Abstract
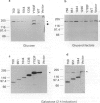
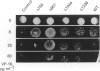
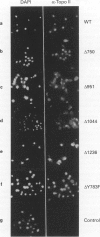
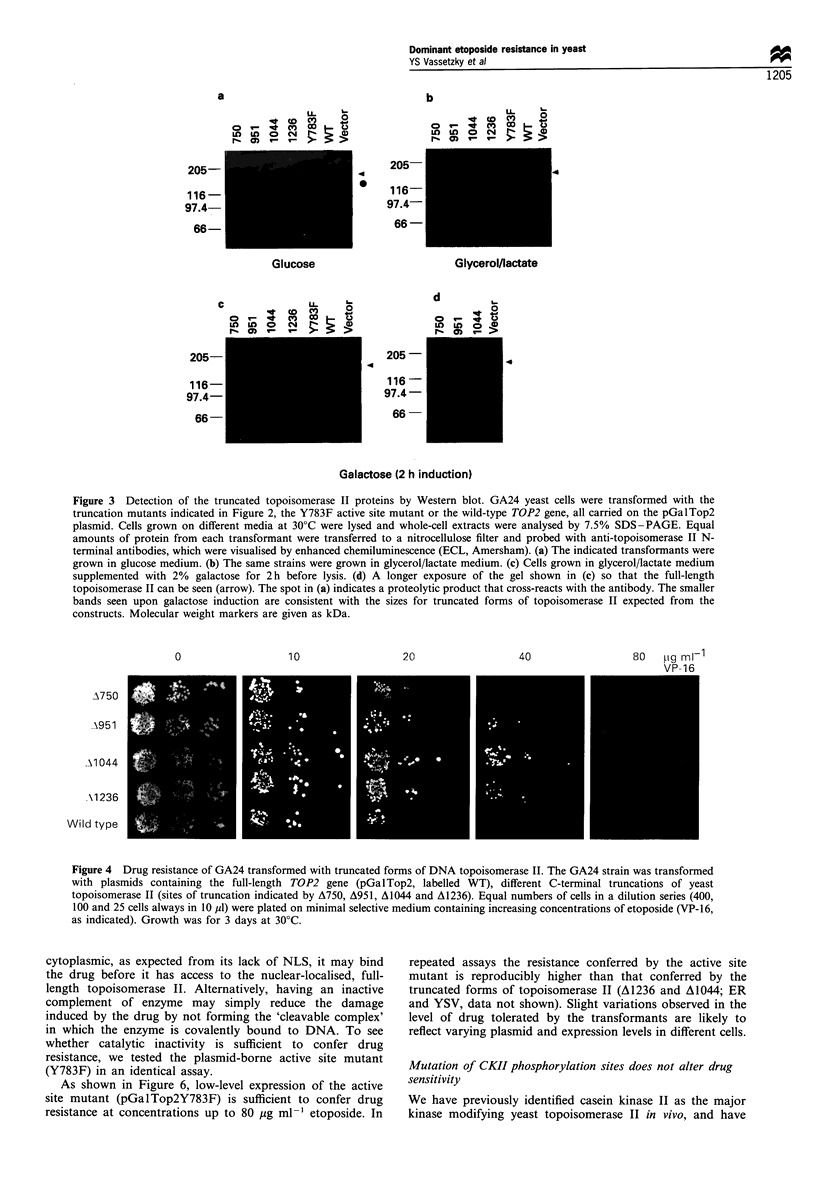
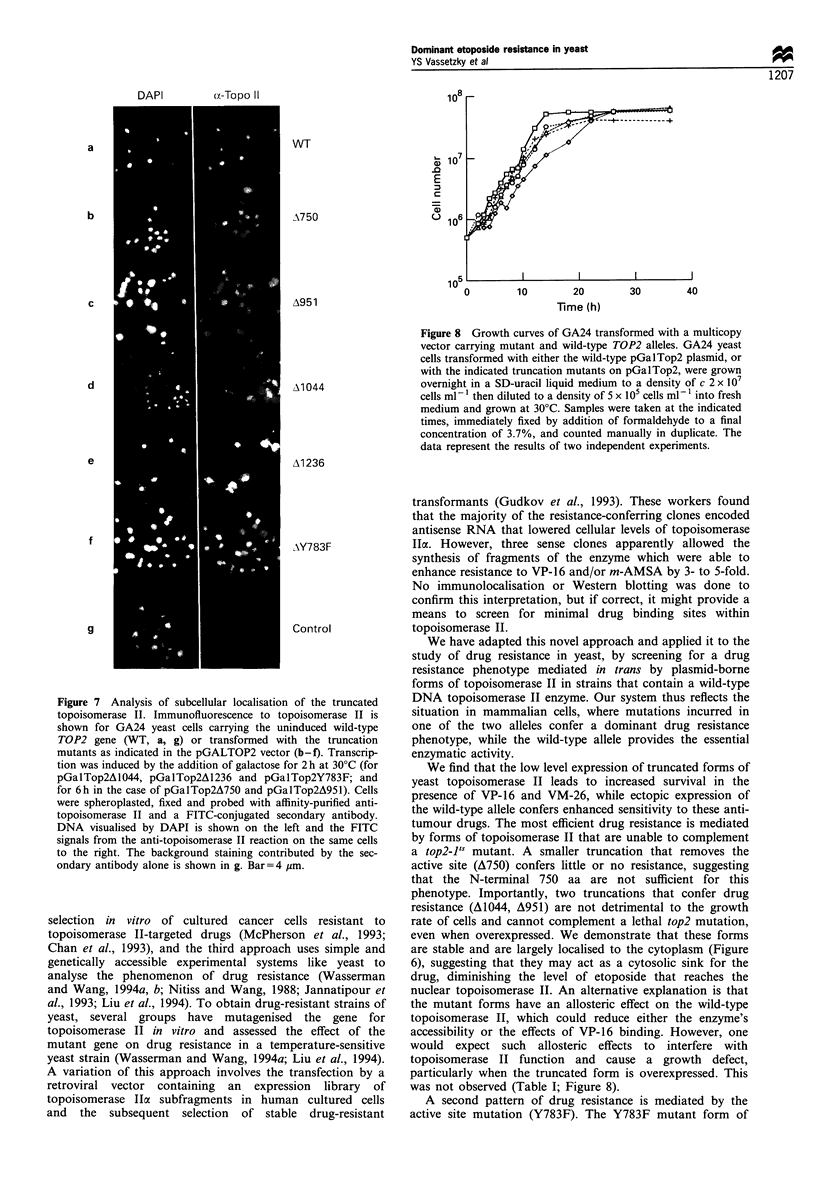
Drug resistance to anti-tumour agents often coincides with mutations in the gene encoding DNA topoisomerase II alpha. To examine how inactive forms of topoisomerase II can influence resistance to the chemotherapeutic agent VP-16 (etoposide) in the presence of a wild-type allele, we have expressed point mutations and carboxy-terminal truncations of yeast topoisomerase II from a plasmid in budding yeast. Truncations that terminate the coding region of topoisomerase II at amino acid (aa) 750, aa 951 and aa 1044 are localised to both the cytosol and the nucleus and fail to complement a temperature-sensitive top2-1 allele at non-permissive temperature. In contrast, the plasmid-borne wild-type TOP2 allele and a truncation at aa 1236 are nuclear localised and complement the top2-1 mutation. At low levels of expression, truncated forms of topoisomerase II render yeast resistant to levels of etoposide 2- and 3-fold above that tolerated by cells expressing the full-length enzyme. Maximal resistance is conferred by the full-length enzyme carrying a mutated active site (Y783F) or a truncation at aa 1044. The level of phosphorylation of topoisomerase II was previously shown to correlate with drug resistance in cultured cells, hence we tested mutants in the major casein kinase II acceptor sites in the C-terminal domain of yeast topoisomerase II for changes in drug sensitivity. Neither ectopic expression of the C-terminal domain alone nor phosphoacceptor site mutants significantly alter the host cell's sensitivity to etoposide.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alghisi G. C., Roberts E., Cardenas M. E., Gasser S. M. The regulation of DNA topoisomerase II by casein kinase II. Cell Mol Biol Res. 1994;40(5-6):563–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alton P. A., Harris A. L. The role of DNA topoisomerases II in drug resistance. Br J Haematol. 1993 Oct;85(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb03162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T., Danks M. K., Wolverton J. S., Kim R., Chen M. Drug resistance associated with altered DNA topoisomerase II. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1993;33:113–127. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(93)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugg B. Y., Danks M. K., Beck W. T., Suttle D. P. Expression of a mutant DNA topoisomerase II in CCRF-CEM human leukemic cells selected for resistance to teniposide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7654–7658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campain J. A., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. A novel mutant topoisomerase II alpha present in VP-16-resistant human melanoma cell lines has a deletion of alanine 429. Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 20;33(37):11327–11332. doi: 10.1021/bi00203a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Dang Q., Glover C. V., Gasser S. M. Casein kinase II phosphorylates the eukaryote-specific C-terminal domain of topoisomerase II in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1785–1796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Gasser S. M. Regulation of topoisomerase II by phosphorylation: a role for casein kinase II. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):219–225. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Watt P., Wang J. C. The C-terminal domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3197–3207. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. T., Ng S. W., Eder J. P., Schnipper L. E. Molecular cloning and identification of a point mutation in the topoisomerase II cDNA from an etoposide-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2160–2165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. H., Osheroff N. When good enzymes go bad: conversion of topoisomerase II to a cellular toxin by antineoplastic drugs. Chem Res Toxicol. 1993 Sep-Oct;6(5):585–597. doi: 10.1021/tx00035a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw D. G., Hsieh T. Function of the hydrophilic carboxyl terminus of type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. I. In vitro studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21328–21334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw D. G., Hsieh T. Function of the hydrophilic carboxyl terminus of type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. II. In vivo studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21335–21343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang Q., Alghisi G. C., Gasser S. M. Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of yeast topoisomerase II by casein kinase II affects DNA-protein interaction. J Mol Biol. 1994 Oct 14;243(1):10–24. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks M. K., Warmoth M. R., Friche E., Granzen B., Bugg B. Y., Harker W. G., Zwelling L. A., Futscher B. W., Suttle D. P., Beck W. T. Single-strand conformational polymorphism analysis of the M(r) 170,000 isozyme of DNA topoisomerase II in human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1373–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVore R. F., Corbett A. H., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of topoisomerase II by casein kinase II and protein kinase C: effects on enzyme-mediated DNA cleavage/religation and sensitivity to the antineoplastic drugs etoposide and 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methane-sulfon-m-anisidide. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 15;52(8):2156–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder J. P., Jr, Chan V. T., Niemierko E., Teicher B. A., Schnipper L. E. Conditional expression of wild-type topoisomerase II complements a mutant enzyme in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13844–13849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Ling V. The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:137–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldhoff P. W., Mirski S. E., Cole S. P., Sullivan D. M. Altered subcellular distribution of topoisomerase II alpha in a drug-resistant human small cell lung cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):756–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi R., Zwelling L., Constantinou A., Ford J., Grabowski D. Altered phosphorylation, biosynthesis and degradation of the 170 kDa isoform of topoisomerase II in amsacrine-resistant human leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 14;192(3):1274–1280. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granzen B., Graves D. E., Baguley B. C., Danks M. K., Beck W. T. Structure-activity studies of amsacrine analogs in drug resistant human leukemia cell lines expressing either altered DNA topoisomerase II or P-glycoprotein. Oncol Res. 1992;4(11-12):489–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudkov A. V., Zelnick C. R., Kazarov A. R., Thimmapaya R., Suttle D. P., Beck W. T., Roninson I. B. Isolation of genetic suppressor elements, inducing resistance to topoisomerase II-interactive cytotoxic drugs, from human topoisomerase II cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3231–3235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds M., Deisseroth K., Mayes J., Altschuler E., Jansen R., Ledley F. D., Zwelling L. A. Identification of a point mutation in the topoisomerase II gene from a human leukemia cell line containing an amsacrine-resistant form of topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 1;51(17):4729–4731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannatipour M., Liu Y. X., Nitiss J. L. The top2-5 mutant of yeast topoisomerase II encodes an enzyme resistant to etoposide and amsacrine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18586–18592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Laroche T., Cardenas M. E., Hofmann J. F., Schweizer D., Gasser S. M. Localization of RAP1 and topoisomerase II in nuclei and meiotic chromosomes of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):935–948. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Wang J. C., Beran M. Two independent amsacrine-resistant human myeloid leukemia cell lines share an identical point mutation in the 170 kDa form of human topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):837–843. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90245-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., D'Arpa P. Topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs: mechanisms of cytotoxicity and resistance. Important Adv Oncol. 1992:79–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. X., Hsiung Y., Jannatipour M., Yeh Y., Nitiss J. L. Yeast topoisomerase II mutants resistant to anti-topoisomerase agents: identification and characterization of new yeast topoisomerase II mutants selected for resistance to etoposide. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):2943–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long B. H., Wang L., Lorico A., Wang R. C., Brattain M. G., Casazza A. M. Mechanisms of resistance to etoposide and teniposide in acquired resistant human colon and lung carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5275–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J. P., Brown G. A., Goldenberg G. J. Characterization of a DNA topoisomerase IIalpha gene rearrangement in adriamycin-resistant P388 leukemia: expression of a fusion messenger RNA transcript encoding topoisomerase IIalpha and the retinoic acid receptor alpha locus. