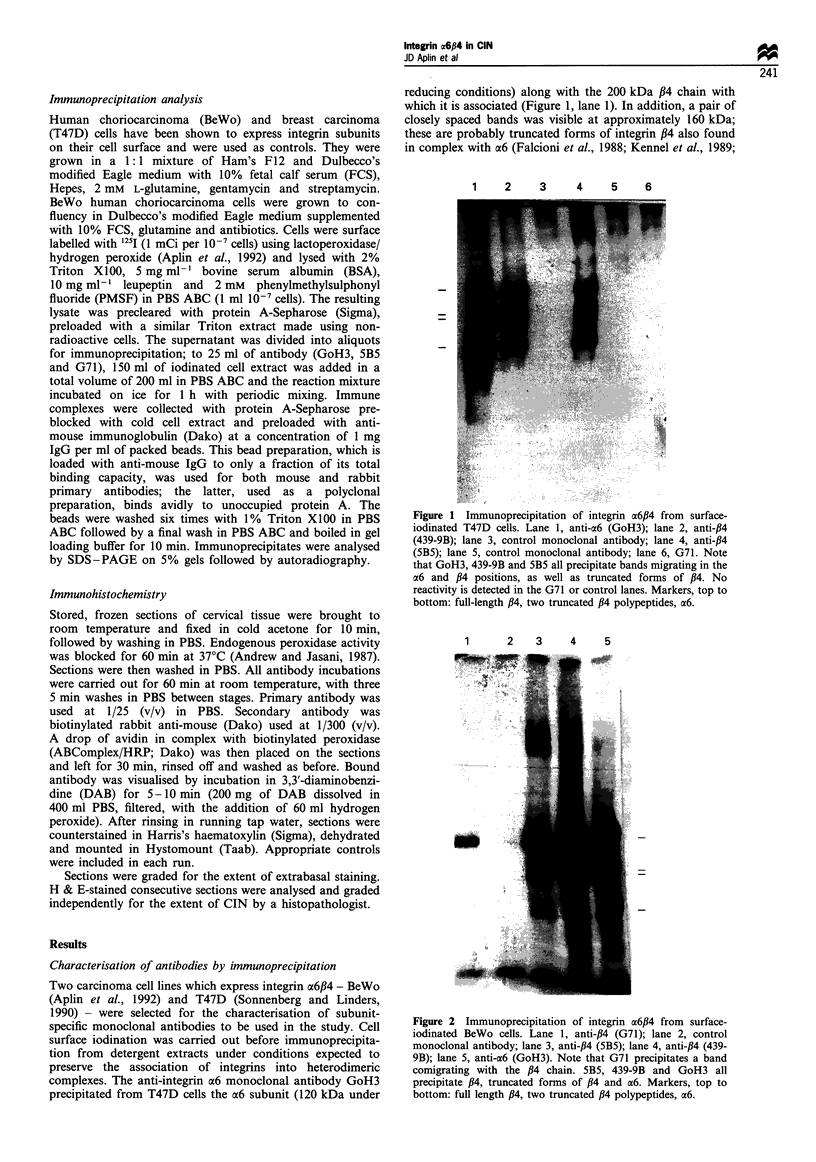
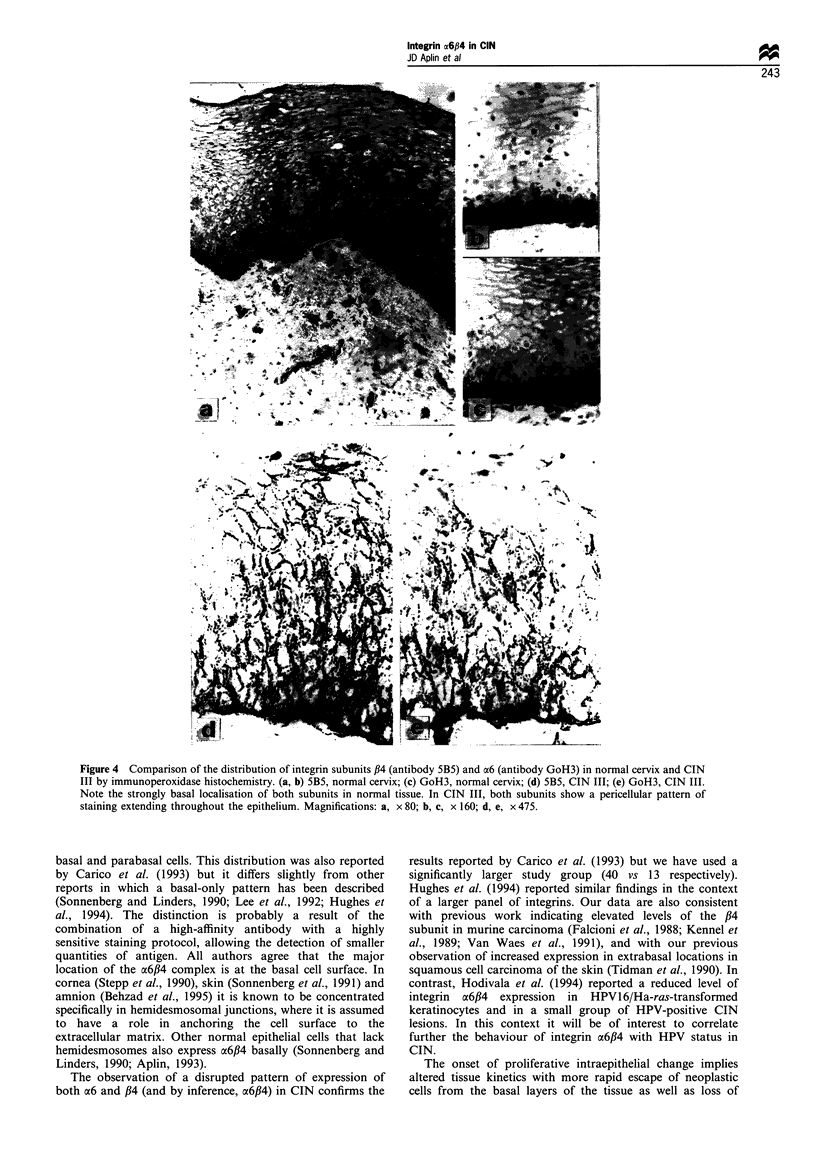
Abstract
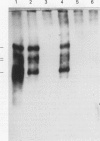
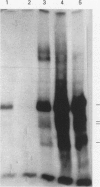
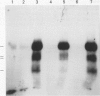
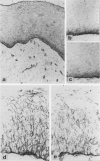
We have used subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and immunohistochemistry to examine the distribution of integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in normal ectocervical epithelium and various grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Antibodies were first characterised by immunoprecipitation from two surface-labelled tumour cell lines. Monoclonal antibody G71 was found to precipitate integrin beta 4 from BeWo but not T47D cells, while other anti-beta 4 antibodies precipitated beta 4 from both cell lines. Both G71 and an antiserum to the C-terminal peptide of beta 4 precipitated free beta 4 from surface-iodinated BeWo cells. Neither antibody recognised truncated beta 4 chains observed at approximately 160 kDa. These data suggest that different isoforms of beta 4 are expressed in different tumour cell lines, and that there may be a pool of beta 4 at the cell surface that is not complexed to alpha 6. In normal cervix, both the alpha 6 and beta 4 subunits occur at the basal surface of the basal cell layer. In CIN, the distribution is markedly altered, with strong expression of alpha 6 and beta 4 in the upper cell layers of the ectocervical epithelium. All 40 cases of CIN that were studied exhibited this alteration. Furthermore, the extent of extrabasal staining appeared to correspond with the grade of CIN. The form of integrin beta 4 recognised by antibody G71 also appears in the upper cell layers in CIN, but it shows a more restricted distribution than the normal isoform.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. H., Boyes D. A., Benedet J. L., Le Riche J. C., Matisic J. P., Suen K. C., Worth A. J., Millner A., Bennett O. M. Organisation and results of the cervical cytology screening programme in British Columbia, 1955-85. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Apr 2;296(6627):975–978. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6627.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew S. M., Jasani B. An improved method for the inhibition of endogenous peroxidase non-deleterious to lymphocyte surface markers. Application to immunoperoxidase studies on eosinophil-rich tissue preparations. Histochem J. 1987 Aug;19(8):426–430. doi: 10.1007/BF01675753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aplin J. D. Expression of integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in human trophoblast and its loss from extravillous cells. Placenta. 1993 Mar-Apr;14(2):203–215. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aplin J. D., Sattar A., Mould A. P. Variant choriocarcinoma (BeWo) cells that differ in adhesion and migration on fibronectin display conserved patterns of integrin expression. J Cell Sci. 1992 Oct;103(Pt 2):435–444. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.2.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aplin J. D., Seif M. W. Basally located epithelial cell surface component identified by a novel monoclonal antibody technique. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):550–555. