):749–755. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.9.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmeyer T., Peter S., Hartmann M., Munemitsu S., Ackermann R., Ullrich A., Slamon D. J. Expression of the hst-1 and c-kit protooncogenes in human testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 1;51(7):1811–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Yunis J., Onorato-Showe L., Erikson J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Molecular cloning of the chromosomal breakpoint of B-cell lymphomas and leukemias with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.6610211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbright T. M., Roth L. M. Recent developments in the pathology of germ cell tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1987 Nov;4(4):304–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Haecker G., Strasser A. An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P., Kos F. J., Müllbacher A. Apoptosis or programmed cell death. Med Res Rev. 1991 Mar;11(2):219–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijsman J. H., Jonker R. R., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J., van Dierendonck J. H. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jan;41(1):7–12. doi: 10.1177/41.1.7678025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T. Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]