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 15;53(24):5885–5889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J. L., Liu Y. X., Harbury P., Jannatipour M., Wasserman R., Wang J. C. Amsacrine and etoposide hypersensitivity of yeast cells overexpressing DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4467–4472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J., Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs can be studied in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7501–7505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino F., Laroche T., Gilson E., Axelrod A., Pillus L., Gasser S. M. SIR3 and SIR4 proteins are required for the positioning and integrity of yeast telomeres. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):543–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y. DNA topoisomerase I and II in cancer chemotherapy: update and perspectives. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1993;32(2):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00685611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. A functional 125-kDa core polypeptide of fission yeast DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6093–6102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano H., Kohno K., Ono M., Uchida Y., Kuwano M. Increased phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II in etoposide-resistant mutants of human cancer KB cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):3951–3957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassetzky Y. S., Alghisi G. C., Gasser S. M. DNA topoisomerase II mutations and resistance to anti-tumor drugs. Bioessays. 1995 Sep;17(9):767–774. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. A., Austin C. A., Fisher L. M., Wang J. C. Use of yeast in the study of anticancer drugs targeting DNA topoisomerases: expression of a functional recombinant human DNA topoisomerase II alpha in yeast. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 1;53(15):3591–3596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. A., Wang J. C. Analysis of yeast DNA topoisomerase II mutants resistant to the antitumor drug amsacrine. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1795–1800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. A., Wang J. C. Mechanistic studies of amsacrine-resistant derivatives of DNA topoisomerase II. Implications in resistance to multiple antitumor drugs targeting the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):20943–20951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. M., Hickson I. D. Structure and function of type II DNA topoisomerases. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 1;303(Pt 3):681–695. doi: 10.1042/bj3030681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worland S. T., Wang J. C. Inducible overexpression, purification, and active site mapping of DNA topoisomerase II from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4412–4416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]