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behzad F., Jones C. J., Ball S., Alvares T., Aplin J. D. Studies of hemidesmosomes in human amnion: the use of a detergent extraction protocol for compositional and ultrastructural analysis and preparation of a hemidesmosome-enriched fraction from tissue. Acta Anat (Basel) 1995;152(3):170–184. doi: 10.1159/000147695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carico E., French D., Bucci B., Falcioni R., Vecchione A., Mariani-Costantini R. Integrin beta 4 expression in the neoplastic progression of cervical epithelium. Gynecol Oncol. 1993 Apr;49(1):61–66. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1993.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Kaur P., Gil S. G., Gahr P. J., Wayner E. A. Distinct functions for integrins alpha 3 beta 1 in focal adhesions and alpha 6 beta 4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3141–3154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca M., Tamura R. N., Kajiji S., Bondanza S., Rossino P., Cancedda R., Marchisio P. C., Quaranta V. Polarized integrin mediates human keratinocyte adhesion to basal lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6888–6892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcioni R., Sacchi A., Resau J., Kennel S. J. Monoclonal antibody to human carcinoma-associated protein complex: quantitation in normal and tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):816–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frixen U. H., Behrens J., Sachs M., Eberle G., Voss B., Warda A., Löchner D., Birchmeier W. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):173–185. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E. Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Stepp M. A., Suzuki S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Proteolytic processing of endogenous and recombinant beta 4 integrin subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):951–959. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodivala K. J., Pei X. F., Liu Q. Y., Jones P. H., Rytina E. R., Gilbert C., Singer A., Watt F. M. Integrin expression and function in HPV 16-immortalised human keratinocytes in the presence or absence of v-Ha-ras. Comparison with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):943–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., von dem Borne A. E., Sonnenberg A. Cloning and sequence analysis of beta-4 cDNA: an integrin subunit that contains a unique 118 kd cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):765–770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. E., Rebello G., al-Nafussi A. Integrin expression in squamous neoplasia of the cervix. J Pathol. 1994 Jun;173(2):97–104. doi: 10.1002/path.1711730205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Foote L. J., Falcioni R., Sonnenberg A., Stringer C. D., Crouse C., Hemler M. E. Analysis of the tumor-associated antigen TSP-180. Identity with alpha 6-beta 4 in the integrin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15515–15521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurpakus M. A., Quaranta V., Jones J. C. Surface relocation of alpha 6 beta 4 integrins and assembly of hemidesmosomes in an in vitro model of wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1737–1750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. C., Lotz M. M., Steele G. D., Jr, Mercurio A. M. The integrin alpha 6 beta 4 is a laminin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M. M., Korzelius C. A., Mercurio A. M. Human colon carcinoma cells use multiple receptors to adhere to laminin: involvement of alpha 6 beta 4 and alpha 2 beta 1 integrins. Cell Regul. 1990 Feb;1(3):249–257. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessen C. M., Hogervorst F., Jaspars L. H., de Melker A. A., Delwel G. O., Hulsman E. H., Kuikman I., Sonnenberg A. The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin is a receptor for both laminin and kalinin. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Apr;211(2):360–367. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. J., Aplin J. D., Lake B. D. Antigenic expression of integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Histopathology. 1994 Jun;24(6):571–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantefaber L. C., Hynes R. O. Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90902-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risinger J. I., Berchuck A., Kohler M. F., Boyd J. Mutations of the E-cadherin gene in human gynecologic cancers. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):98–102. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., Daams H., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Aplin J. D., Baker J., Loizidou M. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):907–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Linders C. J., Daams J. H., Kennel S. J. The alpha 6 beta 1 (VLA-6) and alpha 6 beta 4 protein complexes: tissue distribution and biochemical properties. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jun;96(Pt 2):207–217. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepp M. A., Spurr-Michaud S., Tisdale A., Elwell J., Gipson I. K. Alpha 6 beta 4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8970–8974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Naitoh Y. Amino acid sequence of a novel integrin beta 4 subunit and primary expression of the mRNA in epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):757–763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington B. E. Fibronectin receptor overexpression and loss of transformed phenotype in a stable variant of the K562 cell line. Cell Regul. 1990 Aug;1(9):637–648. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.9.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Rozzo C., Starr L., Chambers J., Reichardt L. F., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1593–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidman M. J., Aplin J. D., MacDonald D. M. Abnormal expression of G71 antibody at the epidermal basement membrane in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1990 May 1;65(9):1955–1959. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900501)65:9<1955::aid-cncr2820650913>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Waes C., Kozarsky K. F., Warren A. B., Kidd L., Paugh D., Liebert M., Carey T. E. The A9 antigen associated with aggressive human squamous carcinoma is structurally and functionally similar to the newly defined integrin alpha 6 beta 4. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2395–2402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal F., Aberdam D., Miquel C., Christiano A. M., Pulkkinen L., Uitto J., Ortonne J. P., Meneguzzi G. Integrin beta 4 mutations associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nat Genet. 1995 Jun;10(2):229–234. doi: 10.1038/ng0695-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]